Atlantis
Description
There are several ancient Greek texts that
contain descriptions of the fabled island Atlantis. Some of these texts
even include maps of parts of the island. But unfortunately, these maps
describe different regions of Atlantis. Your friend Bill has to know the
total area for which maps exist. You (unwisely) volunteered to write a
program that calculates this quantity.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each
test case starts with a line containing a single integer n (1 <= n
<= 100) of available maps. The n following lines describe one map
each. Each of these lines contains four numbers x1;y1;x2;y2 (0 <= x1
< x2 <= 100000;0 <= y1 < y2 <= 100000), not necessarily
integers. The values (x1; y1) and (x2;y2) are the coordinates of the
top-left resp. bottom-right corner of the mapped area.
The input file is terminated by a line containing a single 0. Don't
process it.
Output
For
each test case, your program should output one section. The first line
of each section must be "Test case #k", where k is the number of the
test case (starting with 1). The second one must be "Total explored
area: a", where a is the total explored area (i.e. the area of the union
of all rectangles in this test case), printed exact to two digits to
the right of the decimal point.
Output a blank line after each test case.
Sample
Input
2
10 10 20 20
15 15 25 25.5
0
Sample Output
Test case #1
Total explored area: 180.00
题意:切割矩形。
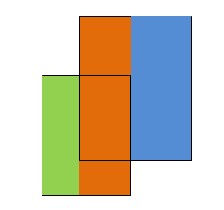 先计算绿色部分,在计算橙色部分,再计算蓝色部分。
先计算绿色部分,在计算橙色部分,再计算蓝色部分。
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdlib.h
>
#define
maxn 500
struct
T
{
int
l, r, cov;
double
len;
}tree[maxn
*
5
];
struct
R
{
double
x, y1, y2;
int
lr;
}rec[maxn
*
2
];
double
y[maxn
*
2
];
int
cmp1(
const
void
*
a,
const
void
*
b)
{
double
aa
=
*
((
double
*
)a), bb
=
*
((
double
*
)b);
if
(aa
>
bb)
{
return
1
;
}
if
(aa
==
bb)
{
return
0
;
}
return
-
1
;
}
int
cmp2(
const
void
*
a,
const
void
*
b)
{
R aa
=
*
((R
*
)a), bb
=
*
((R
*
)b);
if
(aa.x
>
bb.x)
{
return
1
;
}
if
(aa.x
==
bb.x)
{
return
0
;
}
return
-
1
;
}
void
build(
int
l,
int
r,
int
th)
{
tree[th].l
=
l, tree[th].r
=
r, tree[th].cov
=
0
, tree[th].len
=
0
;
if
(l
+
1
==
r)
{
return
;
}
int
m
=
(l
+
r)
>>
1
;
build(l, m, th
*
2
), build(m, r, th
*
2
+
1
);
}
void
op(
int
l,
int
r,
int
th,
int
del)
//
由于对于竖直边,肯定先插入在删除,所以这里写的不是很符合所有的插入删除统计。
{
if
(tree[th].l
==
l
&&
tree[th].r
==
r)
{
tree[th].cov
+=
del;
if
(tree[th].cov
>
0
)
{
tree[th].len
=
y[r]
-
y[l];
}
else
{
tree[th].len
=
tree[th
*
2
].len
+
tree[th
*
2
+
1
].len;
}
return
;
}
int
m
=
(tree[th].l
+
tree[th].r)
>>
1
;
if
(r
<=
m)
{
op(l, r, th
*
2
, del);
}
else
if
(l
>=
m)
{
op(l, r, th
*
2
+
1
, del);
}
else
{
op(l, m, th
*
2
, del), op(m, r, th
*
2
+
1
, del);
}
if
(tree[th].cov
>
0
)
{
tree[th].len
=
y[tree[th].r]
-
y[tree[th].l];
}
else
{
tree[th].len
=
tree[th
*
2
].len
+
tree[th
*
2
+
1
].len;
}
}
int
bs(
int
l,
int
r,
double
key)
{
int
m;
while
(l
<=
r)
{
m
=
(l
+
r)
>>
1
;
if
(y[m]
>
key)
{
r
=
m
-
1
;
}
else
if
(y[m]
<
key)
{
l
=
m
+
1
;
}
else
{
return
m;
}
}
}
int
main()
{
int
n, i, j, k, l, r, ca
=
0
;
double
ans, x1, y1, x2, y2;
while
(scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
n), n)
{
ca
++
;
for
(i
=
0
, j
=
0
; i
<
n; i
++
)
{
scanf(
"
%lf%lf%lf%lf
"
,
&
x1,
&
y1,
&
x2,
&
y2);
y[j]
=
y1, rec[j].x
=
x1, rec[j].y1
=
y1, rec[j].y2
=
y2, rec[j
++
].lr
=
1
;
y[j]
=
y2, rec[j].x
=
x2, rec[j].y1
=
y1, rec[j].y2
=
y2, rec[j
++
].lr
=
-
1
;
}
qsort(y, j,
sizeof
(
double
), cmp1);
qsort(rec, j,
sizeof
(R), cmp2);
for
(k
=
i
=
1
; i
<
j; i
++
)
//
坐标离散化
{
if
(y[i]
!=
y[i
-
1
])
{
y[k
++
]
=
y[i];
}
}
build(
0
, k,
1
);
k
--
;
for
(i
=
0
, ans
=
0
; i
<
j
-
1
; i
++
)
{
l
=
bs(
0
, k, rec[i].y1), r
=
bs(
0
, k, rec[i].y2);
op(l, r,
1
, rec[i].lr);
ans
+=
1.0
*
tree[
1
].len
*
(rec[i
+
1
].x
-
rec[i].x);
}
printf(
"
Test case #%d\nTotal explored area: %.2lf\n\n
"
, ca, ans);
}
system(
"
pause
"
);
return
0
;
}