Description
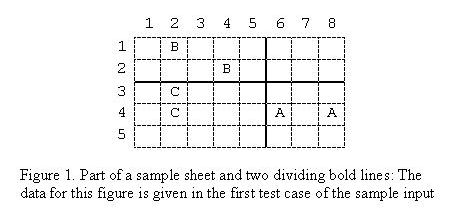
Little Dara has recently learned how to write a few letters of the English alphabet (say k letters). He plays a game with his little sister Sara. He draws a grid on a piece of paper and writes p instances of each of the k letters in the grid cells. He then asks Sara to draw as many side-to-side horizontal and/or vertical bold lines over the grid lines as she wishes, such that in each rectangle containing no bold line, there would be p instances of one letter or nothing. For example, consider the sheet given in Figure 1, where Sara has drawn two bold lines creating four rectangles meeting the condition above. Sara wins if she succeeds in drawing the required lines. Dara being quite fair to Sara, wants to make sure that there would be at least one solution to each case he offers Sara. You are to write a program to help Dara decide on the possibility of drawing the right lines.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a single integer t (1 <= t <= 10), the number of test cases, followed by the input data for each test case. The first line of each test case consists of two integers k (1 <= k <= 26), the number of different letters, and p (1 <= p <= 10), the number of instances of each letter. Followed by the first line, there are k lines, one for each letter, each containing p pairs of integers (xi, yi) for 1 <= i <= p. A pair indicates coordinates of the cell on the paper where one instance of the letter is written. The coordinates of the upper left cell of the paper is assumed to be (1,1). Coordinates are positive integers less than or equal to 1,000,000. You may assume that no cell contains more than one letter.
Output
There should be one line per test case containing a single word YES or NO depending on whether the input paper can be divided successfully according to the constraints stated in the problem.
Sample Input
2
3 2
6 4 8 4
4 2 2 1
2 3 2 4
3 3
1 1 3 1 5 1
2 1 4 1 6 1
2 2 4 2 8 1
Sample Output
YES
NO
代码如下:
 #include<stdio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
 #define max 1000000
#define max 1000000
 #define min 0
#define min 0
 #define MAX(a, b) ( a > b ? a : b)
#define MAX(a, b) ( a > b ? a : b)
 #define MIN(a, b) ( a < b ? a : b)
#define MIN(a, b) ( a < b ? a : b)
 struct N
struct N


 {
{
 int x1, y1, x2, y2;
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
 }N[26];
}N[26];
 int x, y;
int x, y;
 int IsCover(int a, int b, int c, int d)
int IsCover(int a, int b, int c, int d)


 {
{
 if (b <= c)
if (b <= c)


 {
{
 x = b;
x = b;
 y = c;
y = c;
 //printf("unCover\n");
//printf("unCover\n");
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 else if (a >= d)
else if (a >= d)


 {
{
 x = d;
x = d;
 y = a;//printf("unCover\n");
y = a;//printf("unCover\n");
 return 0;
return 0;
 }//printf("isCover\n");
}//printf("isCover\n");
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int Ok(int x, int x1, int x2)
int Ok(int x, int x1, int x2)


 {
{
 if (x <= x1 || x >= x2)
if (x <= x1 || x >= x2)


 {//printf("unThrought\n");
{//printf("unThrought\n");
 return 0;
return 0;
 }//printf("isThrought\n");
}//printf("isThrought\n");
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 int unArrowX(int x, int y, int i, int j, int n)
int unArrowX(int x, int y, int i, int j, int n)


 {
{
 int k, l;
int k, l;
 for (k = x; k <= y; k++)
for (k = x; k <= y; k++)


 {
{
 for (l = 0; l < n; l++)
for (l = 0; l < n; l++)


 {
{
 if (l != i && l != j)
if (l != i && l != j)


 {
{
 if (Ok(k, N[l].x1, N[l].x2))
if (Ok(k, N[l].x1, N[l].x2))


 {
{
 //printf("unIs\n");
//printf("unIs\n");
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 int unArrowY(int x, int y, int i, int j, int n)
int unArrowY(int x, int y, int i, int j, int n)


 {
{
 int k, l;
int k, l;
 for (k = x; k <= y; k++)
for (k = x; k <= y; k++)


 {
{
 for (l = 0; l < n; l++)
for (l = 0; l < n; l++)


 {
{
 if (l != i && l != j)
if (l != i && l != j)


 {
{
 if (Ok(k, N[l].y1, N[l].y2))
if (Ok(k, N[l].y1, N[l].y2))


 {
{
 //printf("unIs\n");
//printf("unIs\n");
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 int Is(int n)
int Is(int n)


 {
{
 int i, j, k, l;
int i, j, k, l;
 for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)


 {
{
 for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)


 {
{
 //printf("-------------------------\n");
//printf("-------------------------\n");
 // printf("%d %d %d %d\n", N[i].x1, N[i].y1, N[i].x2, N[i].y2);
// printf("%d %d %d %d\n", N[i].x1, N[i].y1, N[i].x2, N[i].y2);
 // printf("%d %d %d %d\n", N[j].x1, N[j].y1, N[j].x2, N[j].y2);
// printf("%d %d %d %d\n", N[j].x1, N[j].y1, N[j].x2, N[j].y2);
 if(IsCover(N[i].x1, N[i].x2, N[j].x1, N[j].x2) )
if(IsCover(N[i].x1, N[i].x2, N[j].x1, N[j].x2) )


 {
{
 if (IsCover(N[i].y1, N[i].y2, N[j].y1, N[j].y2))
if (IsCover(N[i].y1, N[i].y2, N[j].y1, N[j].y2))


 {//printf("unIS\n");
{//printf("unIS\n");
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 if (unArrowY(i, j, x, y, n))
if (unArrowY(i, j, x, y, n))


 {
{
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 if (unArrowX(i, j, x, y, n))
if (unArrowX(i, j, x, y, n))


 {
{
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }//printf("IS\n");
}//printf("IS\n");
 return 1;
return 1;
 }
}

 int main()
int main()


 {
{
 int x1, x2, y1, y2, n, i, j, v, m;
int x1, x2, y1, y2, n, i, j, v, m;
 scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &n);
 while (n--)
while (n--)


 {
{
 scanf("%d%d", &m, &v);
scanf("%d%d", &m, &v);
 for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)


 {
{
 x1 = max, x2 = min, y1 = max, y2 = min;
x1 = max, x2 = min, y1 = max, y2 = min;
 for (j = 0; j < v; j++)
for (j = 0; j < v; j++)


 {
{
 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
 x1 = MIN(x1, x);
x1 = MIN(x1, x);
 x2 = MAX(x2, x);
x2 = MAX(x2, x);
 y1 = MIN(y1, y);
y1 = MIN(y1, y);
 y2 = MAX(y2, y);
y2 = MAX(y2, y);
 }
}
 N[i].x1 = y1 - 1;
N[i].x1 = y1 - 1;
 N[i].y1 = x1 - 1;
N[i].y1 = x1 - 1;
 N[i].x2 = y2;
N[i].x2 = y2;
 N[i].y2 = x2;
N[i].y2 = x2;

 }
}
 if (Is(i))
if (Is(i))


 {
{
 printf("YES\n");
printf("YES\n");
 }
}
 else
else


 {
{
 printf("NO\n");
printf("NO\n");
 }
}
 }
}
 system("pause");
system("pause");
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}

