作用:
运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
UML结构图:
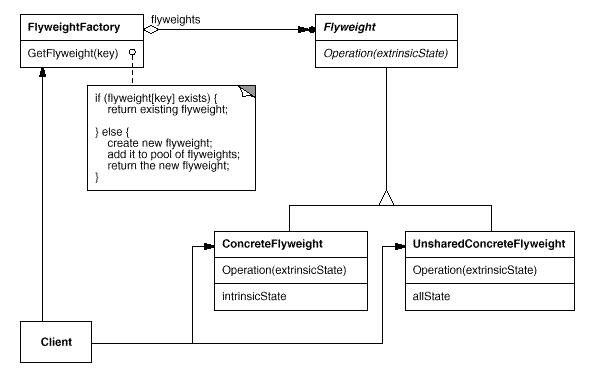
解析:
Flyweight模式在大量使用一些可以被共享的对象的时候经常使用.比如,在QQ聊天的时候很多时候你懒得回复又不得不回复的时候,一般会用一些客套的话语敷衍别人,如"呵呵","好的"等等之类的,这些简单的答复其实每个人都是提前定义好的,在使用的时候才调用出来.Flyweight就是基于解决这种问题的思路而产生的,当需要一个可以在其它地方共享使用的对象的时候,先去查询是否已经存在了同样的对象,如果没有就生成之有的话就直接使用.因此,Flyweight模式和Factory模式也经常混用.
实现:
需要说明的是下面的实现仅仅实现了对可共享对象的使用,非可共享对象的使用没有列出,因为这个不是Flyweight模式的重点.这里的实现要点是采用一个list链表来保存这些可以被共享的对象,需要使用的时候就到链表中查询是不是已经存在了,如果不存在就初始化一个,然后返回这个对象的指针.
1)Flyweight.h

 /**//********************************************************************
/**//********************************************************************
 created: 2006/07/26
created: 2006/07/26
 filename: FlyWeight.h
filename: FlyWeight.h
 author: 李创
author: 李创
 http://www.cppblog.com/converse/
http://www.cppblog.com/converse/

 purpose: FlyWeight模式的演示代码
purpose: FlyWeight模式的演示代码
 *********************************************************************/
*********************************************************************/

 #ifndef FLYWEIGHT_H
#ifndef FLYWEIGHT_H
 #define FLYWEIGHT_H
#define FLYWEIGHT_H

 #include <string>
#include <string>
 #include <list>
#include <list>

 typedef std::string STATE;
typedef std::string STATE;

 class Flyweight
class Flyweight


 {
{
 public:
public:

 virtual ~Flyweight()
virtual ~Flyweight() {}
{}

 STATE GetIntrinsicState();
STATE GetIntrinsicState();
 virtual void Operation(STATE& ExtrinsicState) = 0;
virtual void Operation(STATE& ExtrinsicState) = 0;

 protected:
protected:
 Flyweight(const STATE& state)
Flyweight(const STATE& state)
 :m_State(state)
:m_State(state)


 {
{
 }
}

 private:
private:
 STATE m_State;
STATE m_State;
 };
};

 class FlyweightFactory
class FlyweightFactory


 {
{
 public:
public:

 FlyweightFactory()
FlyweightFactory() {}
{}
 ~FlyweightFactory();
~FlyweightFactory();

 Flyweight* GetFlyweight(const STATE& key);
Flyweight* GetFlyweight(const STATE& key);

 private:
private:
 std::list<Flyweight*> m_listFlyweight;
std::list<Flyweight*> m_listFlyweight;
 };
};

 class ConcreateFlyweight
class ConcreateFlyweight
 : public Flyweight
: public Flyweight


 {
{
 public:
public:
 ConcreateFlyweight(const STATE& state)
ConcreateFlyweight(const STATE& state)
 : Flyweight(state)
: Flyweight(state)


 {
{
 }
}

 virtual ~ConcreateFlyweight()
virtual ~ConcreateFlyweight() {}
{}

 virtual void Operation(STATE& ExtrinsicState);
virtual void Operation(STATE& ExtrinsicState);
 };
};

 #endif
#endif

2)Flyweight.cpp

 /**//********************************************************************
/**//********************************************************************
 created: 2006/07/26
created: 2006/07/26
 filename: FlyWeight.cpp
filename: FlyWeight.cpp
 author: 李创
author: 李创
 http://www.cppblog.com/converse/
http://www.cppblog.com/converse/

 purpose: FlyWeight模式的演示代码
purpose: FlyWeight模式的演示代码
 *********************************************************************/
*********************************************************************/

 #include "FlyWeight.h"
#include "FlyWeight.h"
 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>

 inline STATE Flyweight::GetIntrinsicState()
inline STATE Flyweight::GetIntrinsicState()


 {
{
 return m_State;
return m_State;
 }
}

 FlyweightFactory::~FlyweightFactory()
FlyweightFactory::~FlyweightFactory()


 {
{
 std::list<Flyweight*>::iterator iter1, iter2, temp;
std::list<Flyweight*>::iterator iter1, iter2, temp;

 for (iter1 = m_listFlyweight.begin(), iter2 = m_listFlyweight.end();
for (iter1 = m_listFlyweight.begin(), iter2 = m_listFlyweight.end();
 iter1 != iter2;
iter1 != iter2;
 )
)


 {
{
 temp = iter1;
temp = iter1;
 ++iter1;
++iter1;
 delete (*temp);
delete (*temp);
 }
}

 m_listFlyweight.clear();
m_listFlyweight.clear();
 }
}

 Flyweight* FlyweightFactory::GetFlyweight(const STATE& key)
Flyweight* FlyweightFactory::GetFlyweight(const STATE& key)


 {
{
 std::list<Flyweight*>::iterator iter1, iter2;
std::list<Flyweight*>::iterator iter1, iter2;

 for (iter1 = m_listFlyweight.begin(), iter2 = m_listFlyweight.end();
for (iter1 = m_listFlyweight.begin(), iter2 = m_listFlyweight.end();
 iter1 != iter2;
iter1 != iter2;
 ++iter1)
++iter1)


 {
{
 if ((*iter1)->GetIntrinsicState() == key)
if ((*iter1)->GetIntrinsicState() == key)


 {
{
 std::cout << "The Flyweight:" << key << " already exits"<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The Flyweight:" << key << " already exits"<< std::endl;
 return (*iter1);
return (*iter1);
 }
}
 }
}

 std::cout << "Creating a new Flyweight:" << key << std::endl;
std::cout << "Creating a new Flyweight:" << key << std::endl;
 Flyweight* flyweight = new ConcreateFlyweight(key);
Flyweight* flyweight = new ConcreateFlyweight(key);
 m_listFlyweight.push_back(flyweight);
m_listFlyweight.push_back(flyweight);
 }
}

 void ConcreateFlyweight::Operation(STATE& ExtrinsicState)
void ConcreateFlyweight::Operation(STATE& ExtrinsicState)


 {
{

 }
}

3)Main.cpp

 /**//********************************************************************
/**//********************************************************************
 created: 2006/07/26
created: 2006/07/26
 filename: Main.cpp
filename: Main.cpp
 author: 李创
author: 李创
 http://www.cppblog.com/converse/
http://www.cppblog.com/converse/

 purpose: FlyWeight模式的测试代码
purpose: FlyWeight模式的测试代码
 *********************************************************************/
*********************************************************************/

 #include "FlyWeight.h"
#include "FlyWeight.h"

 int main()
int main()


 {
{
 FlyweightFactory flyweightfactory;
FlyweightFactory flyweightfactory;
 flyweightfactory.GetFlyweight("hello");
flyweightfactory.GetFlyweight("hello");
 flyweightfactory.GetFlyweight("world");
flyweightfactory.GetFlyweight("world");
 flyweightfactory.GetFlyweight("hello");
flyweightfactory.GetFlyweight("hello");

 system("pause");
system("pause");
 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}
