摘要: 刚给引擎设备新加了一个函数GetLuaStateOwner();用于获取引擎中的lua上下文看起来似乎没多大必要但是我有自己的考虑!另外:我修改了粒子脚本如下:
1 2 -- 这是盖莫引擎中使用lua脚本的测试粒子 3 4 -- 定义粒子池粒子...
阅读全文
摘要: 初步做完粒子系统想着如何从脚本中载入数据,配送方法这样不是很好脚本我打算首先支持lua和天使脚本等引擎成熟了再支持python首先来看使用lua语言改写上篇的粒子系统代码.(不过鄙人的lua,python都很菜的,其原因就是一直没有练习的机会)对于Lua,其扩展有luabind,tolua++,luaplus,前2着都与boost有关所以就使用luaplus,简单些开始了先上lua脚本代码(我把l...
阅读全文
摘要: 引擎的粒子系统我一直在考虑,以前也设计过,但是感觉以前做过的过于复杂,这里我本着让粒子系统的接口尽可能的简单,功能尽可能的强大,我把粒子系统设计成了这样的形式:
Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/--> 1 2...
阅读全文
今天由于要写一些东西,遇到了需要把成员函数作为函数参数的问题
总结有以下几个办法:
1.使用类的静态成员:
最简单的.只是这种办法与使用普通函数没有什么区别
2.模板的方法
1 template<class T>
2 void Call(T* ptr,void(T::*MenFn)())
3 {
4 (ptr->*MenFn)();
5 }
1 class MyClass
2 {
3 public:
4 void Call()
5 {
6 
7 }
8 };
9
10 MyClass cs;
11 Call(&cs,&MyCall::Call);
3. 虚拟继承的方法
1 class Base
2 {
3 public:
4 virtual void Call() = 0;
5 };
6
7 class SubClass :public Base
8 {
9 public:
10 void Call(){ }
}
11 };
12
13 void Call(Base *ptr)
14 {
15 ptr->Call();
16 }
4.use boost.
1 #include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
2 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
3 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
4 struct MyClass
struct MyClass
5

 {
{
6 void Print(const char* str)
void Print(const char* str)
7

 {
{
8 cout<<"holle "<<str<<endl;
cout<<"holle "<<str<<endl;
9 }
}
10 };
};
11
12 template<class _Fun>
template<class _Fun>
13 void CallBackFun(_Fun a,const char* str)
void CallBackFun(_Fun a,const char* str)
14

 {
{
15 t(n);
t(n);
16 }
}
17
18 int main()
int main()
19

 {
{
20 MyClass mc;
MyClass mc;
21 CallBackFun(boost::bind(boost::mem_fn(&MyClass::Print),&mc,_1),"world")
CallBackFun(boost::bind(boost::mem_fn(&MyClass::Print),&mc,_1),"world")
22 return 1;
return 1;
23 }
}
24
5.使用静态成员函数或者联合体模拟之
1 union
2 {
3 void(G_CALL ParticleSystem::*PhysicsThreadFun)(void *arg);
4 ThreadFun f;
5 }fn;
6 fn.PhysicsThreadFun = &ParticleSystem::PhysicsThreadFun;
7 thread_id = CreateThread(fn.f,&ps);
6.也许.
对loki库不太熟悉也许上面也有答案吧
我所知的c++插槽系统由3个boost的,sigslot的,sigc++的
这里介绍sigc++的使用
最基本的使用方法:
1.回调函数为一般函数:
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 #include <sigc++/sigc++.h>
4
5 //! 普通函数
6 void Print(const std::string& str)
7 {
8 std::cout << str;
9 }
10
11 int main()
12 {
13 //! 返回值void,参数const std::string&
14 sigc::signal<void, const std::string&> signal_print;
15 //! 链接函数
16 signal_print.connect( sigc::ptr_fun(&Print));
17 //! 发射信号
18 signal_print.emit("hello world\n");
19
20 system("pause");
21 return 0;
22 }
2.回调函数为成员函数
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 #include <sigc++/sigc++.h>
4
5 class Printer :public sigc::trackable
6 {
7 public:
8 void Work(){slot.emit("work\n");}
9 typedef sigc::signal<void, const std::string&> Slot;
10 Slot slot;
11 void Print(const std::string& str){std::cout<<str;}
12 };
13
14 int main()
15 {
16 Printer printer;
17 Printer::Slot::iterator iter = printer.slot.connect(sigc::mem_fun(&printer,&Printer::Print));
18 printer.Work();
19 iter->disconnect();
20 printer.Work();
21
22 system("pause");
23 return 0;
24 }
在sigc++中sigc::ptr_fun负责绑定一般函数
而sigc::men_fun负责绑定成员函数.
可以看到一般的信号插槽系统都具备以下几个函数
a.插槽连接
b.插槽断开
c.信号发射
当然有的插槽信号库还提供其它一些函数
比如对信号设定优先级等等
这是简单实用sigc++的例子
不过若论简单性的话还是sigslot比较好,只有一个头文件
游戏引擎的粒子系统设计大致有2个方式:或者是雪,雨,烟花的具体类实现,或者是类似ogre的那种由粒子发射器,粒子效果器等组成的具有简明数学,物理意义的通用粒子系统。
盖莫引擎采用的是类似于ogre的这种模型
粒子系统由粒子发射器,粒子效果器,粒子开发等组成。
下面这是一个粒子系统的贴图:
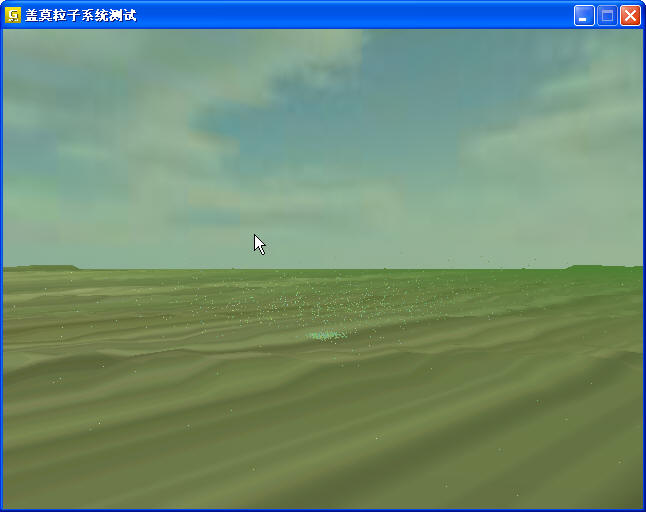
这个粒子场景是采用的点状粒子发射器+重力粒子效果器(当然这是最简单的模式了)
由于粒子系统比较庞大,代码还在修改中故不上代码
摘要: 如何软件设计中总有那么几个比较小巧却比较有用的小段代码比如boost中的utility盖莫游戏引擎也一样有几个比较小的代码片段:如下这是关于指针的:
1 //! 定义一个检测指针是否为空的宏 2 /*! 3 当指针为空的话则返回指定值 4 &nb...
阅读全文
刚改造了以前做的盖莫游戏引擎渲染md2的代码.
对于md2模型来说
一个模型由若干动画组成
一个动画由若干帧构成
每个动画都有自己的名字
具体渲染的时候是对帧做插值的
具体测试例子如下:
1 #include <cstdlib>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <GEngine/Main.hpp>
4
5 using namespace std;
6 using namespace core;
7 core::RefPtr<core::Image> skyimage[5];
8 core::RefPtr<core::Texture> skytexture[5];
9 core::RefPtr<core::Image> terrainimage[2];
10 core::RefPtr<core::Texture> terraintexture[2];
11
12
13 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
14 {
15 Device *device = InitDevice("盖莫引擎md2模型测试");
16 device->SetClearColor(core::Color(80,90,255));
17
18 //! 获取场景管理器
19 RefPtr<SceneManager> scenemanager = SceneManager::GetSceneManager();
20
21 //! 获取资源管理器
22 ResourceManager* resourcemanager = device->GetResourceManager();
23 //! 获取天空图片资源
24 //! 获取天空图形指针
25 skyimage[0] = resourcemanager->GetImage("sky_front","..\\image//sky//front.jpg");
26 skyimage[1] = resourcemanager->GetImage("sky_back","..\\image//sky//back.jpg");
27 skyimage[2] = resourcemanager->GetImage("sky_left","..\\image//sky//left.jpg");
28 skyimage[3] = resourcemanager->GetImage("sky_right","..\\image//sky//right.jpg");
29 skyimage[4] = resourcemanager->GetImage("sky_top","..\\image//sky//top.bmp");
30
31 skytexture[0] = resourcemanager->GetTexture("sky_front",skyimage[0]);
32 skytexture[1] = resourcemanager->GetTexture("sky_back",skyimage[1]);
33 skytexture[2] = resourcemanager->GetTexture("sky_left",skyimage[2]);
34 skytexture[3] = resourcemanager->GetTexture("sky_right",skyimage[3]);
35 skytexture[4] = resourcemanager->GetTexture("sky_top",skyimage[4]);
36 //! 获取天空盒指针
37 RefPtr<SceneNode> skybox = scenemanager->GetSkyBox(NULL,skytexture[0],skytexture[1],skytexture[2],skytexture[3],skytexture[4],500,500,600);
38
39 //! 设置地形数据
40 terrainimage[0] = resourcemanager->GetImage("terrain_image","..\\terrain//terrain.bmp");
41 terrainimage[1] = resourcemanager->GetImage("terrain_detail","..\\terrain//detail.bmp");
42 terraintexture[0] = resourcemanager->GetTexture("terrain_texture1",terrainimage[0]);
43 terraintexture[1] = resourcemanager->GetTexture("terrain_texture2",terrainimage[1]);
44 RefPtr<Terrain> terrain = scenemanager->GetTerrain(NULL,"..\\terrain//terrain.raw",1024,terraintexture[0],terraintexture[1]);
45
46 int height = terrain->GetHeight(440,370);
47 height += 40;
48 //! 获取新的摄像机并设置为活动摄像机
49 RefPtr<Camera> camera = scenemanager->CreateCamera("mycamera", Vector3f(10,height,10),
50 Vector3f(512,height - 30,512),
51 Vector3f(0,1,0));
52 //! 设置当前活动摄像机
53 scenemanager->SetActiveCamera(camera);
54 camera->SetViewport(0,0,640,480);
55
56 //! 雾设置
57 RefPtr<Fog> fog = scenemanager->GetFog();
58 fog->SetColor(core::Color(0.3f,0.5f,0.2f));
59 fog->SetDensity(0.0012f);
60 fog->SetQuality(0.004f);
61 fog->SetBound(0.2f,1000.0f);
62 fog->Render();
63
64 RefPtr<ActiveModel3D> model = scenemanager->GetActiveModel("md2model");
65 model->Load("..\\model\\hobgoblin.md2");
66 RefPtr<Image> md2image = resourcemanager->GetImage("md2image","..\\model//hobgoblin.bmp");
67 RefPtr<Texture> md2texture = resourcemanager->GetTexture("md2texture",md2image);
68 model->LoadTexture(md2texture);
69 model->SetTranslate(Vector3f(180,10+terrain->GetHeight(112,512),180));
70
71 std::vector<AnimationFrame> frames;
72 model->GetFrameList(frames);
73
74 BEGIN_LOOP(device);
75 camera->SetPerspective(45,640.0f/480.0f,6.0f,1000);
76 camera->Render();
77 skybox->Render();
78 terrain->Render();
79 model->Render();
80 static int begin_frame = 0;
81 static int end_frame = begin_frame+1;;
82 static float t = 0.0f;
83 t+=0.02;
84 if(t>1)
85 {
86 t = 0;
87 end_frame++;
88 begin_frame++;
89 }
90 if(begin_frame == frames.back().frame_end)
91 end_frame = begin_frame = 0;
92 model->SetCurrentFrame(begin_frame,end_frame,t);
93
94 static float angle = 0.0f;
95 skybox->SetRotate(core::AXIS_Z,angle);
96
97 angle+=0.000003;
98 if(angle>360)
99 angle-=360;
100 END_LOOP(device);
101
102 device->Close();
103 device->Drop();
104
105 system("PAUSE");
106 return EXIT_SUCCESS;
107 }
108
109
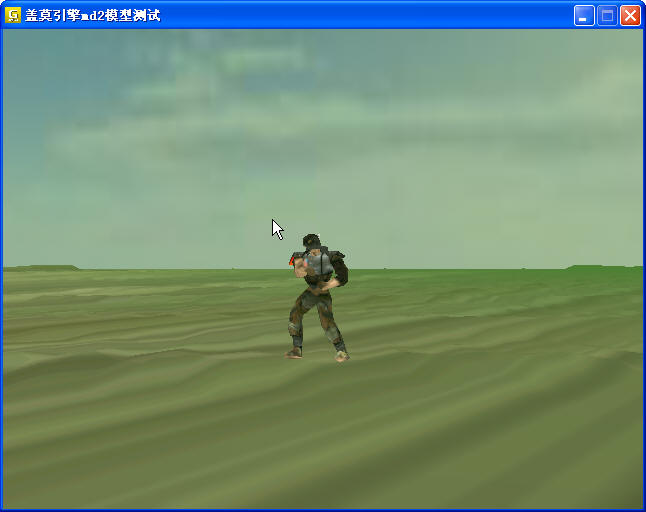
贴图如下:这里的模型是源于opengl游戏开发一书
再来一个Opengl3d游戏开发中士兵的模型例子如下(当然我拿走了他的枪):
我会先让引擎具备常见的功能
之后我就会考虑加入引擎自己的亮点和消除引擎存在的Bug
当然了各类编辑器的设计也是迟早的了
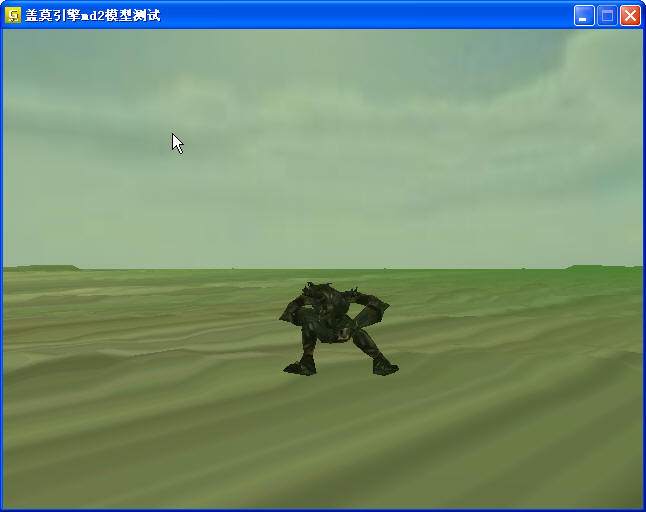
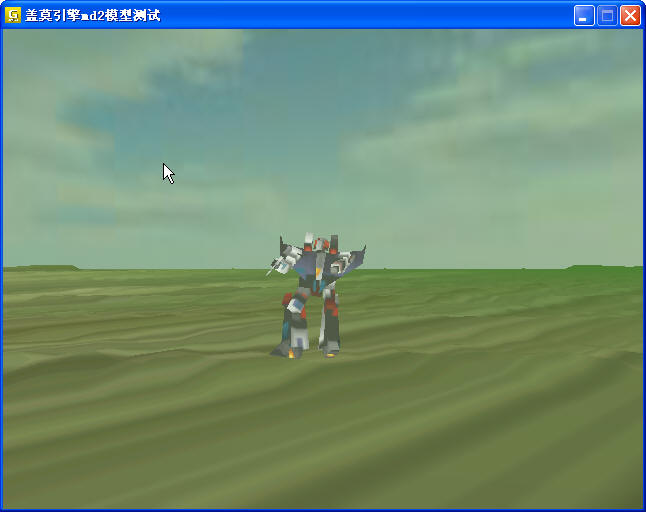
再来一个机器人的md2模型
摘要: 以前早就看过了如何使用opengl绘制3ds静态对象的材料现在总把这个加入到引擎里面了具体代码如下:
1 #include <cstdlib> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <GEngine/Main.hpp> 4 ...
阅读全文
这是盖莫游戏引擎中的坐标系统和输入系统测试的小例子代码如下所示:
1 #include <cstdlib>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <GEngine/Main.hpp>
4
5 using namespace std;
6 using namespace core;
7
8 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
9 {
10 Device *device = InitDevice("盖莫引擎坐标系统测试");
11 device->SetClearColor(core::Color(80,100,230));
12 int x,y,z;
13 //! 使用Opengl坐标系统
14 core::CoordinateSystem cs(COORDINATE_OPENGL);
15 device->SetCoordinateSystem(cs);
16
17 //! 启用2D渲染模式
18 device->Ortho2D();
19 //! 获取资源管理器
20 core::ResourceManager* resmgr = device->GetResourceManager();
21 core::RefPtr<core::Text> defont= resmgr->GetText("default_font");
22
23 char text[255];
24 char fpstext[20];
25 float fps = device->GetFPS();
26 BEGIN_LOOP(device);
27 device->GetInput()->GetMousePosition(x,y,z);
28 sprintf(text,"mouse position is :x = %d, y = %d,z = %d",x,y,z);
29 fps = device->GetFPS();
30 sprintf(fpstext,"fps is:%f",fps);
31 defont->Render(20,20,text);
32 defont->Render(540,20,fpstext);
33 END_LOOP(device);
34
35 device->Close();
36 device->Drop();
37
38 system("PAUSE");
39 return EXIT_SUCCESS;
40 }
41
对于opengl坐标系,其原点位于屏幕左下角
当前字体的渲染坐标固定为x轴向右,y轴向下,以屏幕左上角为原点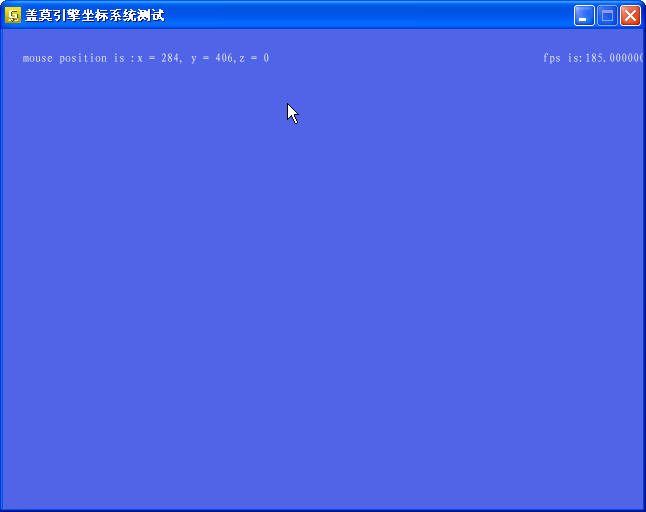
这是贴图 不过看上去帧速有点偏低