类型转换操作符(type conversion operator)是一种特殊的类成员函数,它定义将类类型值转变为其他类型值的转换。转换操作符在类定义体内声明,在保留字 operator 之后跟着转换的目标类型。boost::ref和boost::cref就使用到了类型转换操作符。
函数原型
 T1::operator T2() const; //T1的成员函数,"(T2)a"类型转换
T1::operator T2() const; //T1的成员函数,"(T2)a"类型转换1. 转换函数必须是成员函数,不能指定返回类型,并且形参表必须为空;返回值是隐含的,返回值是与转换的类型相同的,即为上面原型中的T2;
2. T2表示内置类型名(built-in type)、类类型名(class type)或由类型别名(typedef)定义的名字;对任何可作为函数返回类型的类型(除了 void 之外)都可以定义转换函数,一般而言,不允许转换为数组或函数类型,转换为指针类型(数据和函数指针)以及引用类型是可以的;
3. 转换函数一般不应该改变被转换的对象,因此转换操作符通常应定义为 const 成员;
4. 支持继承,可以为虚函数;
5. 只要存在转换,编译器将在可以使用内置转换的地方自动调用它;
for an example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class D{
public:
D(double d):
d_(d){}
operator int()const{
cout<<"(int)d called!!"<<endl;
return static_cast<int>(d_);
}
private:
double d_;
};
int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
int main(){
D d1=1.1;
D d2=2.2;
cout<<"add(d1,d2)="<<add(d1,d2)<<endl;
return 0;
}
(int)d called!!
(int)d called!!
add(d1,d2)=3
Press any key to continue
类型转换构造函数(conversion constructor)
先来说下类型转换构造函数:C++中的explicit用来修饰类的构造函数,表明该构造函数是显示的,既然有显示的,那么就有隐式的
若果一个类的构造函数时一个单自变量的构造函数,所谓的单自变量是可能声明一个单一参数,也可能声明一个拥有多个参数,并且除了第一参数外都其他参数都有默认值
这样的constructor称为单自变量constructor.
若果类中有这样一个constructor那么在编译的时候编译器将会产生一个省却的操作:将该constructor参数对应 的 数据类型 的 数据转换为该类的对象
class MyClass
{
public:
MyClass( int num );
}
....
MyClass obj = 10; //ok,convert int to MyClass
在上面的操作中编译器其实产生代码如下:
Myclass temp(10);
Myclass obj=temp;
若果要避免编译器产生上诉的隐式转换,那么此时explicit将产生作用。
explicit的作用:
explicit关键字将作用在类的构造函数,被修饰的构造函数,将再不能发生隐式转换了,只能以显示的进行类型转换
explicit 的注意:
只能作用在类的内部的构造函数上
只能作用在单自变量的构造函数上
class Circle {
public:
Circle(double r) : R(r) {}
Circle(int x, int y = 0) : X(x), Y(y) {}
Circle(const Circle& c) : R(c.R), X(c.X), Y(c.Y) {}
private:
double R;
int X;
int Y;
};
int main(){
Circle A = 1.23;
//发生隐式类型转换
//编译器会将它变成如下代码
//tmp = Circle(1.23)
//Circle A(tmp);
//tmp.~Circle();
Circle B = 123;
//注意是int型的,调用的是Circle(int x, int y = 0)
//它虽然有2个参数,但后一个有默认值,任然能发生隐式转换
Circle C = A;
//这个算隐式调用了拷贝构造函数
return 0;
}
加了explicit关键字后,可防止以上隐式类型转换发生
class Circle {
public:
explicit Circle(double r) : R(r) {}
explicit Circle(int x, int y = 0) : X(x), Y(y) {}
explicit Circle(const Circle& c) : R(c.R), X(c.X), Y(c.Y) {}
private:
double R;
int X;
int Y;
};
int _main() {
//一下3句,都会报错
//Circle A = 1.23;
//Circle B = 123;
//Circle C = A;
//只能用显示的方式调用了
//未给拷贝构造函数加explicit之前可以这样
Circle A = Circle(1.23);
Circle B = Circle(123);
Circle C = A;
//给拷贝构造函数加了explicit后只能这样了
Circle A(1.23);
Circle B(123);
Circle C(A);
return 0;
}
类型转换操作符 vs 类型转换构造函数(conversion constructor)
有时候使用conversion constructor就能实现类型转换,这种方式效率更高而且也更直观,下面举例说明:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3 class A{
4 public:
5 A(int num=0)
6 :dat(num){
7 cout<<"A单参数构造函数called!!"<<endl;
8 }
9 operator int(){
10 cout<<"A::operator int() called!!"<<endl;
11 return dat;
12 }
13 private:
14 int dat;
15 };
16
17 class X{
18 public:
19 X(int num=0)
20 :dat(num){
21 cout<<"X单参数构造函数called!!"<<endl;
22 }
23 operator int(){
24 cout<<"X::operator int() called!!"<<endl;
25 return dat;
26 }
27 operator A(){
28 cout<<"operator x() called!!"<<endl;
29 A temp=dat;
30 return temp;
31 }
32 private:
33 int dat;
34 };
35
36 int main(){
37 cout<<"///////trace more///////"<<endl;
38 A more=0;
39
40 cout<<"///////trace stuff///////"<<endl;
41 X stuff=2;
42
43 cout<<"//////trace hold dingyi////// "<<endl;
44 int hold;
45
46 cout<<"///////trace hold=stuff//////"<<endl;
47 hold=stuff;
48 cout<<"///////two trace hold=stuff//////"<<endl;
49 cout<<"hold:"<<hold<<endl;
50
51 cout<<"//////trace more=stuff//////"<<endl;
52 more =stuff;
53 cout<<"//////two trace more=stuff//////"<<endl;
54 cout<<"more:"<<more<<endl;
55
56 return 0;
57 }
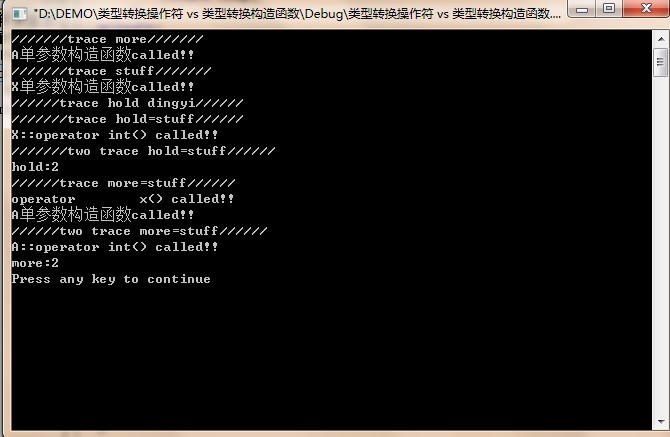
上面这个程序中X类通过“operator A()”类型转换来实现将X类型对象转换成A类型,这种方式需要先创建一个临时A对象再用它去赋值目标对象;更好的方式是为A类增加一个构造函数:
A(const X& rhs) : dat(rhs) {}
同时,请注意上面程序的more的类型在调用std::cout时被隐式地转成了int!
一个简单boost::ref实现
通过重载type conversion operator,我们就可以自己实现一个简版的boost::ref。
1 #include <iostream>
2
3 template <class T>
4 class RefHolder{
5 public:
6 RefHolder(T& ref) : ref_(ref) {}
7
8 /* “(T&)A”类型转换操作符 */
9 operator T& () const {
10 return ref_;
11 }
12 private:
13 T& ref_;
14 };
15
16
17 template <class T>
18 inline RefHolder<T> ByRef(T& t) {
19 return RefHolder<T>(t);
20 }
21
22 int inc(int& num) {
23 num++;
24 return num;
25 }
26
27
28 int main() {
29 int n = 1;
30 std::cout << inc(ByRef(n)) << std::endl; //RefHolder<int>被转换成了"int&"类型
31
32 return 0;
33 }
34
35