一
OpenGL抛弃glEnable(),glColor(),glVertex(),glEnable()这一套流程的函数和管线以后,就需要一种新的方法来传递数据到Graphics Card来渲染几何体,我们可以用VBO, 在3+版本我们可以使用Vertex Array Object-VAO,VAO是一个对象,其中包含一个或者更多的Vertex Buffer Objects。而VBO是Graphics Card中的一个内存缓冲区,用来保存顶点信息,颜色信息,法线信息,纹理坐标信息和索引信息等等。
VAO在Graphics Card线性的存储几个对象信息,替代了以前发送我们需要的数据到Graphics Card上,这也是Direct3D没有立即模式情况下工作的方法,这就意味着应用程序不需要传输数据到Graphics Card上而得到较高的性能。
Coding:
unsigned int vaoID[1]; // Our Vertex Array Object
unsigned int vboID[1]; // Our Vertex Buffer Object
float* vertices = new float[18]; // Vertices for our square
最后不能忘记
delete [] vertices; // Delete our vertices from memory
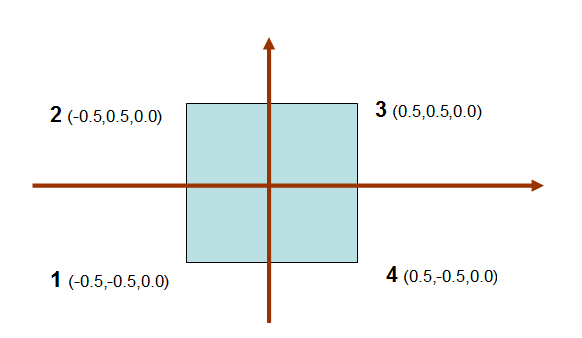
现在要填充顶点的数据值,把所有顶点的Z轴值设置为0,正方形的边长为1,左上角(-0.5, 0.5, 0.0),右下角(0.5,-0.5, 0.0):
/**
createSquare is used to create the Vertex Array Object which will hold our square. We will
be hard coding in the vertices for the square, which will be done in this method.
*/
void OpenGLContext::createSquare(void) {
float* vertices = new float[18]; // Vertices for our square
vertices[0] = -0.5; vertices[1] = -0.5; vertices[2] = 0.0; // 左下 1
vertices[3] = -0.5; vertices[4] = 0.5; vertices[5] = 0.0; // 左上 2
vertices[6] = 0.5; vertices[7] = 0.5; vertices[8] = 0.0; // 右上 3
vertices[9] = 0.5; vertices[10] = -0.5; vertices[11] = 0.0; // 右下 4
vertices[12] = -0.5; vertices[13] = -0.5; vertices[14] = 0.0; //左下1vertices[15] = 0.5; vertices[16] = 0.5; vertices[17] = 0.0; // 右上 3
delete [] vertices; // Delete our vertices from memory
}
设置数据以后,我们需要用 glGenVertexArrays 创建一个Vertex Array Object, 然后使用glBindVertexArray绑定VAO,一旦VAO绑定后,使glGenBuffers 创建一个Vertex Buffer Object, 当然仍然需要使用glBindBuffer绑定VBO;
顺序如下:
1. Generate Vertex Array Object
2. Bind Vertex Array Object
3. Generate Vertex Buffer Object
4. Bind Vertex Buffer Object
下面要使用glBufferData来初始化和用刚VAO创建的数据分配数据给VBO,再告诉VBO的数据是从VAO而来,需要清理Vertex Attributr Array和Vertex Array Object.
glGenVertexArrays(1, &vaoID[0]); // Create our Vertex Array Object
glBindVertexArray(vaoID[0]); // Bind our Vertex Array Object so we can use it
glGenBuffers(1, vboID); // Generate our Vertex Buffer Object
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vboID[0]); // Bind our Vertex Buffer Object
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 18 * sizeof(GLfloat), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW); // Set the size and data of our VBO and set it to STATIC_DRAW
glVertexAttribPointer((GLuint)0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, 0); // Set up our vertex attributes pointer
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); // Disable our Vertex Array Object
glBindVertexArray(0); // Disable our Vertex Buffer Object
delete [] vertices; // Delete our vertices from memory
绘制:
glBindVertexArray(vaoID[0]); // Bind our Vertex Array Object
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6); // Draw our square
glBindVertexArray(0); // Unbind our Vertex Array Object
二
主要使用API:
void glGenVertexArrays(GLSize n, GLuint * *arrays);
返回n个当前未使用的名字,用作数组arrays中的顶点数组对象,
创建了VAO以后,需要初始化新的对象,并且把要使用的顶点数组数据的对象的集合与单个已分配的对象关联起来,
GLvoid glBingVertexArray(GLuint array);
glBingVertexArray做了三件事,当使用的值array 不是零并且是从glGenVertexArrays()返回的值时,创建一个新的VAO,,并且分配该名字;当绑定到之前创建的一个VAO的时候,该VAO就是当前活动的;当绑定到一个为0的数组时,就停止使用VAO,并且返回顶点数组的默认状态。
如果array不是之前从glGenVertexArray返回的值,如果是glDeleteVertexArray()已经释放的值,如果调用任何一个gl*Pointer()函数来指定一个顶点数组,而在绑定一个非0VAO的时候,它没有和缓冲区对象关联起来,将会返回GL_INVALID_OPERATION错误。
这个函数是绑定VAO到上下文,并没有像glBindBuffer那样take a target。
void glVertexAttribPointer()
首先要清楚关联a buffer object和 a vertex attribute并不发生在glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER),而是发生在glVertexAttribPointer();当你调用glVertexAttribPointer() ,OpenGL 获取缓冲区绑定到GL_ARRAY_BUFFER 并且关联顶点属性,想象一下GL_ARRAY_BUFFER就像一个全局指针。
void glDrawArrays(GLenum type ,GLint start, GLint count);
ArrayDraw的方式:
void glDrawArrays(GLenum type, GLint start, GLint count)
{
for(GLint element = start; element < start + count; element++)
{
VertexShader(positionAttribArray[element], colorAttribArray[element]);
}
}
void glDrawElements(GLenum type, GLint count, GLenum type, GLsizeiptr indices)
Indexed Draw 的方式:
GLvoid *elementArray;
void glDrawElements(GLenum type, GLint count, GLenum type, GLsizeiptr indices)
{
GLtype *ourElementArray = (type*)((GLbyte *)elementArray + indices);
for(GLint elementIndex = 0; elementIndex < count; elementIndex++)
{
GLint element = ourElementArray[elementIndex];
VertexShader(positionAttribArray[element], colorAttribArray[element]);
}
}假设顶点属性是:
Position Array: Pos0, Pos1, Pos2, Pos3
Color Array: Clr0, Clr1, Clr2, Clr3
可以使用这些顶点数据以arraydraw的方式先绘制一个三角形,在绘制另外一个三角形(start=0,count=2),而如果使用index draw使用这个四个顶点能绘制4个三角行
Element Array: 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2, 3
即:
(Pos0, Clr0), (Pos1, Clr1), (Pos2, Clr2),
(Pos0, Clr0), (Pos2, Clr2), (Pos3, Clr3),
(Pos0, Clr0), (Pos3, Clr3), (Pos1, Clr1),
(Pos1, Clr1), (Pos2, Clr2), (Pos3, Clr3),
使用index draw需要准备两件事:a properly constructed element array ,using a drawing command
Element arrays, 是存储在buffer object:GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER 用法上是和GL_ARRAY_BUFFER一样,但是必须要知道indexed drawing is only possible when a buffer object is bound to this binding point, and the element array comes from this buffer object.
so In order to do indexed drawing, we must bind the buffer to GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER and then call glDrawElements
void glDrawElements(GLenum mode, GLsizei count, GLenum type, GLsizeiptr indices);
The first parameter is the same as the first parameter of glDrawArrays.
The count parameter defines how many indices will be pulled from the element array.
The type field defines what the basic type of the indices in the element array are. For example, if the indices are stored as 16-bit unsigned shorts (GLushort), then this field should be GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT. This allows the user the freedom to use whatever size of index they want.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE and GL_UNSIGNED_INT (32-bit) are also allowed; indices must be unsigned.
The last parameter is the byte-offset into the element array at which the index data begins. Index data (and vertex data, for that matter) should always be aligned to its size. So if we are using 16-bit unsigned shorts for indices, then indices should be an even number.
有一个实例:
const int numberOfVertices = 36;
#define RIGHT_EXTENT 0.8f
#define LEFT_EXTENT -RIGHT_EXTENT
#define TOP_EXTENT 0.20f
#define MIDDLE_EXTENT 0.0f
#define BOTTOM_EXTENT -TOP_EXTENT
#define FRONT_EXTENT -1.25f
#define REAR_EXTENT -1.75f
#define GREEN_COLOR 0.75f, 0.75f, 1.0f, 1.0f
#define BLUE_COLOR 0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f
#define RED_COLOR 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f
#define GREY_COLOR 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f, 1.0f
#define BROWN_COLOR 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f
const float vertexData[] = {
//Object 1 positions
LEFT_EXTENT, TOP_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, MIDDLE_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, MIDDLE_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, TOP_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, BOTTOM_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, MIDDLE_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, MIDDLE_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, BOTTOM_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, TOP_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, MIDDLE_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, BOTTOM_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, TOP_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, MIDDLE_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, BOTTOM_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, BOTTOM_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
LEFT_EXTENT, TOP_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, TOP_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
RIGHT_EXTENT, BOTTOM_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
//Object 2 positions
TOP_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
MIDDLE_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
MIDDLE_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
TOP_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
BOTTOM_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
MIDDLE_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
MIDDLE_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
BOTTOM_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
TOP_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
MIDDLE_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
BOTTOM_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
TOP_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
MIDDLE_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, FRONT_EXTENT,
BOTTOM_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
BOTTOM_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
TOP_EXTENT, RIGHT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
TOP_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
BOTTOM_EXTENT, LEFT_EXTENT, REAR_EXTENT,
//Object 1 colors
GREEN_COLOR,
GREEN_COLOR,
GREEN_COLOR,
GREEN_COLOR,
BLUE_COLOR,
BLUE_COLOR,
BLUE_COLOR,
BLUE_COLOR,
RED_COLOR,
RED_COLOR,
RED_COLOR,
GREY_COLOR,
GREY_COLOR,
GREY_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
//Object 2 colors
RED_COLOR,
RED_COLOR,
RED_COLOR,
RED_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
BROWN_COLOR,
BLUE_COLOR,
BLUE_COLOR,
BLUE_COLOR,
GREEN_COLOR,
GREEN_COLOR,
GREEN_COLOR,
GREY_COLOR,
GREY_COLOR,
GREY_COLOR,
GREY_COLOR,
};
const GLshort indexData[] =
{
0, 2, 1,
3, 2, 0,
4, 5, 6,
6, 7, 4,
8, 9, 10,
11, 13, 12,
14, 16, 15,
17, 16, 14,
};
GLuint vertexBufferObject;
GLuint indexBufferObject;
GLuint vaoObject1, vaoObject2;
void InitializeVertexBuffer()
{
glGenBuffers(1, &vertexBufferObject);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBufferObject);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertexData), vertexData, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
glGenBuffers(1, &indexBufferObject);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexBufferObject);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indexData), indexData, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
}
void InitializeVertexArrayObjects()
{
glGenVertexArrays(1, &vaoObject1);
glBindVertexArray(vaoObject1);
size_t colorDataOffset = sizeof(float) * 3 * numberOfVertices;
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBufferObject);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, 0);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 4, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)colorDataOffset);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexBufferObject);
glBindVertexArray(0);
glGenVertexArrays(1, &vaoObject2);
glBindVertexArray(vaoObject2);
size_t posDataOffset = sizeof(float) * 3 * (numberOfVertices/2);
colorDataOffset += sizeof(float) * 4 * (numberOfVertices/2);
//Use the same buffer object previously bound to GL_ARRAY_BUFFER.
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)posDataOffset);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 4, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)colorDataOffset);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexBufferObject);
glBindVertexArray(0);
}
Draw:
glBindVertexArray(vaoObject1);
glUniform3f(offsetUniform, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, ARRAY_COUNT(indexData), GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, 0);
glBindVertexArray(vaoObject2);
glUniform3f(offsetUniform, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, ARRAY_COUNT(indexData), GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, 0);
glBindVertexArray(0);例子:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* Ensure we are using opengl's core profile only */
#define GL3_PROTOTYPES 1
#include <GL3/gl3.h>
#include <SDL.h>
#define PROGRAM_NAME "Tutorial2"
/* A simple function that will read a file into an allocated char pointer buffer */
char* filetobuf(char *file)
{
FILE *fptr;
long length;
char *buf;
fptr = fopen(file, "rb"); /* Open file for reading */
if (!fptr) /* Return NULL on failure */
return NULL;
fseek(fptr, 0, SEEK_END); /* Seek to the end of the file */
length = ftell(fptr); /* Find out how many bytes into the file we are */
buf = (char*)malloc(length+1); /* Allocate a buffer for the entire length of the file and a null terminator */
fseek(fptr, 0, SEEK_SET); /* Go back to the beginning of the file */
fread(buf, length, 1, fptr); /* Read the contents of the file in to the buffer */
fclose(fptr); /* Close the file */
buf[length] = 0; /* Null terminator */
return buf; /* Return the buffer */
}
/* A simple function that prints a message, the error code returned by SDL, and quits the application */
void sdldie(char *msg)
{
printf("%s: %s\n", msg, SDL_GetError());
SDL_Quit();
exit(1);
}
void setupwindow(SDL_WindowID *window, SDL_GLContext *context)
{
if (SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO) < 0) /* Initialize SDL's Video subsystem */
sdldie("Unable to initialize SDL"); /* Or die on error */
/* Request an opengl 3.2 context.
* SDL doesn't have the ability to choose which profile at this time of writing,
* but it should default to the core profile */
SDL_GL_SetAttribute(SDL_GL_CONTEXT_MAJOR_VERSION, 3);
SDL_GL_SetAttribute(SDL_GL_CONTEXT_MINOR_VERSION, 2);
/* Turn on double buffering with a 24bit Z buffer.
* You may need to change this to 16 or 32 for your system */
SDL_GL_SetAttribute(SDL_GL_DOUBLEBUFFER, 1);
SDL_GL_SetAttribute(SDL_GL_DEPTH_SIZE, 24);
/* Create our window centered at 512x512 resolution */
*window = SDL_CreateWindow(PROGRAM_NAME, SDL_WINDOWPOS_CENTERED, SDL_WINDOWPOS_CENTERED,
512, 512, SDL_WINDOW_OPENGL | SDL_WINDOW_SHOWN);
if (!*window) /* Die if creation failed */
sdldie("Unable to create window");
/* Create our opengl context and attach it to our window */
*context = SDL_GL_CreateContext(*window);
/* This makes our buffer swap syncronized with the monitor's vertical refresh */
SDL_GL_SetSwapInterval(1);
}
void drawscene(SDL_WindowID window)
{
int i; /* Simple iterator */
GLuint vao, vbo[2]; /* Create handles for our Vertex Array Object and two Vertex Buffer Objects */
int IsCompiled_VS, IsCompiled_FS;
int IsLinked;
int maxLength;
char *vertexInfoLog;
char *fragmentInfoLog;
char *shaderProgramInfoLog;
/* We're going to create a simple diamond made from lines */
const GLfloat diamond[4][2] = {
{ 0.0, 1.0 }, /* Top point */ |
{ 1.0, 0.0 }, /* Right point */ |
{ 0.0, -1.0 }, /* Bottom point */
{ -1.0, 0.0 } }; /* Left point */
const GLfloat colors[4][3] = {
{ 1.0, 0.0, 0.0 }, /* Red */
{ 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 }, /* Green */
{ 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 }, /* Blue */
{ 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 } }; /* White */
/* These pointers will receive the contents of our shader source code files */
GLchar *vertexsource, *fragmentsource;
/* These are handles used to reference the shaders */
GLuint vertexshader, fragmentshader;
/* This is a handle to the shader program */
GLuint shaderprogram;
/* Allocate and assign a Vertex Array Object to our handle */
glGenVertexArrays(1, &vao);
/* Bind our Vertex Array Object as the current used object */
glBindVertexArray(vao);
/* Allocate and assign two Vertex Buffer Objects to our handle */
glGenBuffers(2, vbo);
/* Bind our first VBO as being the active buffer and storing vertex attributes (coordinates) */
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vbo[0]);
/* Copy the vertex data from diamond to our buffer */
/* 8 * sizeof(GLfloat) is the size of the diamond array, since it contains 8 GLfloat values */
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), diamond, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
/* Specify that our coordinate data is going into attribute index 0, and contains two floats per vertex */
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, 0);
/* Enable attribute index 0 as being used */
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
/* Bind our second VBO as being the active buffer and storing vertex attributes (colors) */
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vbo[1]);
/* Copy the color data from colors to our buffer */
/* 12 * sizeof(GLfloat) is the size of the colors array, since it contains 12 GLfloat values */
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 12 * sizeof(GLfloat), colors, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
/* Specify that our color data is going into attribute index 1, and contains three floats per vertex */
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, 0);
/* Enable attribute index 1 as being used */
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
/* Read our shaders into the appropriate buffers */
vertexsource = filetobuf("tutorial2.vert");
fragmentsource = filetobuf("tutorial2.frag");
/* Create an empty vertex shader handle */
vertexshader = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
/* Send the vertex shader source code to GL */
/* Note that the source code is NULL character terminated. */
/* GL will automatically detect that therefore the length info can be 0 in this case (the last parameter) */
glShaderSource(vertexshader, 1, (const GLchar**)&vertexsource, 0);
/* Compile the vertex shader */
glCompileShader(vertexshader);
glGetShaderiv(vertexshader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &IsCompiled_VS);
if(IsCompiled_VS == FALSE)
{
glGetShaderiv(vertexshader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &maxLength);
/* The maxLength includes the NULL character */
vertexInfoLog = (char *)malloc(maxLength);
glGetShaderInfoLog(vertexshader, maxLength, &maxLength, vertexInfoLog);
/* Handle the error in an appropriate way such as displaying a message or writing to a log file. */
/* In this simple program, we'll just leave */
free(vertexInfoLog);
return;
}
/* Create an empty fragment shader handle */
fragmentshader = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
/* Send the fragment shader source code to GL */
/* Note that the source code is NULL character terminated. */
/* GL will automatically detect that therefore the length info can be 0 in this case (the last parameter) */
glShaderSource(fragmentshader, 1, (const GLchar**)&fragmentsource, 0);
/* Compile the fragment shader */
glCompileShader(fragmentshader);
glGetShaderiv(fragmentshader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &IsCompiled_FS);
if(IsCompiled_FS == FALSE)
{
glGetShaderiv(fragmentshader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &maxLength);
/* The maxLength includes the NULL character */
fragmentInfoLog = (char *)malloc(maxLength);
glGetShaderInfoLog(fragmentshader, maxLength, &maxLength, fragmentInfoLog);
/* Handle the error in an appropriate way such as displaying a message or writing to a log file. */
/* In this simple program, we'll just leave */
free(fragmentInfoLog);
return;
}
/* If we reached this point it means the vertex and fragment shaders compiled and are syntax error free. */
/* We must link them together to make a GL shader program */
/* GL shader programs are monolithic. It is a single piece made of 1 vertex shader and 1 fragment shader. */
/* Assign our program handle a "name" */
shaderprogram = glCreateProgram();
/* Attach our shaders to our program */
glAttachShader(shaderprogram, vertexshader);
glAttachShader(shaderprogram, fragmentshader);
/* Bind attribute index 0 (coordinates) to in_Position and attribute index 1 (color) to in_Color */
/* Attribute locations must be setup before calling glLinkProgram. */
glBindAttribLocation(shaderprogram, 0, "in_Position");
glBindAttribLocation(shaderprogram, 1, "in_Color");
/* Link our program */
/* At this stage, the vertex and fragment programs are inspected, optimized and a binary code is generated for the shader. */
/* The binary code is uploaded to the GPU, if there is no error. */
glLinkProgram(shaderprogram);
/* Again, we must check and make sure that it linked. If it fails, it would mean either there is a mismatch between the vertex */
/* and fragment shaders. It might be that you have surpassed your GPU's abilities. Perhaps too many ALU operations or */
/* too many texel fetch instructions or too many interpolators or dynamic loops. */
glGetProgramiv(shaderprogram, GL_LINK_STATUS, (int *)&IsLinked);
if(IsLinked == FALSE)
{
/* Noticed that glGetProgramiv is used to get the length for a shader program, not glGetShaderiv. */
glGetProgramiv(shaderprogram, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &maxLength);
/* The maxLength includes the NULL character */
shaderProgramInfoLog = (char *)malloc(maxLength);
/* Notice that glGetProgramInfoLog, not glGetShaderInfoLog. */
glGetProgramInfoLog(shaderprogram, maxLength, &maxLength, shaderProgramInfoLog);
/* Handle the error in an appropriate way such as displaying a message or writing to a log file. */
/* In this simple program, we'll just leave */
free(shaderProgramInfoLog);
return;
}
/* Load the shader into the rendering pipeline */
glUseProgram(shaderprogram);
/* Loop our display increasing the number of shown vertexes each time.
* Start with 2 vertexes (a line) and increase to 3 (a triangle) and 4 (a diamond) */
for (i=2; i <= 4; i++)
{
/* Make our background black */
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
/* Invoke glDrawArrays telling that our data is a line loop and we want to draw 2-4 vertexes */
glDrawArrays(GL_LINE_LOOP, 0, i);
/* Swap our buffers to make our changes visible */
SDL_GL_SwapWindow(window);
/* Sleep for 2 seconds */
SDL_Delay(2000);
}
/* Cleanup all the things we bound and allocated */
glUseProgram(0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(1);
glDetachShader(shaderprogram, vertexshader);
glDetachShader(shaderprogram, fragmentshader);
glDeleteProgram(shaderprogram);
glDeleteShader(vertexshader);
glDeleteShader(fragmentshader);
glDeleteBuffers(2, vbo);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &vao);
free(vertexsource);
free(fragmentsource);
}
void destroywindow(SDL_WindowID window, SDL_GLContext context)
{
SDL_GL_DeleteContext(context);
SDL_DestroyWindow(window);
SDL_Quit();
}
/* Our program's entry point */
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
SDL_WindowID mainwindow; /* Our window handle */
SDL_GLContext maincontext; /* Our opengl context handle */
/* Create our window, opengl context, etc... */
setupwindow(&mainwindow, &maincontext);
/* Call our function that performs opengl operations */
drawscene(mainwindow);
/* Delete our opengl context, destroy our window, and shutdown SDL */
destroywindow(mainwindow, maincontext);
return 0;
}参考:
VAOs,_VBOs,_Vertex_and_Fragment_Shaders
VAO
opengl-3-3-glsl-1-5-sample
Vertex array object
Open GL : Using Vertex Array Objects to Organize Your Buffers
Vertex Buffer Objects