You can Solve a Geometry Problem too
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3077 Accepted Submission(s): 1452
Problem Description
Many geometry(几何)problems were designed in the ACM/ICPC. And now, I also prepare a geometry problem for this final exam. According to the experience of many ACMers, geometry problems are always much trouble, but this problem is very easy, after all we are now attending an exam, not a contest :)
Give you N (1<=N<=100) segments(线段), please output the number of all intersections(交点). You should count repeatedly if M (M>2) segments intersect at the same point.
Note:
You can assume that two segments would not intersect at more than one point.
Input
Input contains multiple test cases. Each test case contains a integer N (1=N<=100) in a line first, and then N lines follow. Each line describes one segment with four float values x1, y1, x2, y2 which are coordinates of the segment’s ending.
A test case starting with 0 terminates the input and this test case is not to be processed.
Output
For each case, print the number of intersections, and one line one case.
Sample Input
2 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.00 3 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 0.000 0.00 0.00 1.00 0.00 0
Sample Output
Author
lcy
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Line
{
double x1,y1,x2,y2;
}node[110];
bool solve(Line a,Line b)
{
if(((a.x1-b.x1)*(a.y2-b.y1)-(a.x2-b.x1)*(a.y1-b.y1))*((a.x1-b.x2)*(a.y2-b.y2)-(a.x2-b.x2)*(a.y1-b.y2))>0)return false;
if(((b.x1-a.x1)*(b.y2-a.y1)-(b.x2-a.x1)*(b.y1-a.y1))*((b.x1-a.x2)*(b.y2-a.y2)-(b.x2-a.x2)*(b.y1-a.y2))>0)return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&node[i].x1,&node[i].y1,&node[i].x2,&node[i].y2);
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(solve(node[i],node[j]))res++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",res);
}
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/11/01/2230923.html
Write a simple HTML Browser
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3398 Accepted Submission(s): 890
Problem Description
If you ever tried to read a html document on a Macintosh, you know how hard it is if no Netscape is installed.
Now, who can forget to install a HTML browser? This is very easy because most of the times you don't need one on a MAC because there is a Acrobate Reader which is native to MAC. But if you ever need one, what do you do?
Your task is to write a small html-browser. It should only display the content of the input-file and knows only the html commands (tags) <br> which is a linebreak and <hr> which is a horizontal ruler. Then you should treat all tabulators, spaces and newlines as one space and display the resulting text with no more than 80 characters on a line.
Input
The input consists of a text you should display. This text consists of words and HTML tags separated by one or more spaces, tabulators or newlines.
A word is a sequence of letters, numbers and punctuation. For example, "abc,123" is one word, but "abc, 123" are two words, namely "abc," and "123". A word is always shorter than 81 characters and does not contain any '<' or '>'. All HTML tags are either <br> or <hr>.
Output
You should display the the resulting text using this rules:
. If you read a word in the input and the resulting line does not get longer than 80 chars, print it, else print it on a new line.
. If you read a <br> in the input, start a new line.
. If you read a <hr> in the input, start a new line unless you already are at the beginning of a line, display 80 characters of '-' and start a new line (again).
The last line is ended by a newline character.
Sample Input
Hallo, dies ist eine ziemlich lange Zeile, die in Html aber nicht umgebrochen wird. <br> Zwei <br> <br> produzieren zwei Newlines. Es gibt auch noch das tag <hr> was einen Trenner darstellt. Zwei <hr> <hr> produzieren zwei Horizontal Rulers. Achtung mehrere Leerzeichen irritieren Html genauso wenig wie mehrere Leerzeilen.
Sample Output
Hallo, dies ist eine ziemlich lange Zeile, die in Html aber nicht umgebrochen wird. Zwei produzieren zwei Newlines. Es gibt auch noch das tag -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- was einen Trenner darstellt. Zwei -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- produzieren zwei Horizontal Rulers. Achtung mehrere Leerzeichen irritieren Html genauso wenig wie mehrere Leerzeilen.
Source
Recommend
JGShining
刷题练手感!!!!水题啊!
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
//freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("test.out","w",stdout);
char str[100];
int cnt=0;//数每行的字符数
bool first=true;//记录是否是一行的开头,开头不要空格的
while(scanf("%s",&str)!=EOF)
{
if(strcmp(str,"<br>")==0){printf("\n");cnt=0;first=true;continue;}
if(strcmp(str,"<hr>")==0)
{
if(!first){printf("\n");first=true;}
for(int i=0;i<80;i++)printf("-");
printf("\n");first=true;cnt=0;
continue;
}
if(first)
{
printf("%s",str);
cnt+=strlen(str);first=false;
continue;
}
cnt+=(strlen(str)+1);first=false;
if(cnt<=80)
{
printf(" %s",str);
continue;
}
else
{
printf("\n");
printf("%s",str);
cnt=strlen(str);first=false;
}
}
if(!first)printf("\n");//最后以新行结束
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/11/01/2230917.html
Lottery
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1108 Accepted Submission(s): 544
Problem Description
Eddy's company publishes a kind of lottery.This set of lottery which are numbered 1 to n, and a set of one of each is required for a prize .With one number per lottery, how many lottery on average are required to make a complete set of n coupons?
Input
Input consists of a sequence of lines each containing a single positive integer n, 1<=n<=22, giving the size of the set of coupons.
Output
For each input line, output the average number of lottery required to collect the complete set of n coupons. If the answer is an integer number, output the number. If the answer is not integer, then output the integer part of the answer followed by a space and then by the proper fraction in the format shown below. The fractional part should be irreducible. There should be no trailing spaces in any line of ouput.
Sample Input
Sample Output
3 5 11 -- 12 340463 58 ------ 720720
Author
eddy
Recommend
JGShining
题目没有看懂啊~~~~
/*****************************************************************
HDU 1099
*****************************************************************/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
long long gcd(long long a,long long b)
{
if(b==0)return a;
else return gcd(b,a%b);
}
int main()
{
int i,n;
long long number,n1,n2;
long long integer;
long long fenzi,fenmu;
long long a[23];
a[1]=1;
for(i=2;i<=22;i++)a[i]=i*a[i-1]/gcd(i,a[i-1]);
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
fenzi=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++) fenzi+=a[n]/i;
fenzi*=n;
number=gcd(fenzi,a[n]);
fenzi=fenzi/number;
fenmu=a[n]/number;
integer=fenzi/fenmu;
fenzi-=integer*fenmu;
if(fenzi==0)
{
printf("%I64d\n",integer);continue;
}
int size1=0,size2=0;
n1=integer;n2=fenmu;
while(n1!=0){size1++;n1/=10;}
while(n2!=0){size2++;n2/=10;}
for(i=0;i<=size1;i++)printf("");
printf("%I64d\n",fenzi);
printf("%I64d ",integer);
for(i=0;i<size2;i++)printf("-");
printf("\n");
for(i=0;i<=size1;i++)printf("");
printf("%I64d\n",fenmu);
}
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/30/2229004.html
维基百科资料:
卡塔兰数
卡塔兰数是组合数学中一个常出现在各种计数问题中出现的数列。由以比利时的数学家欧仁·查理·卡塔兰 (1814–1894)命名。
卡塔兰数的一般项公式为 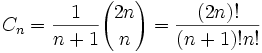 另类递归式: h(n)=((4*n-2)/(n+1))*h(n-1); 另类递归式: h(n)=((4*n-2)/(n+1))*h(n-1);
前几项为 (OEIS中的数列A000108): 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, 208012, 742900, 2674440, 9694845, 35357670, 129644790, 477638700, 1767263190, 6564120420, 24466267020, 91482563640, 343059613650, 1289904147324, 4861946401452, ...
Cn的另一个表达形式为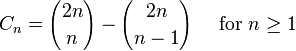 所以,Cn是一个自然数;这一点在先前的通项公式中并不显而易见。这个表达形式也是André对前一公式证明的基础。(见下文的第二个证明。) 所以,Cn是一个自然数;这一点在先前的通项公式中并不显而易见。这个表达形式也是André对前一公式证明的基础。(见下文的第二个证明。)
卡塔兰数满足以下递推关系
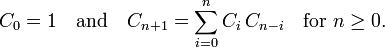
它也满足
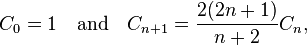
这提供了一个更快速的方法来计算卡塔兰数。
卡塔兰数的渐近增长为
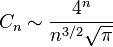
它的含义是左式除以右式的商趋向于1当n → ∞。(这可以用n!的斯特灵公式来证明。)
所有的奇卡塔兰数Cn都满足n = 2k − 1。所有其他的卡塔兰数都是偶数。
组合数学中有非常多.的组合结构可以用卡塔兰数来计数。在Richard P. Stanley的Enumerative Combinatorics: Volume 2一书的习题中包括了66个相异的可由卡塔兰数表达的组合结构。以下用Cn=3和Cn=4举若干例:
- Cn表示长度2n的dyck word的个数。Dyck word是一个有n个X和n个Y组成的字串,且所有的部分字串皆满足X的个数大于等于Y的个数。以下为长度为6的dyck words:
XXXYYY XYXXYY XYXYXY XXYYXY XXYXYY
- 将上例的X换成左括号,Y换成右括号,Cn表示所有包含n组括号的合法运算式的个数:
((())) ()(()) ()()() (())() (()())
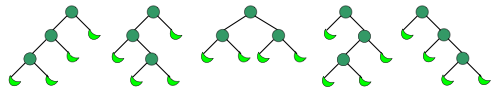
- Cn表示所有不同构的含n个分枝结点的满二叉树的个数。(一个有根二叉树是满的当且仅当每个结点都有两个子树或没有子树。)
证明:
令1表示进栈,0表示出栈,则可转化为求一个2n位、含n个1、n个0的二进制数,满足从左往右扫描到任意一位时,经过的0数不多于1数。显然含n个1、n个0的2n位二进制数共有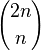 个,下面考虑不满足要求的数目. 个,下面考虑不满足要求的数目.
考虑一个含n个1、n个0的2n位二进制数,扫描到第2m+1位上时有m+1个0和m个1(容易证明一定存在这样的情况),则后面的0-1排列中必有n-m个1和n-m-1个0。将2m+2及其以后的部分0变成1、1变成0,则对应一个n+1个0和n-1个1的二进制数。反之亦然(相似的思路证明两者一一对应)。
从而 。证毕。 。证毕。
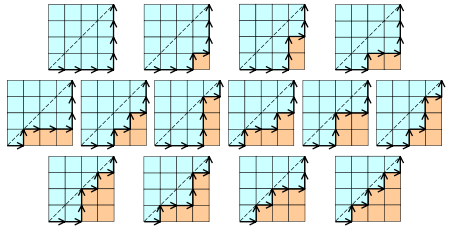
- Cn表示所有在n × n格点中不越过对角线的单调路径的个数。一个单调路径从格点左下角出发,在格点右上角结束,每一步均为向上或向右。计算这种路径的个数等价于计算Dyck word的个数: X代表“向右”,Y代表“向上”。下图为n = 4的情况:
-
- Cn表示通过连结顶点而将n + 2边的凸多边形分成三角形的方法个数。下图中为n = 4的情况:
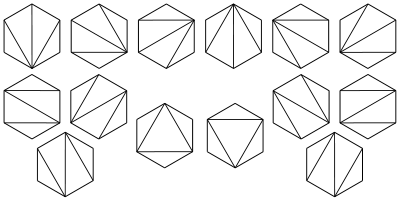
- Cn表示对{1, ..., n}依序进出栈的置换个数。一个置换w是依序进出栈的当S(w) = (1, ..., n), 其中S(w)递归定义如下:令w = unv,其中n为w的最大元素,u和v为更短的数列;再令S(w) =S(u)S(v)n,其中S为所有含一个元素的数列的单位元。
- Cn表示用n个长方形填充一个高度为n的阶梯状图形的方法个数。下图为 n = 4的情况:

百度百科资料:
简介
中文:卡特兰数
Catalan数是组合数学中一个常出现在各种计数问题中出现的数列。由以比利时的数学家欧仁·查理·卡塔兰 (1814–1894)命名。
原理:
令h(0)=1,h(1)=1,catalan数满足递归式:
h(n)= h(0)*h(n-1) + h(1)*h(n-2) +  + h(n-1)h(0) (其中n>=2) + h(n-1)h(0) (其中n>=2)
该递推关系的解为:
h(n)=C(2n,n)/(n + 1) (n=1,2,3, ) )
另类递归式: h(n)=((4*n-2)/(n+1))*h(n-1);
前几项为 (OEIS中的数列A000108): 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, 208012, 742900, 2674440, 9694845, 35357670, 129644790, 477638700, 1767263190, 6564120420, 24466267020, 91482563640, 343059613650, 1289904147324, 4861946401452, 
应用
我总结了一下,最典型的四类应用:(实质上却都一样,无非是递归等式的应用,就看你能不能分解问题写出递归式了)
1.括号化问题。
矩阵链乘: P=a1×a2×a3×……×an,依据乘法结合律,不改变其顺序,只用括号表示成对的乘积,试问有几种括号化的方案?(h(n)种)
2.出栈次序问题。
一个栈(无穷大)的进栈序列为1,2,3,..n,有多少个不同的出栈序列?
类似:
(1)有2n个人排成一行进入剧场。入场费5元。其中只有n个人有一张5元钞票,另外n人只有10元钞票,剧院无其它钞票,问有多少中方法使得只要有10元的人买票,售票处就有5元的钞票找零?(将持5元者到达视作将5元入栈,持10元者到达视作使栈中某5元出栈)
(2)在圆上选择2n个点,将这些点成对连接起来,使得所得到的n条线段不相交的方法数。
3.将多边行划分为三角形问题。
将一个凸多边形区域分成三角形区域的方法数?
类似:一位大城市的律师在她住所以北n个街区和以东n个街区处工作。每天她走2n个街区去上班。如果她
从不穿越(但可以碰到)从家到办公室的对角线,那么有多少条可能的道路?
类似:在圆上选择2n个点,将这些点成对连接起来使得所得到的n条线段不相交的方法数?
4.给顶节点组成二叉树的问题。
给定N个节点,能构成多少种形状不同的二叉树?
(一定是二叉树!
先去一个点作为顶点,然后左边依次可以取0至N-1个相对应的,右边是N-1到0个,两两配对相乘,就是h(0)*h(n-1) + h(2)*h(n-2) +  + h(n-1)h(0)=h(n)) + h(n-1)h(0)=h(n))
(能构成h(N)个)
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/13/2210935.html
Random Sequence
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 202 Accepted Submission(s): 124
Problem Description
There is a random sequence L whose element are all random numbers either -1 or 1 with the same possibility. Now we define MAVS, the abbreviate of Maximum Absolute Value Subsequence, to be any (if more than one) subsequences of L whose absolute value is maximum among all subsequences. Given the length of L, your task is to find the expectation of the absolute value of MAVS.
Input
There is only one input file. The first line is the number of test cases T. T positive integers follow, each of which contains one positive number not greater than 1500 denoted the length of L.
Output
For each test case, output the expectation you are required to calculate. Answers are rounded to 6 numbers after the decimal point.(as shown in the sample output)
Sample Input
Sample Output
Case 1: 1.000000 Case 2: 2.750000 Case 3: 4.167969
Source
Recommend
lcy
数论神题啊!!!!
卡特兰数
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
long double a[2000];
long double p;
long double C(int n){
long double t=1;
for(int i=n+1;i<=2*n+1;i++){
t*=i;
t/=i-n;
}
// for(int i=1;i<=n+1;i++) t/=i;
return t;
}
int main(){
int t,n,cnt=0;
a[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=1500;i++){
if(i%2==0) a[i]=(a[i-1]*2+C(i/2-1));
else a[i]=(a[i-1]*2+C(i/2-1)*2);
//cout<<"i="<<i<<","<<a[i]<<endl;
}
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n;
p=pow(2.0,n-1);
cout<<"Case "<<++cnt<<": "<<fixed<<setprecision(6)<<a[n]/p<<endl;
}
// system("pause");
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/13/2210930.html
A Card Game
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4 Accepted Submission(s): 3
Problem Description
There are N cards on the table, whose front side is writen one integer number from 1 to M. We call one card "a type k card" if its number is k. The quantity of type i cards is a_i.
Let's play a game with these cards. We divide these cards into M piles by random with the only constrains that the quantity of cards in i-th (indexed from 1) pile must exactly be a_i. The possbility of each card appears in i-th pile is directly proportional to the size of this pile. That is to say, if the size of a pile is A, the possibility for each card appears in this pile is A/N assuming that N is the amount of all cards. We choose pile 1 to start the game. Assuming the we now play this game at pile k, we randomly choose a card from pile k with the same possibility for all cards in it, remember the number written on this card and throw it away. If the number on the chosen card is j, we continue this game at pile j on next round. The game terminates when we are going to get a card from an empty pile.
Now the question is, when the game ends, what is the possibility that all piles are empty?
Input
There is only one input file. The first line is the number of test cases T. T cases follow, each of which contains two lines. The first line is an integer M (1 <= M <= 100), the number of type of cards (and the number of piles, they are exactly the same). The second line contains M positive integers not greater than 1000, the i-th number of which is a_i.
Output
For each test case, output the possibility you are required to calculate. Answers are rounded to 6 numbers after the decimal point.(as shown in the sample output)
Sample Input
Sample Output
Case 1: 1.000000 Case 2: 0.333333
水题,看代码:
这样的题目很爽!
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int T;
int iCase=0;
int a;
int n;
int ans,res;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
iCase++;
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%d",&ans);
res=ans;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
res+=a;
}
printf("Case %d: %.6lf\n",iCase,(double)ans/res);
}
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/07/2200549.html
Working in Beijing
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65768/65768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 659 Accepted Submission(s): 333
Problem Description
Mr. M is an undergraduate student of FDU. He finds an intern position in Beijing, so that he cannot attend all the college activities. But in some conditions, he must come back to Shanghai on certain date. We can assume the important activities that Mr. M must attend are occupy a whole day. Mr. M must take flight to Shanghai before that day and leave after that day. On the other hand, Mr. M is absent in Beijing and he will lose his salary for his absent.
Sometimes the cost of flight is much higher than the loss of salary, so to save the cost on the travel, Mr. M can stay in Shanghai to wait for another important date before he back to Beijing.
Now, Mr. M knows all of the important date in the next year. Help him schedule his travel to optimize the cost.
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of single integer indicates the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains three integers: n, a and b, denoting the number of important events, the cost of a single flight from Beijing to Shanghai or Shanghai to Beijing and the salary for a single day stay in Beijing. (1 <= n <= 100000, 1 <= a <= 1000000000, 1 <= b <=100)
Next line contains n integers ti, denoting the time of the important events. You can assume the ti are in increasing order and they are different from each other. (0 <= ti <= 10000000)
Output
For each test case, output a single integer indicating the minimum cost for this year.
Sample Input
2 1 10 10 5 5 10 2 5 10 15 65 70
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
lcy
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
long long res;
int n,a,b;
int t1,t2;
int i,T;
int iCase=0;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
iCase++;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&a,&b);
res=a+b;
scanf("%d",&t1);
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t2);
if((t2-t1-1)*b>2*a) res+=2*a+b;
else res+=b*(t2-t1);
t1=t2;
}
res+=a;
printf("Case #%d: %I64d\n",iCase,res);
}
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/04/2198939.html
Parsing URL
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65768/65768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 520 Accepted Submission(s): 321
Problem Description
In computing, a Uniform Resource Locator or Universal Resource Locator (URL) is a character string that specifies where a known resource is available on the Internet and the mechanism for retrieving it.
The syntax of a typical URL is:
scheme://domain:port/path?query_string#fragment_id
In this problem, the scheme, domain is required by all URL and other components are optional. That is, for example, the following are all correct urls:
http://dict.bing.com.cn/#%E5%B0%8F%E6%95%B0%E7%82%B9
http://www.mariowiki.com/Mushroom
https://mail.google.com/mail/?shva=1#inbox
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bowser_(character)
ftp://fs.fudan.edu.cn/
telnet://bbs.fudan.edu.cn/
http://mail.bashu.cn:8080/BsOnline/
Your task is to find the domain for all given URLs.
Input
There are multiple test cases in this problem. The first line of input contains a single integer denoting the number of test cases.
For each of test case, there is only one line contains a valid URL.
Output
For each test case, you should output the domain of the given URL.
Sample Input
3 http://dict.bing.com.cn/#%E5%B0%8F%E6%95%B0%E7%82%B9 http://www.mariowiki.com/Mushroom https://mail.google.com/mail/?shva=1#inbox
Sample Output
Case #1: dict.bing.com.cn Case #2: www.mariowiki.com Case #3: mail.google.com
Source
Recommend
lcy
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
char str[5000];
char tt[5000];
int main()
{
int T;
int iCase=0;
bool start;
int i;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
iCase++;
scanf("%s",&str);
start=false;
int len=strlen(str);
int t=0;
for(i=2;i<len;i++)
{
if(start==false&&str[i-2]==':'&&str[i-1]=='/'&&str[i]=='/') {start=true;continue;}
if(start&&(str[i]=='/'||str[i]==':')) break;
if(start) tt[t++]=str[i];
}
tt[t]='\0';
printf("Case #%d: %s\n",iCase,tt);
}
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/04/2198937.html
Mario and Mushrooms
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65768/65768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 265 Accepted Submission(s): 220
Problem Description
Mario usually relaxes himself by walking along the shady track near the Mushroom Kingdom. The evil King Koopa noticed that and placed a lot of mushroom on the road. There are two types of mushrooms, max mushrooms and bad mushrooms. The bad mushrooms will decrease Mario's HP by m points, on the other hand, max mushrooms will increase Mario's HP by one point. The mushrooms are randomly placed on the track and Mario will receive them one by one. Once Mario's HP becomes zero or below after he received a mushroom, he will die.
Notice that Mario begins with HP zero, so if the first mushroom is bad, Mario will die immediately. Fortunately, if Mario receives all the mushrooms, he will be alive with HP 1. In the other words, if there are k bad mushrooms on the way, there will also be m*k+1 max mushrooms.
Princess Peach wants to know the possibility for Mario staying alive. Please help her to calculate it out.
Input
There are several test cases. The first line contains only one integer T, denoting the number of test cases.
For each test case, there is only one line including two integers: m and k, denoting the amount of points of HP the Mario will decrease if he receives a bad mushroom, and the number of bad mushrooms on the track. (1 <= m <= 1000, 1 <= k <= 1000)
Output
For each test case, output only real number denoting the possibility that Mario will survive if he receives all the randomly placed mushrooms one by one. The answer should be rounded to eight digits after the decimal point.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Case #1: 0.33333333 Case #2: 0.00020488
Source
Recommend
lcy
明显的概率题。。。。
结果通过样例猜想就得出来了。。。很简单的结果,秒过
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int T;
int m,k;
int iCase=0;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
iCase++;
scanf("%d%d",&m,&k);
printf("Case #%d: %.8lf\n",iCase,(double)1/(k+m*k+1));
}
return 0;
}
文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/04/2198936.html
接触ACM以来的第一场正式比赛,也许会是最后一场比赛了,ACM,短暂的时间通过ACM也学到了不少东西,认识到了不少人,哈哈~~~~~ 文章来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/kuangbin/archive/2011/10/04/2198904.html
|
|
|
| | 日 | 一 | 二 | 三 | 四 | 五 | 六 |
|---|
| 30 | 31 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 1 | 2 | 3 | | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|
公告
导航
统计
- 随笔: 100
- 文章: 0
- 评论: 2
- 引用: 0
常用链接
留言簿
随笔分类
随笔档案
博客
搜索
最新评论

阅读排行榜
评论排行榜
|
|