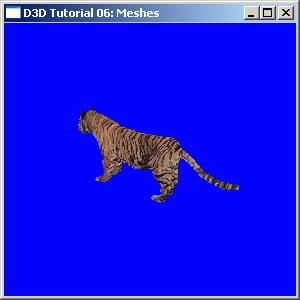
效果:
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// File: Meshes.cpp
//
// Desc: For advanced geometry, most apps will prefer to load pre-authored
// meshes from a file. Fortunately, when using meshes, D3DX does most of
// the work for this, parsing a geometry file and creating vertx buffers
// (and index buffers) for us. This tutorial shows how to use a D3DXMESH
// object, including loading it from a file and rendering it. One thing
// D3DX does not handle for us is the materials and textures for a mesh,
// so note that we have to handle those manually.
//
// Note: one advanced (but nice) feature that we don't show here is that
// when cloning a mesh we can specify the FVF. So, regardless of how the
// mesh was authored, we can add/remove normals, add more texture
// coordinate sets (for multi-texturing), etc.
//
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <Windows.h>
#include <mmsystem.h>
#include <d3dx9.h>
#pragma warning( disable : 4996 ) // disable deprecated warning
#include <strsafe.h>
#pragma warning( default : 4996 )
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Global variables
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
LPDIRECT3D9 g_pD3D = NULL; // Used to create the D3DDevice
LPDIRECT3DDEVICE9 g_pd3dDevice = NULL; // Our rendering device
LPD3DXMESH g_pMesh = NULL; // Our mesh object in sysmem
D3DMATERIAL9* g_pMeshMaterials = NULL; // Materials for our mesh
LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9* g_pMeshTextures = NULL; // Textures for our mesh
DWORD g_dwNumMaterials = 0L; // Number of mesh materials
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: InitD3D()
// Desc: Initializes Direct3D
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
HRESULT InitD3D( HWND hWnd )
{
// Create the D3D object.
if( NULL == ( g_pD3D = Direct3DCreate9( D3D_SDK_VERSION ) ) )
return E_FAIL;
// Set up the structure used to create the D3DDevice. Since we are now
// using more complex geometry, we will create a device with a zbuffer.
D3DPRESENT_PARAMETERS d3dpp;
ZeroMemory( &d3dpp, sizeof(d3dpp) );
d3dpp.Windowed = TRUE;
d3dpp.SwapEffect = D3DSWAPEFFECT_DISCARD;
d3dpp.BackBufferFormat = D3DFMT_UNKNOWN;
d3dpp.EnableAutoDepthStencil = TRUE;
d3dpp.AutoDepthStencilFormat = D3DFMT_D16;
// Create the D3DDevice
if( FAILED( g_pD3D->CreateDevice( D3DADAPTER_DEFAULT, D3DDEVTYPE_HAL, hWnd,
D3DCREATE_SOFTWARE_VERTEXPROCESSING,
&d3dpp, &g_pd3dDevice ) ) )
{
return E_FAIL;
}
// Turn on the zbuffer
g_pd3dDevice->SetRenderState( D3DRS_ZENABLE, TRUE );
// Turn on ambient lighting
g_pd3dDevice->SetRenderState( D3DRS_AMBIENT, 0xffffffff );
return S_OK;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: InitGeometry()
// Desc: Load the mesh and build the material and texture arrays
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
HRESULT InitGeometry()
{
LPD3DXBUFFER pD3DXMtrlBuffer;
// Load the mesh from the specified file
// 从指定文件加载网格
if( FAILED( D3DXLoadMeshFromX( "Tiger.x", D3DXMESH_SYSTEMMEM,
g_pd3dDevice, NULL,
&pD3DXMtrlBuffer, NULL, &g_dwNumMaterials,
&g_pMesh ) ) )
{
// If model is not in current folder, try parent folder
if( FAILED( D3DXLoadMeshFromX( "..\\Tiger.x", D3DXMESH_SYSTEMMEM,
g_pd3dDevice, NULL,
&pD3DXMtrlBuffer, NULL, &g_dwNumMaterials,
&g_pMesh ) ) )
{
MessageBox(NULL, "Could not find tiger.x", "Meshes.exe", MB_OK);
return E_FAIL;
}
}
// We need to extract the material properties and texture names from the
// pD3DXMtrlBuffer
// 从pD3DXMtrlBuffer里面析取出材质属性和纹理名字
D3DXMATERIAL* d3dxMaterials = (D3DXMATERIAL*)pD3DXMtrlBuffer->GetBufferPointer();
g_pMeshMaterials = new D3DMATERIAL9[g_dwNumMaterials]; // 放材质
if( g_pMeshMaterials == NULL )
return E_OUTOFMEMORY;
g_pMeshTextures = new LPDIRECT3DTEXTURE9[g_dwNumMaterials]; // 放纹理
if( g_pMeshTextures == NULL )
return E_OUTOFMEMORY;
for( DWORD i=0; i<g_dwNumMaterials; i++ )
{
// Copy the material
// 拷贝材质
g_pMeshMaterials[i] = d3dxMaterials[i].MatD3D;
// Set the ambient color for the material (D3DX does not do this)
g_pMeshMaterials[i].Ambient = g_pMeshMaterials[i].Diffuse;
g_pMeshTextures[i] = NULL;
if( d3dxMaterials[i].pTextureFilename != NULL &&
lstrlen(d3dxMaterials[i].pTextureFilename) > 0 )
{
// Create the texture
// 创建纹理
if( FAILED( D3DXCreateTextureFromFile( g_pd3dDevice,
d3dxMaterials[i].pTextureFilename,
&g_pMeshTextures[i] ) ) )
{
// If texture is not in current folder, try parent folder
const TCHAR* strPrefix = TEXT("..\\");
TCHAR strTexture[MAX_PATH];
StringCchCopy( strTexture, MAX_PATH, strPrefix );
StringCchCat( strTexture, MAX_PATH, d3dxMaterials[i].pTextureFilename );
// If texture is not in current folder, try parent folder
if( FAILED( D3DXCreateTextureFromFile( g_pd3dDevice,
strTexture,
&g_pMeshTextures[i] ) ) )
{
MessageBox(NULL, "Could not find texture map", "Meshes.exe", MB_OK);
}
}
}
}
// Done with the material buffer
pD3DXMtrlBuffer->Release();
return S_OK;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: Cleanup()
// Desc: Releases all previously initialized objects
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID Cleanup()
{
if( g_pMeshMaterials != NULL )
delete[] g_pMeshMaterials;
if( g_pMeshTextures )
{
for( DWORD i = 0; i < g_dwNumMaterials; i++ )
{
if( g_pMeshTextures[i] )
g_pMeshTextures[i]->Release();
}
delete[] g_pMeshTextures;
}
if( g_pMesh != NULL )
g_pMesh->Release();
if( g_pd3dDevice != NULL )
g_pd3dDevice->Release();
if( g_pD3D != NULL )
g_pD3D->Release();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: SetupMatrices()
// Desc: Sets up the world, view, and projection transform matrices.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID SetupMatrices()
{
// Set up world matrix
D3DXMATRIXA16 matWorld;
D3DXMatrixRotationY( &matWorld, timeGetTime()/1000.0f );
g_pd3dDevice->SetTransform( D3DTS_WORLD, &matWorld );
// Set up our view matrix. A view matrix can be defined given an eye point,
// a point to lookat, and a direction for which way is up. Here, we set the
// eye five units back along the z-axis and up three units, look at the
// origin, and define "up" to be in the y-direction.
D3DXVECTOR3 vEyePt( 0.0f, 3.0f,-5.0f );
D3DXVECTOR3 vLookatPt( 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f );
D3DXVECTOR3 vUpVec( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f );
D3DXMATRIXA16 matView;
D3DXMatrixLookAtLH( &matView, &vEyePt, &vLookatPt, &vUpVec );
g_pd3dDevice->SetTransform( D3DTS_VIEW, &matView );
// For the projection matrix, we set up a perspective transform (which
// transforms geometry from 3D view space to 2D viewport space, with
// a perspective divide making objects smaller in the distance). To build
// a perpsective transform, we need the field of view (1/4 pi is common),
// the aspect ratio, and the near and far clipping planes (which define at
// what distances geometry should be no longer be rendered).
D3DXMATRIXA16 matProj;
D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH( &matProj, D3DX_PI/4, 1.0f, 1.0f, 100.0f );
g_pd3dDevice->SetTransform( D3DTS_PROJECTION, &matProj );
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: Render()
// Desc: Draws the scene
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
VOID Render()
{
// Clear the backbuffer and the zbuffer
g_pd3dDevice->Clear( 0, NULL, D3DCLEAR_TARGET|D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER,
D3DCOLOR_XRGB(0,0,255), 1.0f, 0 );
// Begin the scene
if( SUCCEEDED( g_pd3dDevice->BeginScene() ) )
{
// Setup the world, view, and projection matrices
SetupMatrices();
// Meshes are divided into subsets, one for each material. Render them in
// a loop
// 网格被划分成子集,每个子集对应着一个材质
for( DWORD i=0; i<g_dwNumMaterials; i++ )
{
// Set the material and texture for this subset
g_pd3dDevice->SetMaterial( &g_pMeshMaterials[i] );
g_pd3dDevice->SetTexture( 0, g_pMeshTextures[i] );
// Draw the mesh subset
g_pMesh->DrawSubset( i );
}
// End the scene
g_pd3dDevice->EndScene();
}
// Present the backbuffer contents to the display
g_pd3dDevice->Present( NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL );
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: MsgProc()
// Desc: The window's message handler
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT WINAPI MsgProc( HWND hWnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam )
{
switch( msg )
{
case WM_DESTROY:
Cleanup();
PostQuitMessage( 0 );
return 0;
}
return DefWindowProc( hWnd, msg, wParam, lParam );
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Name: WinMain()
// Desc: The application's entry point
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
INT WINAPI WinMain( HINSTANCE hInst, HINSTANCE, LPSTR, INT )
{
// Register the window class
WNDCLASSEX wc = { sizeof(WNDCLASSEX), CS_CLASSDC, MsgProc, 0L, 0L,
GetModuleHandle(NULL), NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL,
"D3D Tutorial", NULL };
RegisterClassEx( &wc );
// Create the application's window
HWND hWnd = CreateWindow( "D3D Tutorial", "D3D Tutorial 06: Meshes",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, 100, 100, 300, 300,
NULL, NULL, wc.hInstance, NULL );
// Initialize Direct3D
if( SUCCEEDED( InitD3D( hWnd ) ) )
{
// Create the scene geometry
if( SUCCEEDED( InitGeometry() ) )
{
// Show the window
ShowWindow( hWnd, SW_SHOWDEFAULT );
UpdateWindow( hWnd );
// Enter the message loop
MSG msg;
ZeroMemory( &msg, sizeof(msg) );
while( msg.message!=WM_QUIT )
{
if( PeekMessage( &msg, NULL, 0U, 0U, PM_REMOVE ) )
{
TranslateMessage( &msg );
DispatchMessage( &msg );
}
else
Render();
}
}
}
UnregisterClass( "D3D Tutorial", wc.hInstance );
return 0;
}
posted on 2007-02-16 18:28
七星重剑 阅读(810)
评论(0) 编辑 收藏 引用 所属分类:
Game Graphics