#
schindlerlee原创,禁止转载和用于商业用途
边看 见过大爷 边写竟然5分钟不到秒了~
拓扑排序有两种做法,一种是不断找入度为0的点,然后删点和关联的边,一种是利用dfs退栈的顺序
如下:
1 /*
2 * SOUR:pku 2367
3 * ALGO:top sort
4 * DATE: Mon, 12 Oct 2009 00:56:07 +0800
5 * COMM:2
6 * */
7 #include<iostream>
8 #include<cstdio>
9 #include<cstdlib>
10 #include<cstring>
11 #include<algorithm>
12 #include<vector>
13 using namespace std;
14 typedef long long LL;
15 const int maxint = 0x7fffffff;
16 const long long max64 = 0x7fffffffffffffffll;
17 #define pr(x ) fprintf(stderr, x)
) fprintf(stderr, x)
18 /* #define pr(x ) for(;0;) */
) for(;0;) */
19 const int N = 128;
20 vector < int >g[N];
21 int dfn[N], n, vis[N], st[N], top;
22
23 void dfs(int u)
24 {
25 if (vis[u]) return;
26 vis[u] = true;
27 for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++) {
28 dfs(g[u][i]);
29 }
30 st[top++] = u;
31 }
32
33 int main()
34 {
35 int i, j, k, u, v;
36 scanf("%d", &n);
37 for (u = 1; u <= n; u++) {
38 while (1) {
39 scanf("%d", &v);
40 if (0 == v)
41 break;
42 g[u].push_back(v);
43 }
44 }
45 for (u = 1; u <= n; u++) {
46 if (!vis[u]) {
47 dfs(u);
48 }
49 }
50 for (i = top - 1; i > 0; i--) {
51 printf("%d ", st[i]);
52 }
53 printf("%d\n", st[i]);
54 return 0;
55 }
56
当出现环时,找入度为0的方法显然当不能找到入度为0的点时且还有剩余点则有环
利用dfs的方法就是找搜索树种的回边,利用染色的方法,算法导论上有介绍
我写的代码如下:
初始化:memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
对所有vis[i] == 0,调用dfs
bool dfs(int u)
{
if(vis[u] == 1) return false;
if(vis[u] == 2) return true;
vis[u] = 1;
for(i = 0;i < g[u].size();i++) {
if(false == dfs(g[u][i])) {
return false;
}
}
vis[u] = 2;
stack[top++] = u;
return true;
}
下图描述了dfs的过程,建议仔细体会一下,求图的割点,桥,LCA的 tarjen算法主要过程基本和此dfs过程非常相似
图中白色是还未访问的,黑色是已经完全访问过的,蓝色的是正在访问的
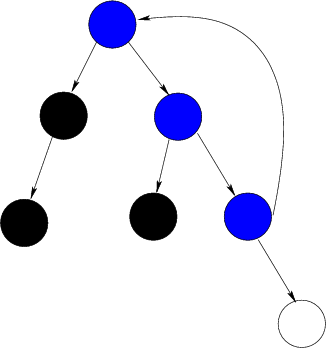
又有好长时间没写了解题报告了,保研总算搞定了,月底去武汉,磨枪中....
1 /*
2 * SOUR:pku 1696
3 * ALGO:computional geometry
4 * DATE: Tue, 13 Oct 2009 10:42:25 +0800
5 * COMM:3
6 * 叉积点积转啊转啊
7 * */
8 #include<iostream>
9 #include<cstdio>
10 #include<cstdlib>
11 #include<cstring>
12 #include<algorithm>
13 #include<cmath>
14 using namespace std;
15 typedef long long LL;
16 const int maxint = 0x7fffffff;
17 const long long max64 = 0x7fffffffffffffffll;
18 #define pr(x ) fprintf(stderr, x)
) fprintf(stderr, x)
19 /* #define pr(x ) for(;0;) */
) for(;0;) */
20 const int N = 128;
21 struct point_t {
22 int x, y, idx;
23 point_t() {
24 } point_t(int a, int b) {
25 x = a, y = b;
26 }
27 } p[N], st[N];
28
29 bool vis[N];
30
31 #define sqr(x) ((x)*(x))
32 double dist(point_t a)
33 { return sqrt(sqr(a.x) + sqr(a.y)); }
34 double dist(point_t a, point_t b)
35 { return sqrt(sqr(a.x - b.x) + sqr(a.y - b.y)); }
36
37 point_t operator +(point_t a, point_t b)
38 { return point_t(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y); }
39 point_t operator -(point_t a, point_t b)
40 { return point_t(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y); }
41
42 int cross_mul(point_t a, point_t b)
43 { return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x; }
44 int cross_mul(point_t a, point_t b, point_t c)
45 { return cross_mul(a - c, b - c); }
46 int dot_mul(point_t a, point_t b)
47 { return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y; }
48 int dot_mul(point_t a, point_t b, point_t c)
49 { return dot_mul(a - c, b - c); }
50
51 double angle(point_t a, point_t b)
52 {
53 double val = dot_mul(a, b);
54 val /= dist(a);
55 val /= dist(b);
56 return val;
57 }
58
59 int n, idx, top;
60 const int inf = (1 << 29);
61 void graham()
62 {
63 int i, j, k;
64 memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
65 top = 2, st[0] = p[0], st[1] = p[1];
66 vis[0] = vis[1] = true;
67 for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
68 double val = -inf;
69 int idx;
70 for (j = 2; j <= n; j++) {
71 if (!vis[j]) {
72 int c = cross_mul(st[top - 1], p[j], st[top - 2]);
73 double d = angle(st[top - 1] - st[top - 2], p[j] - st[top - 1]);
74 if (c > 0) {
75 if ((d > val) || (d == val && dist(p[j], st[top - 1]) < dist(p[idx], st[top - 1]))) {
76 idx = j;
77 val = d;
78 }
79 }
80 }
81 }
82 if (val == -inf)
83 break;
84 st[top++] = p[idx], vis[idx] = true;
85 }
86 }
87
88 int main()
89 {
90 int i, j, k, testid;
91 scanf("%d", &testid);
92 while (testid-- > 0) {
93 scanf("%d", &n);
94 idx = 1;
95 scanf("%d%d%d", &p[1].idx, &p[1].x, &p[1].y);
96 for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
97 scanf("%d%d%d", &p[i].idx, &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
98 if ((p[i].y < p[idx].y) || (p[i].y == p[idx].y && p[i].x < p[idx].x)) {
99 idx = i;
100 }
101 }
102 swap(p[1], p[idx]);
103 p[0].idx = 0, p[0].x = 0, p[0].y = p[1].y;
104 graham();
105 printf("%d", top - 1);
106 for (i = 1; i < top - 1; i++) {
107 printf(" %d", st[i].idx);
108 }
109 printf(" %d\n", st[i].idx);
110 }
111 return 0;
112 }
113
国家集训队2000论文集/方奇论文中的一题
1.dp ,算最小完成时间, 论文中貌似把max写成min了。。
二分求最小完成时间亦可,而且更快,谁让咱们看了论文了呢
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
dp[1][i] = sum[1][i];
}
for(i = 2;i <= m;i++) {
for(j = 1;j <= n;j++) {
dp[i][j] = inf;
}
}
for(i = 2;i <= m;i++) {
for(j = i;j <= n;j++) {
for(k = 1;k < j;k++) { // 至少抄一本
int t = max( dp[i-1][k] , sum[k+1][j]);
if(dp[i][j] > t) {
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] ,t);
}
}
}
}
2.从后向前推把更大的工作量留给后面的人,标记'/'出现的位置
int limit = dp[m][n],sum,cnt;
pre[n] = 0,cnt = 1;
for(i = n-1,sum = num[n];i > 0;i--) {
if(sum + num[i] > limit) {
pre[i] = 1;
cnt ++;
sum = num[i];
}else {
pre[i] = 0;
sum += num[i];
}
}
3.如果'/'的数量小于题目给出的,从头寻找第一个不是'/'的位置,标记之
for(i = 1,j = cnt;j < m && i <= n;i++) {
if(pre[i] == 0) {
pre[i] = 1;
j++;
}
}
4.输出
for(i = 1;i < n;i++) {
printf("%d ",num[i]);
if(pre[i])
printf("/ ");
}
printf("%d\n",num[i]);
注意:不要尝试再dp转移的时候标记转移方向,试图得出标记‘/’的位置,这个想法是错的,仔细想一下就知道了,
再不济AC以后再试试
schindlerlee原创,禁止转载和用于商业用途
此题意思很明显
把一个数从进制a转化到进制b
用C/C++写实在是太麻烦了,用java搞了一下,还是不熟啊,写了好久
1 //java catalan 数
2 import java.math.*;
3 import java.util.*;
4 import java.io.*;
5
6 public class Main {
7
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 Scanner cin = new Scanner(
10 new BufferedReader(
11 new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
12 //That is (in decimal) A = 10, B = 11,  , Z = 35, a = 36, b = 37,
, Z = 35, a = 36, b = 37,  , z = 61
, z = 61
13 int c = cin.nextInt();
14 while (c-- > 0) {
15 int a = cin.nextInt();
16 int b = cin.nextInt();
17 BigInteger r = BigInteger.valueOf(0);
18 BigInteger idx = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
19 String s = cin.next();
20 System.out.println(a + " " + s);
21 for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--, idx = idx.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(a))) {
22 char t = s.charAt(i);
23 //8 62 2 abcdefghiz System.out.println("char t = " + t);
24 int add;
25 if (t >= '0' && t <= '9') {
26 add = t - '0';
27 } else if (t >= 'A' && t <= 'Z') {
28 add = t - 'A' + 10;
29 } else {
30 add = t - 'a' + 36;
31 }
32 r = r.add(idx.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(add)));
33 }
34
35 // System.out.println(r.toString());
36 String res = "";
37 idx = BigInteger.valueOf(b);
38 if (s.equals("0")) {
39 System.out.println(b + " 0");
40 } else {
41 while (r.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO) > 0) {
42 BigInteger ad[];
43 ad = r.divideAndRemainder(idx);
44 r = ad[0];
45 int t = ad[1].intValue();
46 char ch;
47 if (t >= 0 && t <= 9) {
48 ch = (char) (t + '0');
49 } else if (t >= 10 && t <= 35) {
50 ch = (char) (t - 10 + 'A');
51 } else {
52 ch = (char) (t - 36 + 'a');
53 }
54 res = ch + res;
55 // System.out.println("ad[0]= "+ad[0]);
56 // System.out.println("ad[1]= "+ad[1]);
57 }
58 System.out.println(b + " " + res);
59 }
60 System.out.print('\n');
61 //System.out.println("res = "+res);
62 }
63 }
64 }
65
66
schindlerlee原创,禁止转载和用于商业用途
题目描述:
给定一个矩阵,找一个起始点,由该点开始不断马跳,要求跳到的后一节点比前一节点的值大,问最多可以跳多少步,并且输出跳跃的序列,如果两个跳跃序列步数相同,给出字典序较小的
1 2 4
1 2 3
两个序列当然是后一个较小
第一感觉可以求出每个节点的跳跃序列,比较长度得出结果。但是我们发现其中有很多重复的路径,由此想到dp。
本来此题如果只要求最长的跳跃步数的话,就是一道比较简单的dp了。但是题目要求输出最小的序列,需要稍微复杂一点的处理。
可以考虑为每个点增加一个pre坐标,指向前一个点,但是这就带来一个问题,要寻找最小的序列,如果有两个相同长度的序列可供当前点选择的话,直接贪心是错误的,下图为反例
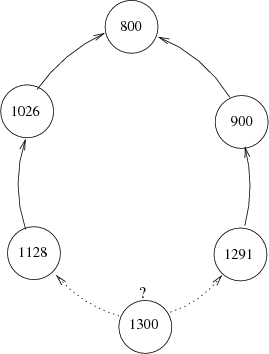
可以发现,如果只比较前一点的话,左边的路线是正确的,但是实际上右边的是正确的。注意这一点基本就没问题了。
1 /*
2 * SOUR:pku 2111
3 * ALGO:dp or search
4 * DATE: 2009年 08月 29日 星期六 04:16:26 CST
5 * COMM:
6 * */
7 #include<iostream>
8 #include<cstdio>
9 #include<cstdlib>
10 #include<cstring>
11 #include<algorithm>
12 using namespace std;
13 const int maxint = 0x7fffffff;
14 const long long max64 = 0x7fffffffffffffffll;
15 #define debug 1
16 const int N = 410;
17 int mov[8][2] = { {1, 2}, {2, 1}, {-1, 2}, {2, -1}, //
18 {1, -2}, {-2, 1}, {-1, -2}, {-2, -1}
19 };
20
21 int g[N][N], pre[N][N][2], n, dp[N][N], out[N], on;
22 struct L {
23 int x, y;
24 int val;
25 } query[N * N];
26 bool operator <(L a, L b)
27 {
28 return a.val < b.val;
29 }
30 int a[N*N],b[N*N];
31 bool judge(int tx,int ty,int px,int py)
32 {
33 int sp = 0,ta,tb,i;
34 while(tx != -1) {
35 a[sp] = g[tx][ty];
36 b[sp] = g[px][py];
37 sp ++;
38 ta = pre[tx][ty][0];
39 tb = pre[tx][ty][1];
40 tx = ta,ty = tb;
41
42 ta = pre[px][py][0];
43 tb = pre[px][py][1];
44 px = ta,py = tb;
45 }
46 for(i = sp - 1;i >= 0 && a[i] == b[i];i--);
47 if(a[i] < b[i])
48 return true;
49 return false;
50 }
51
52 int main()
53 {
54 int i, j, k, x, y, big, tx, ty;
55 scanf("%d", &n);
56 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
57 for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
58 scanf("%d", &g[i][j]);
59 query[i * n + j].val = g[i][j];
60 query[i * n + j].x = i;
61 query[i * n + j].y = j;
62 pre[i][j][0] = pre[i][j][1] = -1;
63 }
64 }
65
66 sort(query, query + n * n);
67 for (i = 0; i < n * n; i++) {
68 x = query[i].x;
69 y = query[i].y;
70 for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
71 int tx = x + mov[j][0];
72 int ty = y + mov[j][1];
73 if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n
74 && g[x][y] > g[tx][ty]) {
75 if (dp[x][y] < dp[tx][ty] + 1) {
76 dp[x][y] = dp[tx][ty] + 1;
77 pre[x][y][0] = tx;
78 pre[x][y][1] = ty;
79 } else if (dp[x][y] == dp[tx][ty] + 1) {
80 int px = pre[x][y][0];
81 int py = pre[x][y][1];
82 if (judge(tx,ty,px,py)) {
83 pre[x][y][0] = tx;
84 pre[x][y][1] = ty;
85 }
86 }
87 }
88 }
89 }
90 on = 0, big = 0;
91 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
92 for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
93 if (dp[i][j] > big) {
94 big = dp[i][j];
95 x = i, y = j;
96 }
97 }
98 }
99 while (x != -1 && y != -1) {
100 out[on++] = g[x][y];
101 tx = pre[x][y][0];
102 ty = pre[x][y][1];
103 x = tx, y = ty;
104 }
105 printf("%d\n", on);
106 for (i = on - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
107 printf("%d\n", out[i]);
108 }
109 return 0;
110 }
111
schindlerlee原创,禁止转载和用于商业用途
刚比赛完,先贴代码
1 /*
2 * SOUR:pku 3744
3 * ALGO:compulicted
4 * DATE: 2009年 08月 23日 星期日 12:37:44 CST
5 * COMM:3
6 * */
7 #include<iostream>
8 #include<cstdio>
9 #include<cstdlib>
10 #include<cstring>
11 #include<algorithm>
12 using namespace std;
13 #define inf 0x7fffffff
14 #define debug 1
15 double p;
16 int mine[26], n;
17
18 struct M {
19 double v11, v12, v21, v22;
20 M operator*( M b)
21 {
22 M c;
23 c.v11 = v11 * b.v11 + v12 * b.v21;
24 c.v12 = v11 * b.v12 + v12 * b.v22;
25 c.v21 = v21 * b.v11 + v22 * b.v21;
26 c.v22 = v21 * b.v12 + v22 * b.v22;
27 return c;
28 }
29
30 M operator*( double c)
31 {
32 v11 *= c, v12 *= c;
33 v21 *= c, v22 *= c;
34 return *this;
35 }
36 } unit,self;
37
38
39 M f(int t)
40 {
41 if (t == 0) {
42 M a;
43 a.v11 = 1, a.v12 = 0;
44 a.v21 = 0, a.v22 = 1;
45 return a;
46 }
47 if (t == 1) {
48 return unit;
49 }
50 if (t % 2 == 0) {
51 M tmp = f(t / 2);
52 return tmp * tmp;
53 }
54 M tmp = f(t / 2);
55 return tmp * tmp * unit;
56 }
57
58 /*
59 f(n) { p ,1-p } f(n-1)
60 f(n-1) = { 1 , 0 } * f(n-2)
61 * */
62 int main()
63 {
64 int i, j;
65 while (scanf("%d %lf", &n, &p) == 2) {
66 unit.v11 = p, unit.v12 = 1 - p;
67 unit.v21 = 1, unit.v22 = 0;
68
69 self.v11 = 1, self.v12 = 0;
70 self.v21 = 0, self.v22 = 1;
71
72 bool flag = false;
73 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
74 scanf("%d", mine + i);
75 }
76 sort(mine, mine + n);
77 n = unique(mine, mine + n) - mine;
78 for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
79 if (mine[i] - mine[i - 1] == 1) {
80 flag = true;
81 break;
82 }
83 }
84 if (flag || mine[0] == 1) {
85 printf("%.7f\n", 0.0);
86 continue;
87 }
88 int t = 1;
89 M res = self, tmp;
90 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
91 tmp = f(mine[i] - 1 - t);
92 t = mine[i] + 1;
93 res = res * tmp * (1 - p);
94 res.v12 = 0; //跳地雷
95 }
96 if(res.v11 <= 0) {
97 printf("%.7f\n", 0.0);
98 }else {
99 printf("%.7f\n", res.v11);
100 }
101 }
102 return 0;
103 }
104
很久没更新了,题刷了不少,但是一直没怎么总结先贴一篇
1 /*
2 * SOUR:pku 1451
3 * ALGO:trie
4 * DATE: 2009年 08月 17日 星期一 13:29:46 CST
5 * COMM:3
6 * */
7 #include<iostream>
8 #include<cstdio>
9 #include<cstdlib>
10 #include<cstring>
11 #include<algorithm>
12 using namespace std;
13 #define inf 0x7fffffff
14 #define debug 1
15 const int N = 1000 * 11;
16 int mov[10][5] =
17 { {-1}, {-1}, {0, 1, 2, -1}, {3, 4, 5, -1}, {6, 7, 8, -1}, {9, 10, 11, -1},
18 {12, 13, 14, -1}, {15, 16, 17, 18, -1}, {19, 20, 21, -1}, {22, 23, 24, 25, -1}
19 };
20
21 struct Trie {
22 int c;
23 Trie *next[26];
24 Trie() {
25 c = 0;
26 memset(next, 0, sizeof(next));
27 }
28 void insert(char *s, int f);
29 void getMax(char *s, int step, int len);
30 } *root, pool[N];
31 int pt;
32 void Trie::insert(char *s, int f)
33 {
34 c += f;
35 if (*s == 0)
36 return;
37 if (next[*s - 'a'] == NULL) {
38 next[*s - 'a'] = &pool[pt++];
39 }
40 next[*s - 'a']->insert(s + 1, f);
41 }
42
43 char tmp[61], res[61];
44 int freq;
45 void Trie::getMax(char *s, int step, int len)
46 {
47 if (step >= len) {
48 tmp[len] = 0;
49 if (c > freq) {
50 //strcpy(res, tmp);
51 for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
52 res[i] = tmp[i];
53 }
54 freq = c;
55 }
56 return;
57 }
58
59 int idx;
60 for (int i = 0; mov[*s - '0'][i] >= 0; i++) {
61 idx = mov[*s - '0'][i];
62 if (next[idx] != NULL) {
63 tmp[step] = idx + 'a';
64 next[idx]->getMax(s + 1, step + 1, len);
65 }
66 }
67 }
68
69 int main()
70 {
71 int i, k, C, D, f;
72 char buf[30];
73 scanf("%d", &C);
74 for (k = 1; k <= C; k++) {
75 root = &pool[0];
76 pt = 1, memset(pool, 0, sizeof(pool));
77 printf("Scenario #%d:\n", k);
78 scanf("%d", &D);
79 while (D-- > 0) {
80 scanf("%s %d", buf, &f); //哥一开始buf开小了,报了stack smashing 。。。。。。。。
81 root->insert(buf, f);
82 }
83 scanf("%d", &D), getchar();
84 while (D-- > 0) {
85 scanf("%s", buf);
86 buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = 0;
87
88 int len = strlen(buf);
89 for (i = 1; i <= len; i++) {
90 freq = 0;
91 root->getMax(buf, 0, i);
92 if (freq > 0) {
93 printf("%s\n", res);
94 } else {
95 puts("MANUALLY");
96 }
97 }
98 printf("\n");
99 }
100 printf("\n");
101 }
102 return 0;
103 }
104
autocomplpop.vim
http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1879
把omnicomplete 装上,再装上这个,加上两个不去分大小写的选项
let g:AutoComplPop_IgnoreCaseOption=1
set ignorecase
哇,边打字,边补全
文本是schindlerlee原创,查看原文请访问
www.cppblog.com/schindlerlee
转载请保留此信息,本人保留关于本文的一切信息
const int PRECISION = 525;
const int SENTINAL = 0x7fffffff;
struct bignum {
int s[PRECISION];
int len;
void reset() {
for (int i = 0; i < PRECISION; i++) {
s[i] = SENTINAL;
} len = 0;
}
};
void justify(bignum & a, int step)
/*
* 调整乘法产生的结果
* 例如将:
*-------------------------------------------------------------
*| 64 | 64 |SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|
*-------------------------------------------------------------
*调整为
*-------------------------------------------------------------
*| 4 | 0 | 7 |SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|SENT|
*-------------------------------------------------------------
* */
{
if (step < PRECISION && a.s[step] != SENTINAL) {
if (a.s[step] > 9) {
if (a.s[step + 1] == SENTINAL)
a.s[step + 1] = 0;
a.s[step + 1] += a.s[step] / 10;
a.s[step] = a.s[step] % 10;
}
justify(a, step + 1);
} else {
a.len = step;
for (int i = step; i < PRECISION; i++) {
a.s[i] = SENTINAL;
}
}
}
void mul(bignum a, bignum b, bignum & c) //a b result
{
int i, j;
c.reset();
for (i = 0; i < a.len; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < b.len; j++) {
if(i+j < PRECISION) {
if (c.s[i + j] == SENTINAL) c.s[i + j] = 0;
c.s[i + j] += a.s[i] * b.s[j];
}
}
}
justify(c, 0);
}
看到网上写的很多说装pm-utils之类的。但是我的情况是,休眠以后系统根本就启动不了,直接黑屏在那里了。
也有人写把主板电池扣下来放电,我是笔记本,也不太现实。
想进windows试试,无意中发现grub菜单中有recovery mode ,选进去,一切解决。。。。。。。。。。。
原来一切是如此简单,反正我是重启了n次。。。。
摘要: ubuntu下写的,在linux shell可运行 ,想编译请安装 libncurses5-dbg libncurses5-dev使用参数 : g++ -lcurses snake.c 编译方向键使用vim 默认的hjkl进行移动,可以熟悉vim的方向键菜单中 L 是确定 ,游戏中q是退出
Code highlighting produced by...
阅读全文
切換使用emerald的主題
按alt-f2
執行
emerald --replace
切換回原來的主題
按alt-f2
執行
metacity --replace
在ubuntu把ape文件转换成mp3文件一直都是一个问题。
昨天第一次使用linux进行这项工作,现在将方法记录如下。
# 安装soundconverter和mp3splt
# 使用soundconverter将ape文件转换成一个mp3文件
# 使用mp3splt 分割生成的单个mp3文件
使用命令
mp3splt -c CDImage.cue -o @n.@t a.mp3
@n是音轨号
@t是音轨标题
其中的信息都是根据CDImage.cue文件中来的。
还有其他参数可选,具体参见
man mp3splt
首先创建一个文件
写入
#!/bin/sh
shutdown -h now
保存为power文件
之后
chmod +x power
之后就能使用定时关机了
但是需要有root权限才能关机
所以需要输入的命令如下
sudo at 02:00 tomorrow -f power
之后使用
sudo atq
可以查选定时执行的任务
sudo atrm
可以删除已经预定好的任务
indent是linux下一个能力极强的代码整理软件,使用他,可以轻松的写出代码风格十分精良的代码。
但是indent的参数太多,使用起来不是很容易,怎么办呢?
查看
/usr/src/linux-headers-<版本>/scripts/Lindent
文件 ,可以看到一行代码:
indent -npro -kr -i8 -ts8 -sob -l80 -ss -ncs -cp1
这一行就是linux内核使用indent整理代码的格式,使用这条命令就可以实现风格十分良好的C或C++代码
其中-l80是每一行最多80个字母,超出会拆行,如果不喜欢可以使用更长的行字数