来自于《大话设计模式》
迭代器模式(Iterator):提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不暴露该对象的内部表示。
UML 类图:
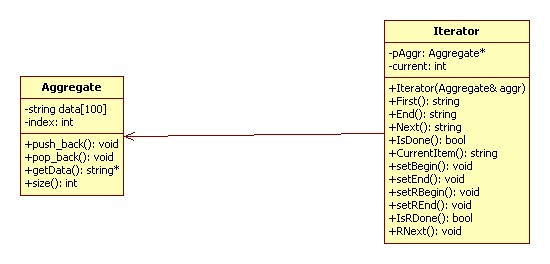
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class Aggregate
6 {
7 private:
8 string data[100];
9 int index;
10 public:
11 Aggregate() : index(0){}
12 void push_back(const string& s)
13 {
14 data[index++] = s;
15 }
16 void push_pop()
17 {
18 --index;
19 }
20 string* getData()
21 {
22 return data;
23 }
24 int size()
25 {
26 return index;
27 }
28 };
29
30 class Iterator
31 {
32 private:
33 Aggregate* pAggr;
34 int current;
35 public:
36 Iterator(Aggregate& aggr)
37 {
38 pAggr = &aggr;
39 current = 0;
40 }
41 string First()
42 {
43 if (pAggr->size() > 0)
44 {
45 return (pAggr->getData())[0];
46 }
47 else
48 {
49 return "";
50 }
51 }
52 string End()
53 {
54 if (pAggr->size() > 0)
55 {
56 return (pAggr->getData())[pAggr->size() - 1];
57 }
58 else
59 {
60 return "";
61 }
62 }
63 void Next()
64 {
65 ++current;
66 }
67 bool IsDone()
68 {
69 return current == pAggr->size();
70 }
71 string CurrentItem()
72 {
73 if (pAggr->size() > 0)
74 {
75 return (pAggr->getData())[current];
76 }
77 else
78 {
79 return "";
80 }
81 }
82 void setBegin()
83 {
84 current = 0;
85 }
86 void setEnd()
87 {
88 current = pAggr->size();
89 }
90
91 void setRBegin()
92 {
93 current = pAggr->size() - 1;
94 }
95 void setREnd()
96 {
97 current = -1;
98 }
99 bool IsRDone()
100 {
101 return current == -1;
102 }
103 void RNext()
104 {
105 --current;
106 }
107 };
108
109 int main()
110 {
111 Aggregate aggr;
112 aggr.push_back("a");
113 aggr.push_back("b");
114 aggr.push_back("c");
115 aggr.push_back("d");
116 aggr.push_back("e");
117
118 Iterator iter(aggr);
119
120 while (!iter.IsDone())
121 {
122 cout << iter.CurrentItem() << ", hello!" << endl;
123 iter.Next();
124 }
125
126 iter.setBegin();
127 while (!iter.IsDone())
128 {
129 cout << iter.CurrentItem() << ", bye!" << endl;
130 iter.Next();
131 }
132
133
134 iter.setRBegin();
135 while (!iter.IsRDone())
136 {
137 cout << iter.CurrentItem() << ", reverse!" << endl;
138 iter.RNext();
139 }
140
141 iter.setBegin();
142
143 return 0;
144 }
posted @
2011-04-29 16:52 unixfy 阅读(236) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
来自于《大话设计模式》
组合模式(Composite):将对象组合成树形结构以表示‘部分-整体’的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
UML 类图:
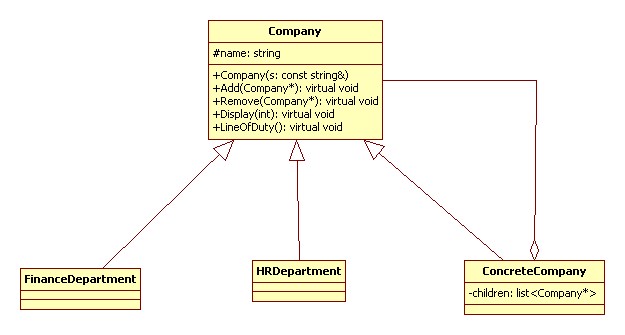
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 #include <list>
4 #include <algorithm>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 class Company
8 {
9 protected:
10 string name;
11 public:
12 Company(const string& s) : name(s) {}
13 virtual void Add(Company* c) = 0;
14 virtual void Remove(Company* c) = 0;
15 virtual void Display(int depth) = 0;
16 virtual void LineOfDuty() = 0;
17 };
18
19 class ConcreteCompany : public Company
20 {
21 private:
22 list<Company*> children;
23 public:
24 ConcreteCompany(const string& s) : Company(s) {}
25 virtual void Add(Company* c)
26 {
27 children.push_back(c);
28 }
29 virtual void Remove(Company* c)
30 {
31 list<Company*>::iterator iter = find(children.begin(), children.end(), c);
32 if (iter != children.end())
33 {
34 children.erase(iter);
35 }
36 }
37 virtual void Display(int depth)
38 {
39 string str(depth, '-');
40 str += name;
41 cout << str << endl;
42 for (list<Company*>::iterator iter = children.begin(); iter != children.end(); ++iter)
43 {
44 (*iter)->Display(depth + 2);
45 }
46 }
47 virtual void LineOfDuty()
48 {
49 for (list<Company*>::iterator iter = children.begin(); iter != children.end(); ++iter)
50 {
51 (*iter)->LineOfDuty();
52 }
53 }
54 };
55
56 class HRDepartment : public Company
57 {
58 public:
59 HRDepartment(const string& s) : Company(s) {}
60 virtual void Add(Company* c) {}
61 virtual void Remove(Company* c) {}
62 virtual void Display(int depth)
63 {
64 string str(depth, '-');
65 str += name;
66 cout << str << endl;
67 }
68 virtual void LineOfDuty()
69 {
70 cout << name << " 员工招聘培训管理!" << endl;
71 }
72 };
73
74 class FinanceDepartment : public Company
75 {
76 public:
77 FinanceDepartment(const string& s) : Company(s) {}
78 virtual void Add(Company* c) {}
79 virtual void Remove(Company* c) {}
80 virtual void Display(int depth)
81 {
82 string str(depth, '-');
83 str += name;
84 cout << str << endl;
85 }
86 virtual void LineOfDuty()
87 {
88 cout << name << " 公司财务收支管理!" << endl;
89 }
90 };
91
92 int main()
93 {
94 ConcreteCompany root("北京总公司");
95 root.Add(new HRDepartment("总公司人力资源部"));
96 root.Add(new FinanceDepartment("总公司财务部"));
97
98 ConcreteCompany* comp = new ConcreteCompany("上海华东分公司");
99 comp->Add(new HRDepartment("华东分公司人力资源部"));
100 comp->Add(new FinanceDepartment("华东分公司财务部"));
101 root.Add(comp);
102
103 ConcreteCompany* comp2 = new ConcreteCompany("南京办事处");
104 comp2->Add(new HRDepartment("南京办事处人力资源部"));
105 comp2->Add(new FinanceDepartment("南京办事处财务部"));
106 root.Add(comp2);
107
108 ConcreteCompany* comp3 = new ConcreteCompany("杭州办事处");
109 comp3->Add(new HRDepartment("杭州办事处人力资源部"));
110 comp3->Add(new FinanceDepartment("杭州办事处财务部"));
111 root.Add(comp3);
112
113 cout << "结构图:" << endl;
114 root.Display(1);
115
116 cout << "职责:" << endl;
117 root.LineOfDuty();
118
119 return 0;
120 }
posted @
2011-04-29 16:14 unixfy 阅读(247) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
备忘录模式(Memento):在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态。这样以后就可以将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
UML 类图:
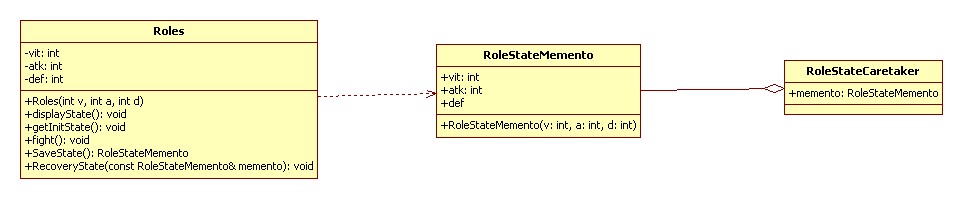
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class RoleStateMemento
5 {
6 public:
7 int vit;
8 int atk;
9 int def;
10 public:
11 RoleStateMemento(int v = 0, int a = 0, int d = 0) : vit(v), atk(a), def(d) {}
12 };
13
14 class Roles
15 {
16 private:
17 int vit;
18 int atk;
19 int def;
20 public:
21 Roles(int v = 100, int a = 100, int d = 100) : vit(v), atk(a), def(d) {}
22 void getInitState()
23 {
24 vit = 100;
25 atk = 100;
26 def = 100;
27 }
28 void fight()
29 {
30 vit = 0;
31 atk = 0;
32 def = 0;
33 }
34 void displayState()
35 {
36 cout << "体力:" << vit << endl;
37 cout << "攻击力:" << atk << endl;
38 cout << "防御力:" << def << endl;
39 }
40 RoleStateMemento SaveState()
41 {
42 return RoleStateMemento(vit, atk, def);
43 }
44 void RecoveryState(const RoleStateMemento& memento)
45 {
46 vit = memento.vit;
47 atk = memento.atk;
48 def = memento.def;
49 }
50 };
51
52 class RoleStateCaretaker
53 {
54 private:
55 public:
56 RoleStateMemento memento;
57 };
58
59 int main()
60 {
61 Roles* r = new Roles;
62 r->getInitState();
63 r->displayState();
64
65 RoleStateCaretaker* stateAdmin = new RoleStateCaretaker;
66 stateAdmin->memento = r->SaveState();
67
68 r->fight();
69 r->displayState();
70
71 r->RecoveryState(stateAdmin->memento);
72 r->displayState();
73
74 return 0;
75 }
posted @
2011-04-29 08:43 unixfy 阅读(152) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏隐式类型转换,其他类型的变量可以通过构造函数隐式转换为一个类类型的对象,这里隐式转换会产生一个无名的临时对象,这个对象是常量不能被修改。所以说,不能将其赋值给一个非 const 的引用,这样编译不通过,最好是赋值给 const 型的引用 const T&。也可以赋值给 值类型,const、非 const 都行,但是这种效率不高。
这里只需注意通过隐式类型转换产生的临时对象是无名的常量对象。
通过隐式类型转换产生的临时对象和通过函数返回值返回的一个临时的无名对象不同。通过函数返回的临时对象,可以是常量也可以是变量。如果是变量,我们还可以修改这个无名的变量,虽然这样做没有意义,一般情况下有副作用。因为本该修改的没有得到修改。
通过函数返回值得到的无名的临时对象是否具有常量性,是由函数的返回值类型决定的。是有程序员自己定义函数的时候决定的。而隐式类型转换生成的无名的临时对象的常量性是由编译器自动决定的,与程序员无关。
防止隐式类型转换可以通过 explicit 关键字。
class T
{
public:
T(int a = 1, int b = 2) { }
}
};
T t;
t = 5;
这样是首先 5 转换为一个无名的常量性临时对象,然后复制给 t,这里用的赋值运算符是编译器提供的默认 operator =。其形参类型为 const T&。
如果程序员自己提供了 operator =,并且形参类型为 T& 而非 const T&。这样编译就会报错。因为不能将常量复制给 非 const 引用。只是由 C++ 的语法决定的。
一般情况下,如果不改变实参,在定义函数的时候都尽量将形参类型声明为 const T&。这样做的好处是效率高,并且避免不必要的麻烦。这是一种最为可靠和安全的方法。
另外,隐式类型转换和类型转换操作符在一起的时候还容易产生二义性。这种情况下,最好针对各种不同的参数类型,进行各种重载。但是还要考虑模板带来的二义性等。
posted @
2011-04-29 00:56 unixfy 阅读(309) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
设计一个长方形类Triangle,包含长和宽两个私有数据成员。
要求重载运算符
·=
能够支持:对象=数值 普通变量=对象 对象=对象 支持连续的赋值
·+= :自定义加法功能
联系与=的联系
·> :实现比较两个矩形对象面积大小的比较
能够支持:两个对象的比较,对象和数字的比较,数字和对象的比较
·>> :实现矩形对象的输入
·<< :实现矩形对象的输出
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class Triangle
5 {
6 private:
7 double length;
8 double width;
9 public:
10 Triangle(double l = 0.0, double w = 0.0) : length(l), width(w) {}
11 ~Triangle() {}
12 Triangle(const Triangle& t) : length(t.length), width(t.width) {}
13 Triangle& operator =(const Triangle& t)
14 {
15 if (this != &t)
16 {
17 length = t.length;
18 width = t.width;
19 }
20 return *this;
21 }
22 Triangle& operator =(double d)
23 {
24 length = width = d;
25 return *this;
26 }
27 operator double ()
28 {
29 return length * width;
30 }
31 Triangle& operator +=(const Triangle& t)
32 {
33 length += t.length;
34 width += t.width;
35 return *this;
36 }
37 friend bool operator > (const Triangle& lhs, const Triangle& rhs);
38 friend bool operator > (const Triangle& lhs, double rhs);
39 friend bool operator > (double lhs, const Triangle& rhs);
40 friend istream& operator >>(istream& in, Triangle& rhs);
41 friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, const Triangle& rhs);
42 };
43
44 bool operator >(const Triangle& lhs, const Triangle& rhs)
45 {
46 return lhs.length * lhs.width > rhs.length * rhs.width;
47 }
48
49 bool operator >(const Triangle& lhs, double rhs)
50 {
51 return lhs.length * lhs.width > rhs;
52 }
53
54 bool operator >(double lhs, const Triangle& rhs)
55 {
56 return lhs > rhs.length * rhs.width;
57 }
58
59 istream& operator >>(istream& in, Triangle& rhs)
60 {
61 in >> rhs.length >> rhs.width;
62 if (!in)
63 {
64 cerr << "Input error!" << endl;
65 exit(1);
66 }
67 return in;
68 }
69
70 ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, const Triangle& rhs)
71 {
72 out << rhs.length << '\t' << rhs.width;
73 return out;
74 }
75
76 Triangle& operator +(const Triangle& lhs, const Triangle& rhs)
77 {
78 Triangle tmp(lhs);
79 return tmp += rhs;
80 }
81
82 int main()
83 {
84 Triangle t1(1.0, 2.0);
85 Triangle t2;
86 t1 = t2;
87
88 cin >> t1 >> t2;
89 cout << t1 << endl;
90 cout << t2 << endl;
91
92 t1 = t2;
93 cout << t1 << endl;
94 cout << t2 << endl;
95
96 t1 = 10.0;
97 cout << t1 << endl;
98 double d = 0.0;
99 d = t1;
100 cout << d << endl;
101
102 cout << (t1 > t2) << endl;
103 cout << (t1 > 5.0) << endl;
104 cout << (5.0 > t1) << endl;
105
106 t1 += t2;
107 cout << t1 << endl;
108 cout << t2 << endl;
109
110 return 0;
111 }
posted @
2011-04-29 00:40 unixfy 阅读(213) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏单链表的逆转
带头结点的单链表
一种方法是判断是否没有数据节点、只有一个数据节点。这种情况不翻转,在翻转循环里还要判断是否只有是第一个结点,如果是则将该结点的 next 置为 0。
一种效率更好的方式是:
void reverse(Node* head)
{
Node* p1, *p2, *p3;
p1 = p2 = 0;
p3 = head->next;
while (p3 != 0)
{
p2 = p3;
p3 = p3->next;
p2->next = p1;
p1 = p2;
}
head->next = p2;
}
这种方式即包括了没有数据节点、只有一个数据节点的情况,也可以处理将第一个结点的 next 置为 0 的情况。
所以这种方式既明确效率也更高。
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 template <typename T>
5 class Link
6 {
7 public:
8 template <typename T>
9 struct Node
10 {
11 T data;
12 Node<T>* next;
13 };
14 private:
15 Node<T>* head;
16 public:
17 Link()
18 {
19 head = new Node<T>;
20 head->next = 0;
21 }
22 ~Link()
23 {
24 Node<T>* p = head->next, *q = 0;
25 while (p != 0)
26 {
27 q = p->next;
28 delete p;
29 p = q;
30 }
31 delete head;
32 }
33 Node<T>* Head()
34 {
35 return head;
36 }
37 void insert(T item, Node<T>* p)
38 {
39 Node<T>* q = new Node<T>;
40 q->next = p->next;
41 q->data = item;
42 p->next = q;
43 }
44
45 void reverse()
46 {
47 Node<T>* p1, *p2, *p3;
48 p1 = p2 = 0;
49 p3 = head->next;
50 while (p3 != 0)
51 {
52 p2 = p3;
53 p3 = p3->next;
54 p2->next = p1;
55 p1 = p2;
56 }
57 head->next = p2;
58 }
59
60 // friend template <typename T> ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, Link<T>& link);
61 };
62
63 template <typename T>
64 ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, Link<T>& link)
65 {
66 const Link<T>::Node<T>* p = link.Head()->next;
67 while (p)
68 {
69 out << p->data << ' ';
70 p = p->next;
71 }
72 return out;
73 }
74
75 int main()
76 {
77 Link<int> link;
78 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
79 {
80 link.insert(i, link.Head());
81 }
82 cout << link << endl;
83
84 link.reverse();
85
86 cout << link << endl;
87 }
posted @
2011-04-29 00:13 unixfy 阅读(318) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏适配器模式(Adapter):将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口。Adapter 模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能在一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。
结构型
·类
·对象
UML 类图:
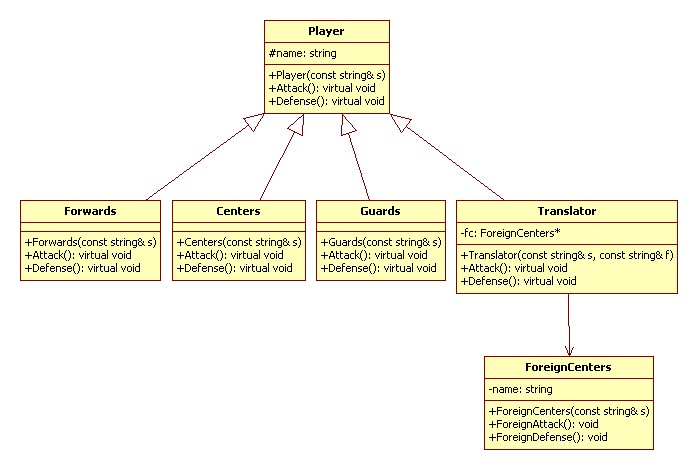
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class Player
6 {
7 protected:
8 string name;
9 public:
10 Player(const string& s = "") : name(s) {}
11 virtual void Attack() = 0;
12 virtual void Defense() = 0;
13 };
14
15 class Forwards : public Player
16 {
17 public:
18 Forwards(const string& s = "") : Player(s) {}
19 virtual void Attack()
20 {
21 cout << "前锋 " << name << " 进攻!" << endl;
22 }
23 virtual void Defense()
24 {
25 cout << "前锋 " << name << " 防守!" << endl;
26 }
27 };
28
29 class Center : public Player
30 {
31 public:
32 Center(const string& s = "") : Player(s) {}
33 virtual void Attack()
34 {
35 cout << "中锋 " << name << " 进攻!" << endl;
36 }
37 virtual void Defense()
38 {
39 cout << "中锋 " << name << " 防守!" << endl;
40 }
41 };
42
43 class Guards : public Player
44 {
45 public:
46 Guards(const string& s) : Player(s) {}
47 virtual void Attack()
48 {
49 cout << "后卫 " << name << " 进攻!" << endl;
50 }
51 virtual void Defense()
52 {
53 cout << "后卫 " << name << " 防守!" << endl;
54 }
55 };
56
57 class ForeignCenters
58 {
59 private:
60 string name;
61 public:
62 ForeignCenters(const string& s = "") : name(s) {}
63 void ForeignAttack()
64 {
65 cout << "外籍中锋 " << name << " 进攻!" << endl;
66 }
67 void ForeignDefense()
68 {
69 cout << "外籍中锋 " << name << " 防守!" << endl;
70 }
71 };
72
73 class Translators : public Player
74 {
75 private:
76 ForeignCenters* fc;
77 public:
78 Translators(const string& s = "", const string& f = "") : Player(s), fc(new ForeignCenters(f)) {}
79 ~Translators()
80 {
81 delete fc;
82 }
83 virtual void Attack()
84 {
85 fc->ForeignAttack();
86 }
87 virtual void Defense()
88 {
89 fc->ForeignDefense();
90 }
91 };
92
93 int main()
94 {
95 Player* b = new Forwards("巴蒂尔");
96 b->Attack();
97 b->Defense();
98
99 Player* m = new Guards("麦克格雷迪");
100 m->Attack();
101 m->Defense();
102
103 Player* y = new Translators("翻译者", "姚明");
104 y->Attack();
105 y->Defense();
106
107 return 0;
108 }
posted @
2011-04-28 14:31 unixfy 阅读(133) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
来自于《大话设计模式》
状态模式(State):当一个对象的内在状态改变时允许改变其行为,这个对象看起来像是改变了其类。
UML 类图:
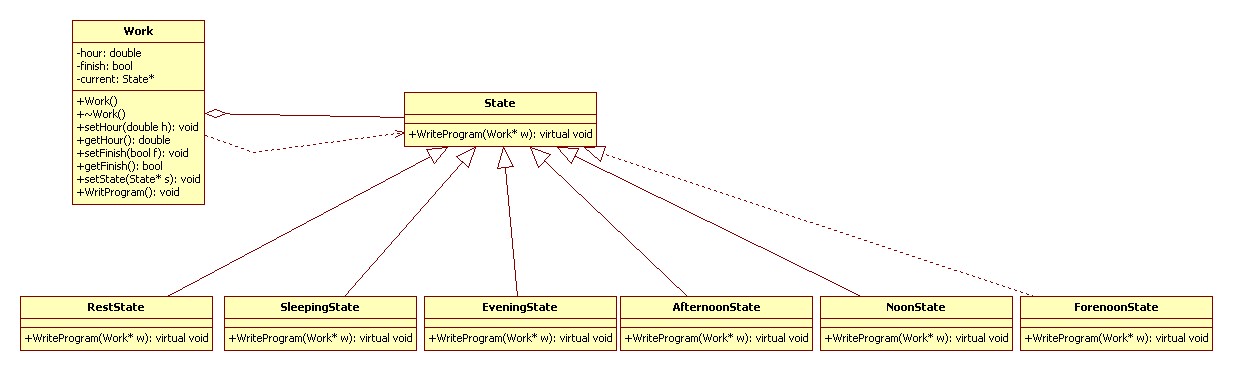
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class Work;
5 class State;
6 double getHour(Work* w);
7 void setState(Work * w, State * s);
8 bool getFinish(Work* w);
9 void WriteProgramOutside(Work * w);
10
11 class State
12 {
13 public:
14 virtual void WriteProgram(Work * w) = 0;
15 };
16
17 class RestState : public State
18 {
19 public:
20 virtual void WriteProgram(Work * w)
21 {
22 cout << "当前时间:" << getHour(w) << " 点下班回家了。" << endl;
23 }
24 };
25
26 class SleepingState : public State
27 {
28 public:
29 virtual void WriteProgram(Work * w)
30 {
31 cout << "当前时间:" << getHour(w) << " 点不行了,睡着了。" << endl;
32 }
33 };
34
35 class EveningState : public State
36 {
37 public:
38 virtual void WriteProgram(Work * w)
39 {
40 if (getFinish(w))
41 {
42 setState(w, static_cast<State*>(new RestState));
43 WriteProgramOutside(w);
44 }
45 else
46 {
47 if (getHour(w) < 21.0)
48 {
49 cout << "当前时间:" << getHour(w) << " 点 加班哦,疲惫之极。" << endl;
50 }
51 else
52 {
53 setState(w, new SleepingState);
54 WriteProgramOutside(w);
55 }
56 }
57 }
58 };
59
60 class AfternoonState : public State
61 {
62 public:
63 virtual void WriteProgram(Work * w)
64 {
65 if (getHour(w) < 17.0)
66 {
67 cout << "当前时间:" << getHour(w) << " 点 下午状态还不错,继续努力。" << endl;
68 }
69 else
70 {
71 setState(w, new EveningState);
72 WriteProgramOutside(w);
73 }
74 }
75 };
76
77 class NoonState : public State
78 {
79 public:
80 virtual void WriteProgram(Work * w)
81 {
82 if (getHour(w) < 13.0)
83 {
84 cout << "当前时间:" << getHour(w) << " 点 饿了,午饭;犯困,午休。" << endl;
85 }
86 else
87 {
88 setState(w, new AfternoonState);
89 WriteProgramOutside(w);
90 }
91 }
92 };
93
94 class ForenoonState : public State
95 {
96 public:
97 virtual void WriteProgram(Work* w)
98 {
99 if (getHour(w) < 12.0)
100 {
101 cout << "当前时间:" << getHour(w) << " 点 上午工作,精神百倍!" << endl;
102 }
103 else
104 {
105 setState(w, new NoonState);
106 WriteProgramOutside(w);
107 }
108 }
109 };
110
111 class Work
112 {
113 private:
114 State * current;
115 double hour;
116 bool finish;
117 public:
118 double getHour()
119 {
120 return hour;
121 }
122 void setHour(double h)
123 {
124 hour = h;
125 }
126 bool getFinish()
127 {
128 return finish;
129 }
130 void setFinsh(bool f)
131 {
132 finish = f;
133 }
134 void setState(State * w)
135 {
136 delete current;
137 current = w;
138 }
139 void WriteProgram()
140 {
141 current->WriteProgram(this);
142 }
143 Work()
144 {
145 current = new ForenoonState;
146 finish = false;
147 }
148 ~Work()
149 {
150 delete current;
151 }
152 };
153
154 double getHour(Work * w)
155 {
156 return w->getHour();
157 }
158 void setHour(Work * w, double h)
159 {
160 w->setHour(h);
161 }
162 bool getFinish(Work * w)
163 {
164 return w->getFinish();
165 }
166 void setFinish(Work * w, bool f)
167 {
168 w->setFinsh(f);
169 }
170 void setState(Work * w, State * s)
171 {
172 w->setState(s);
173 }
174
175 void WriteProgramOutside(Work * w)
176 {
177 w->WriteProgram();
178 }
179
180 int main()
181 {
182 Work* emergencyProjects = new Work;
183 emergencyProjects->setHour(9.0);
184 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
185 emergencyProjects->setHour(10.0);
186 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
187 emergencyProjects->setHour(12.0);
188 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
189 emergencyProjects->setHour(13.0);
190 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
191 emergencyProjects->setHour(14.0);
192 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
193 emergencyProjects->setHour(17.0);
194 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
195
196 // emergencyProjects->setFinsh(true);
197 emergencyProjects->setFinsh(false);
198
199 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
200 emergencyProjects->setHour(19.0);
201 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
202 emergencyProjects->setHour(22.0);
203 emergencyProjects->WriteProgram();
204
205 delete emergencyProjects;
206 return 0;
207 }
posted @
2011-04-27 16:39 unixfy 阅读(231) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
来自于《大话设计模式》
抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory):提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。
UML 类图:
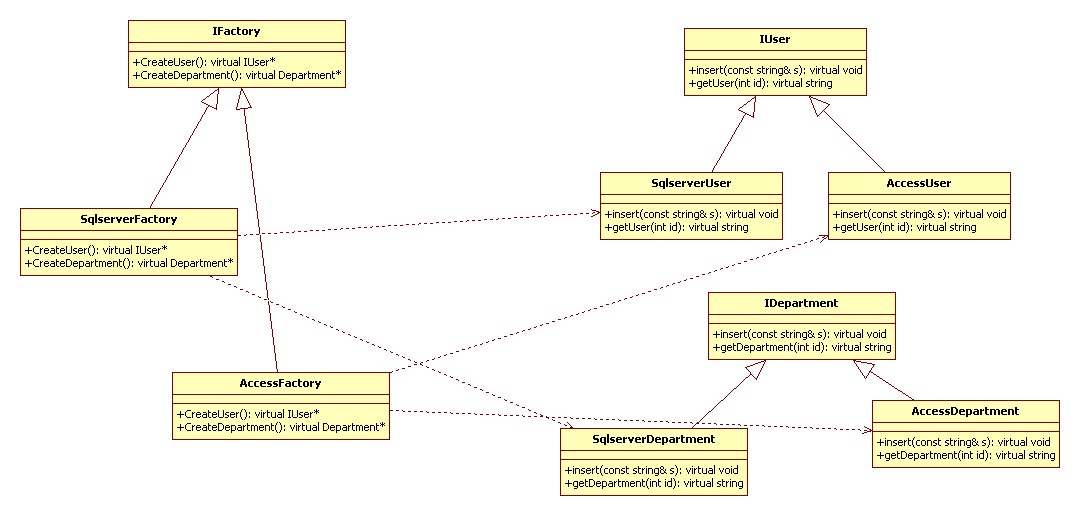
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class IUser
6 {
7 public:
8 virtual void insert(const string& s) = 0;
9 virtual string getUser(int id) = 0;
10 };
11
12 class SqlserverUser : public IUser
13 {
14 public:
15 virtual void insert(const string& s)
16 {
17 cout << "SqlserverUser::insert " << s << endl;
18 }
19 virtual string getUser(int id)
20 {
21 cout << "SqlserverUser::getUser " << id << endl;
22 return "";
23 }
24 };
25
26 class AccessUser : public IUser
27 {
28 public:
29 virtual void insert(const string& s)
30 {
31 cout << "AccessUser::insert " << s << endl;
32 }
33 virtual string getUser(int id)
34 {
35 cout << "AccessUser::getUser " << id << endl;
36 return "";
37 }
38 };
39
40 class IDepartment
41 {
42 public:
43 virtual void insert(const string& s) = 0;
44 virtual string getDepartment(int id) = 0;
45 };
46
47 class SqlserverDepartment : public IDepartment
48 {
49 public:
50 virtual void insert(const string& s)
51 {
52 cout << "SqlserverDepartment::insert " << s << endl;
53 }
54 virtual string getDepartment(int id)
55 {
56 cout << "SqlserverDepartment::getDepartment " << id << endl;
57 return "";
58 }
59 };
60
61 class AccessDepartment : public IDepartment
62 {
63 public:
64 virtual void insert(const string& s)
65 {
66 cout << "AccessDepartment::insert " << s << endl;
67 }
68 virtual string getDepartment(int id)
69 {
70 cout << "AccessDepartment::getDepartment " << id << endl;
71 return "";
72 }
73 };
74
75 class IFactory
76 {
77 public:
78 virtual IUser * CreateUser() = 0;
79 virtual IDepartment * CreateDepartment() = 0;
80 };
81
82 class SqlserverFactory : public IFactory
83 {
84 public:
85 virtual IUser * CreateUser()
86 {
87 return new SqlserverUser;
88 }
89 virtual IDepartment* CreateDepartment()
90 {
91 return new SqlserverDepartment;
92 }
93 };
94
95 class AccessFactory : public IFactory
96 {
97 public:
98 virtual IUser * CreateUser()
99 {
100 return new AccessUser;
101 }
102 virtual IDepartment * CreateDepartment()
103 {
104 return new AccessDepartment;
105 }
106 };
107
108 int main()
109 {
110 string user = "abc";
111 string department = "xyz";
112
113 IFactory * factory = new AccessFactory;
114 IUser * iu = factory->CreateUser();
115 iu->insert(user);
116 iu->getUser(1);
117 IDepartment * id = factory->CreateDepartment();
118 id->insert(department);
119 id->getDepartment(1);
120 delete factory;
121 delete iu;
122 delete id;
123
124 factory = new SqlserverFactory;
125 iu = factory->CreateUser();
126 iu->insert(user);
127 iu->getUser(1);
128 id = factory->CreateDepartment();
129 id->insert(department);
130 id->getDepartment(1);
131 delete factory;
132 delete iu;
133 delete id;
134
135 return 0;
136 }
posted @
2011-04-27 14:53 unixfy 阅读(520) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
单链表的逆转,关键在于三个辅助指针,前两个指针用于逆转,最后一个用于记录剩下来的节点,不然链表就丢失了。
这里是用的带头结点的链表,考虑链表中没有节点和只有一个节点的情况就不用逆转了。
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 struct node
5 {
6 int data;
7 node * next;
8 };
9
10 node * init()
11 {
12 node * head = new node;
13 if (head == 0)
14 {
15 exit(1);
16 }
17 head->next = 0;
18 return head;
19 }
20
21 node * insert(int item, node * pre)
22 {
23 node * tmp = new node;
24 if (tmp == 0)
25 {
26 exit(1);
27 }
28 tmp->data = item;
29 tmp->next = pre->next;
30 pre->next = tmp;
31 return tmp;
32 }
33
34 node * create(node * head)
35 {
36 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
37 {
38 insert(i, head);
39 }
40 return head;
41 }
42
43 node * reverse(node * head)
44 {
45 node * p1 = head->next;
46 if (p1 == 0)
47 {
48 return head;
49 }
50
51 node * p2 = p1->next;
52 if (p2 == 0)
53 {
54 return head;
55 }
56
57 node * p3;
58
59 while (p2 != 0)
60 {
61 p3 = p2->next;
62 p2->next = p1;
63 if (p1 == head->next)
64 {
65 p1->next = 0;
66 }
67 p1 = p2;
68 p2 = p3;
69 }
70 head->next = p1;
71 return head;
72 }
73
74 void clear_(node * head)
75 {
76 node * p = head->next, * q;
77 while (p != 0)
78 {
79 q = p->next;
80 delete p;
81 p = q;
82 }
83 head->next = 0;
84 }
85
86 void clear(node * head)
87 {
88 clear_(head);
89 delete head;
90 }
91
92 node * copy(node * des, node * src)
93 {
94 clear_(des);
95 node * p = src->next, * q, * d = des;
96 while (p != 0)
97 {
98 q = new node;
99 q->data = p->data;
100 q->next = 0;
101 d->next = q;
102 d = q;
103 p = p->next;
104 }
105 return des;
106 }
107
108 void print(node * head)
109 {
110 node * p = head->next;
111 while (p != 0)
112 {
113 cout << p->data << ' ';
114 p = p->next;
115 }
116 cout << endl;
117 }
118
119 int main()
120 {
121 node * t1 = init();
122 create(t1);
123 print(t1);
124
125 node * t2 = init();
126 copy(t2, t1);
127 print(t2);
128 reverse(t2);
129 print(t2);
130
131 return 0;
132 }
posted @
2011-04-27 13:48 unixfy 阅读(494) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏