递增的有序顺序表,插入元素并保持递增有序。
内存分配按照 2 被原则进行分配。
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 // 递增有序的顺序表
5 template <typename Type>
6 class IncTable
7 {
8 public:
9 typedef Type value_type;
10 typedef Type* p_type;
11 typedef unsigned int size_type;
12 typedef p_type iterator;
13 typedef const p_type const_iterator;
14 private:
15 p_type table;
16 size_type size_;
17 size_type capacity_;
18 public:
19 IncTable(int s = 1)
20 {
21 size_ = 0;
22 capacity_ = s * 2;
23 table = new value_type[capacity_];
24 if (table == 0)
25 {
26 exit(0);
27 }
28 }
29 ~IncTable()
30 {
31 delete [] table;
32 }
33 void insert(value_type item)
34 {
35 if (size_ >= capacity_)
36 {
37 reallocate(size_ * 2);
38 }
39 size_type ix = size_;
40 while (ix > 0 && table[ix - 1] > item)
41 {
42 table[ix] = table[ix - 1];
43 --ix;
44 }
45 table[ix] = item;
46 ++size_;
47 }
48 void reallocate(size_type size)
49 {
50 p_type p = new value_type[size];
51 if (p == 0)
52 {
53 exit(1);
54 }
55 memcpy(p, table, sizeof (value_type) * size_);
56 delete table;
57 table = p;
58 capacity_ = size;
59 }
60 size_type size()
61 {
62 return size_;
63 }
64 size_type capacity()
65 {
66 return capacity_;
67 }
68 iterator begin()
69 {
70 return table;
71 }
72 iterator end()
73 {
74 return table + size_;
75 }
76 const_iterator begin() const
77 {
78 return table;
79 }
80 const_iterator end() const
81 {
82 return table + size_;
83 }
84 };
85
86 int main()
87 {
88 IncTable<int> t;
89 for (int i = 10; i > 0; --i)
90 {
91 t.insert(i);
92 }
93 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
94 {
95 t.insert(i);
96 }
97 for (IncTable<int>::iterator iter = t.begin(); iter != t.end(); ++iter)
98 {
99 cout << *iter << ' ';
100 }
101 cout << endl;
102 }
posted @
2011-04-24 01:39 unixfy 阅读(581) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
摘要: 标准库里的 list 实现是通过双向链表实现的。这里没有使用双向链表,自然功能也就不能像标准库里的 list 那样完备。不支持逆向。
这里在单向链表的基础上,加入了泛型,迭代器,尽可能多地添加一些接口,已尽量像标准库里的 list 那样操作。另外,这里没有过多里涉及内存分配的问题。每次插入的时候是直接分配一个元素的空间,而不是采用 2 倍法则。
总体上,还没有看过 STL 里 list 具体是...
阅读全文
posted @
2011-04-24 01:04 unixfy 阅读(354) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
输入一个英文句子,翻转句子中单词的顺序,但单词内字符的顺序不变。句子中单词以空格符隔开。为简单起见,标点符号和普通字母一样处理。
例如输入“I am a student.”,则输出“student. a am I”。
这个问题在多处曾出现过。大体思路是两次翻转,即先翻转各个单词,然后将整个句子翻转。也可将两个翻转顺序颠倒过来,先翻转句子,在翻转单词。
一种无意义的做法是,先把句子中的每个单词存放在一个 vector<string> 中,然后反向遍历输出。
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 void reverseStr(string& s, string::size_type left, string::size_type right)
6 {
7 while (left < right)
8 {
9 swap(s[left++], s[right--]);
10 }
11 }
12
13 string getReverse(const string& s)
14 {
15 if (s.empty())
16 {
17 return string("");
18 }
19 string ret = s;
20 string::size_type left, right;
21 left = s.find_first_not_of(' ', 0);
22 right = s.find_first_of(' ', left);
23 while (right != string::npos)
24 {
25 reverseStr(ret, left, right - 1);
26 left = s.find_first_not_of(' ', right);
27 right = s.find_first_of(' ', left);
28 }
29 if (left != string::npos)
30 {
31 reverseStr(ret, left, ret.size() - 1);
32 }
33 reverseStr(ret, 0, ret.size() - 1);
34 return ret;
35 }
36
37 int main()
38 {
39 string s;
40 while (getline(cin, s))
41 {
42 cout << getReverse(s) << endl;
43 }
44 return 0;
45 }
posted @
2011-04-23 19:26 unixfy 阅读(1290) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
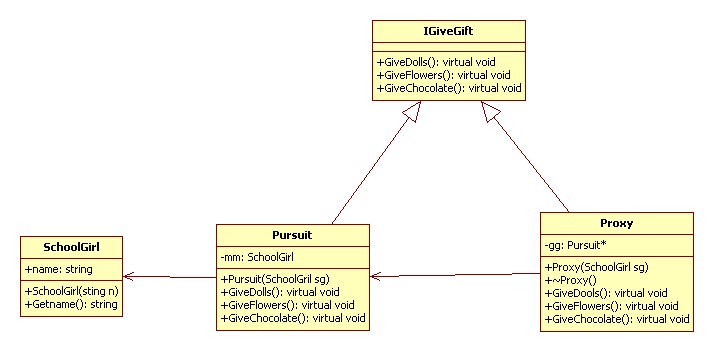
来自于《大话设计模式》
代理模式(Proxy):为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。
代理模式的应用:
·远程代理
·虚拟代理
·安全代理
·智能指针
UML 图:
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class SchoolGirl
6 {
7 private:
8 string name;
9 public:
10 SchoolGirl(string n) : name(n) {}
11 string GetName()
12 {
13 return name;
14 }
15 };
16
17 class IGiveGift
18 {
19 public:
20 virtual void GiveDolls() = 0;
21 virtual void GiveFlowers() = 0;
22 virtual void GiveChocolate() = 0;
23 };
24
25 class Pursuit : public IGiveGift
26 {
27 private:
28 SchoolGirl mm;
29 public:
30 Pursuit(SchoolGirl sg) : mm(sg) {}
31 virtual void GiveDolls()
32 {
33 cout << mm.GetName() << " 送你洋娃娃" << endl;
34 }
35 virtual void GiveFlowers()
36 {
37 cout << mm.GetName() << " 送你鲜花" << endl;
38 }
39 virtual void GiveChocolate()
40 {
41 cout << mm.GetName() << " 送你巧克力" << endl;
42 }
43 };
44
45 class Proxy : public IGiveGift
46 {
47 private:
48 Pursuit* gg;
49 public:
50 Proxy(SchoolGirl sg)
51 {
52 gg = new Pursuit(sg);
53 }
54 ~Proxy()
55 {
56 delete gg;
57 }
58 virtual void GiveDolls()
59 {
60 gg->GiveDolls();
61 }
62 virtual void GiveFlowers()
63 {
64 gg->GiveFlowers();
65 }
66 virtual void GiveChocolate()
67 {
68 gg->GiveChocolate();
69 }
70 };
71
72 int main()
73 {
74 SchoolGirl mm("Lili");
75
76 Proxy* pp = new Proxy(mm);
77 pp->GiveDolls();
78 pp->GiveFlowers();
79 pp->GiveChocolate();
80
81 delete pp;
82 return 0;
83 }
posted @
2011-04-23 18:44 unixfy 阅读(271) |
评论 (0) |
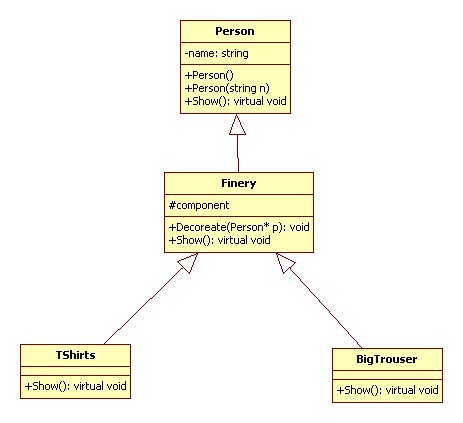
编辑 收藏来自于《大话设计模式》
装饰模式(Decorator):动态地给一个对象添加额外的职责,就增加的功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类更为灵活。
UML 图:
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class Person
6 {
7 private:
8 string name;
9 public:
10 Person() {}
11 Person(string n): name(n) {}
12 virtual void Show()
13 {
14 cout << "装饰的 " << name << endl;
15 }
16 };
17
18 class Finery: public Person
19 {
20 protected:
21 Person* component;
22 public:
23 void Decorate(Person* p)
24 {
25 component = p;
26 }
27 virtual void Show()
28 {
29 if (component != 0)
30 {
31 component->Show();
32 }
33 }
34 };
35
36 class TShirts: public Finery
37 {
38 public:
39 virtual void Show()
40 {
41 cout << "大 T 恤 ";
42 Finery::Show();
43 }
44 };
45
46 class BigTrouser: public Finery
47 {
48 public:
49 virtual void Show()
50 {
51 cout << "垮裤 ";
52 Finery::Show();
53 }
54 };
55
56 int main()
57 {
58 Person* p = new Person("Mark");
59 p->Show();
60
61 TShirts* t = new TShirts;
62 t->Decorate(p);
63 t->Show();
64
65 BigTrouser* b = new BigTrouser;
66 b->Decorate(t);
67 b->Show();
68
69 delete p;
70 delete t;
71 delete b;
72 }
posted @
2011-04-23 18:09 unixfy 阅读(140) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
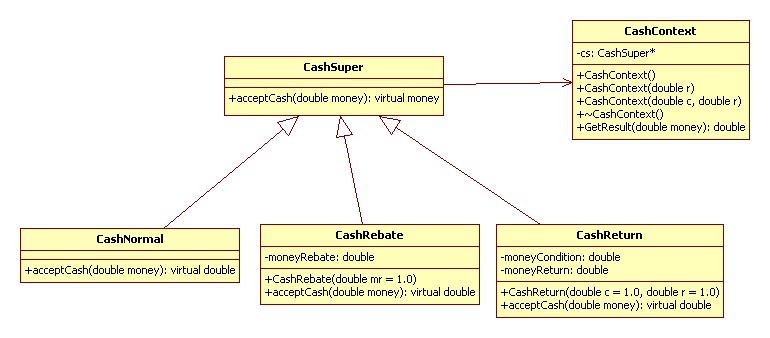
来自于《大话设计模式》
策略模式(Strategy):它定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以相互替换,此模式让算法的变化不会影响到使用算法的客户。
所谓的算法即使 acceptCash 虚函数,由 CashSuper 的派生类实现各个 acceptCash。客户端代码根据使用不同的参数生成不同的 CashContext 对象,来使用不同的策略(acceptCash 虚函数)
UML 图:
代码实现 C++:
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class CashSuper
5 {
6 public:
7 virtual double acceptCash(double money) = 0;
8 };
9
10 class CashNormal : public CashSuper
11 {
12 public:
13 virtual double acceptCash(double money)
14 {
15 return money;
16 }
17 };
18
19 class CashRebate : public CashSuper
20 {
21 private:
22 double moneyRebate;
23 public:
24 CashRebate(double mr = 1.0) : moneyRebate(mr) {}
25 virtual double acceptCash(double money)
26 {
27 return money * moneyRebate;
28 }
29 };
30
31 class CashReturn : public CashSuper
32 {
33 private:
34 double moneyCondition;
35 double moneyReturn;
36 public:
37 CashReturn(double c = 1.0, double r = 1.0) : moneyCondition(c), moneyReturn(r) {}
38 virtual double acceptCash(double money)
39 {
40 return money - money / moneyCondition * moneyReturn;
41 }
42 };
43
44 class CashContext
45 {
46 private:
47 CashSuper* cs;
48 public:
49 CashContext()
50 {
51 cs = new CashNormal;
52 // cs = new CashNormal();
53 }
54 CashContext(double r)
55 {
56 cs = new CashRebate(r);
57 }
58 CashContext(double c, double r)
59 {
60 cs = new CashReturn(c, r);
61 }
62 ~CashContext()
63 {
64 delete cs;
65 }
66 double GetResult(double money)
67 {
68 return cs->acceptCash(money);
69 }
70 };
71
72 int main()
73 {
74 CashContext* cc = new CashContext;
75 cout << cc->GetResult(300) << endl;
76 delete cc;
77
78 cc = new CashContext(0.8);
79 cout << cc->GetResult(300) << endl;
80 delete cc;
81
82 cc = new CashContext(100, 50);
83 cout << cc->GetResult(300) << endl;
84 delete cc;
85
86 return 0;
87 }
posted @
2011-04-23 16:27 unixfy 阅读(178) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
设计一个保护 min 函数的栈,min 函数返回栈的最小元素。并且 min、push、pop 函数的时间复杂度都为 O(1)。
主要思想是定义一个辅助栈记录最小元素在原栈中的索引。
实现中参考:
http://hi.baidu.com/xiangzifengshi/blog/item/2f9e833aef17d6f7828b131e.htmlhttp://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/25411174200712895228171/代码实现:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <ctime>
3 #include <cassert>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 class MinStack
7 {
8 private:
9 int stack[100];
10 int p;
11 int minstack[100];
12 int q;
13
14 bool minEmpty()
15 {
16 return q == 0;
17 }
18 void minPop()
19 {
20 assert(!minEmpty());
21 --q;
22 }
23 int minTop()
24 {
25 assert(!minEmpty());
26 return minstack[q - 1];
27 }
28 public:
29 MinStack() : p(0), q(0) {}
30 bool empty()
31 {
32 return p == 0;
33 }
34 void push(int i)
35 {
36 stack[p++] = i;
37 if (minEmpty())
38 {
39 minstack[q++] = p - 1;
40 }
41 else
42 {
43 if (i <= stack[minTop()])
44 {
45 minstack[q++] = p - 1;
46 }
47 }
48 }
49 void pop()
50 {
51 assert(!empty());
52 if (top() == stack[minTop()])
53 {
54 minPop();
55 }
56 --p;
57 }
58 int min()
59 {
60 assert(!empty());
61 return stack[minTop()];
62 }
63 int top()
64 {
65 assert(!empty());
66 return stack[p - 1];
67 }
68 };
69
70 int main()
71 {
72 MinStack ms;
73 srand(time(0));
74 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
75 {
76 int n = rand() % 100;
77 ms.push(n);
78 }
79 while (!ms.empty())
80 {
81 cout << ms.top() << '\t' << ms.min() << endl;
82 ms.pop();
83 }
84 return 0;
85 }
posted @
2011-04-23 01:28 unixfy 阅读(188) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
设计一个字符串类 String,实现
·+= 连接两个字符串
·+ 连接两个字符串
·== 判断两个字符串是否相等
·< 判断两个字符串大小关系
类的声明:
class String
{
private:
char* mychar;
int len;
public:

};
代码:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstring>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 class String
6 {
7 private:
8 char* mychar;
9 int len;
10 private:
11 void clear()
12 {
13 delete[] mychar;
14 mychar = 0;
15 len = 0;
16 }
17 public:
18 String(char* s = "")
19 {
20 int l = strlen(s);
21 mychar = new char[l + 1];
22 if (mychar != 0)
23 {
24 strcpy(mychar, s);
25 len = l;
26 }
27 }
28 String(const String& s)
29 {
30 mychar = new char[s.len + 1];
31 if (mychar != 0)
32 {
33 strcpy(mychar, s.mychar);
34 len = s.len;
35 }
36 }
37 String& operator=(const String& s)
38 {
39 if (this != &s)
40 {
41 clear();
42 mychar = new char[s.len + 1];
43 if (mychar != 0)
44 {
45 strcpy(mychar, s.mychar);
46 len = s.len;
47 }
48 }
49 return *this;
50 }
51 ~String()
52 {
53 clear();
54 }
55 String& operator +=(const String& s)
56 {
57 int l = len + s.len + 1;
58 char* t = new char[l];
59 if (t != 0)
60 {
61 // 初始化内存
62 memset(t, 0, sizeof (char) * l);
63 strcat(t, mychar);
64 strcat(t, s.mychar);
65 }
66 delete [] mychar;
67 mychar = t;
68 len = l;
69 return *this;
70 }
71
72 friend String operator +(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
73 friend bool operator ==(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
74 friend bool operator < (const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
75 friend istream& operator >>(istream& in, String& s);
76 friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, const String& s);
77 };
78
79 String operator +(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
80 {
81 String t(lhs);
82 return t += rhs;
83 }
84
85 bool operator==(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
86 {
87 return strcmp(lhs.mychar, rhs.mychar) == 0;
88 }
89
90 bool operator<(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
91 {
92 return strcmp(lhs.mychar, rhs.mychar) < 0;
93 }
94
95 bool operator >(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
96 {
97 return !(lhs < rhs) && !(lhs == rhs);
98 }
99
100 bool operator <=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
101 {
102 return lhs < rhs || lhs == rhs;
103 }
104
105 bool operator >=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
106 {
107 return !(lhs < rhs);
108 }
109
110 istream& operator >>(istream& in, String& s)
111 {
112 s.clear();
113 char t[100];
114 in >> t;
115 if (!in)
116 {
117 cerr << "Input error!" << endl;
118 exit(1);
119 }
120 int l = strlen(t);
121 s.mychar = new char[l + 1];
122 if (s.mychar != 0)
123 {
124 strcpy(s.mychar, t);
125 s.len = l;
126 }
127 return in;
128 }
129
130 ostream& operator <<(ostream& out, const String& s)
131 {
132 out << s.mychar;
133 return out;
134 }
135
136 int main()
137 {
138 String s1, s2;
139 while (cin >> s1 >> s2)
140 {
141 cout << s1 << endl;
142 cout << s2 << endl;
143 cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
144 cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
145 cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
146 cout << (s1 <= s2) << endl;
147 cout << (s1 >= s2) << endl;
148
149 cout << s1 + s2 << endl;
150 s1 += s2;
151 cout << s1 << endl;
152 cout << s2 << endl;
153 s2 += s1;
154 cout << s1 << endl;
155 cout << s2 << endl;
156 }
157 return 0;
158 }
posted @
2011-04-22 13:12 unixfy 阅读(186) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
摘要: 设计一个日期类 Date,包括 年月日 三个私有数据成员。设计运算符重载,实现:·两个日期对象之间的“-”,求得两个日期的相差天数。注意两个日期不能相加。·实现日期对象“+”“-”“+=”“-=”一个整型数,求得运算后的日期。
1&n...
阅读全文
posted @
2011-04-22 11:13 unixfy 阅读(292) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
闰年判断就是 能被 400 整除的,后者能被 4 整除且不能被 100 整除的年份。
即
1 int isLeapYear(int y)
2 {
3 if ((y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0) || y % 400 == 0)
4 {
5 return 1;
6 }
7 else
8 {
9 return 0;
10 }
11 }
但是这里有个细节需要注意就是,(y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0) || y % 400 == 0 这个表达式中的三个子表达式的顺序怎样调整。
y % 4 == 0
y % 100 != 0
y % 400 == 0
这里有 4 中组合:
·(y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0) || y % 400 == 0
·(y % 100 != 0 && y % 4 == 0) || y % 400 == 0
·y % 400 == 0 || (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0)
·y % 400 == 0 || (y % 100 != 0 && y % 4 == 0)
我们首先确定 y % 400 是不是应该在最前,对于一般的年份很少有能被 400 整除的年份,其概率为 1 / 400,所以 y % 400 == 0 基本都为假,这样就必须还要判断后面的表达式,所以应该将 y % 400 放在后面。
然后,判断 y % 100 != 0 是否应该在 y % 4 == 0 之前,y % 100 != 0 为真的概率很大及为 99 / 100,而 y % 4 == 0 为真的概率为 1 / 4,也就是说 y % 4 为假的概率更大。根据 && 操作符的性质,当前面一个为假时其就不用判断后面的表达式是否为真假了。所以应该把 y % 4 == 0 放在 y % 100 != 0 前面效率更好。
即判断闰年的表达式顺序应该为这样是,效率最高:
(y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0) || y % 400 == 0
posted @
2011-04-22 00:17 unixfy 阅读(142) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏