题意;
每次可以删除一个木条x=?,y=?或者x=?,z=?或者y=?,z=?,求最后删除的木块总数
:
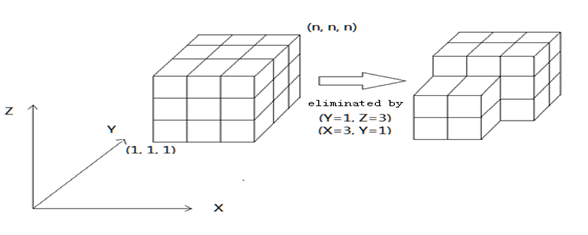
开始写的时候出现个BUG,无奈,上网找题解,更无奈,都是些几句话hash然后就是一堆难懂的代码。。
后来仔细想了想,把重复的操作去除后(就是两次删除的同一个木条),下面就是个很简单的容斥原理了
因为去除了重复操作,一个木块最多被删除3次,然后删除的个数就为被删除至少一次的个数-删除至少两次的个数+删除至少3次的个数。不能强行枚举,可以用map或者传说中的hash记录被删除掉木块的次数。这里,由于操作最多m=1000,删除木块数最多为C(m,2),然后两两枚举操作,把相交木块删除次数+1,然后最后map中所有木块删除次数只能有2个值:1和3,当值为1时,total-1,值为3时,total-2
为什么?因为我说了,一个木块最多被删除3次,然后俩俩枚举的时候,你懂的。
1 # include <cstdio>
2 # include <utility>
3 # include <cstring>
4 # include <algorithm>
5 # include <functional>
6 # include <set>
7 # include <cstdlib>
8 # include <map>
9 using namespace std;
10 struct node
11 {
12 int p[3];
13 bool operator<(const node &pos) const
14 {
15 for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
16 if(p[i]!=pos.p[i])
17 return p[i]<pos.p[i];
18 return false;
19 }
20 };
21 pair<int,int> data[1000][2];
22 set<pair<pair<int,int>,pair<int,int> > > r1;
23 map<node,int> r2;
24 int main()
25 {
26 int test;
27 scanf("%d",&test);
28 while(test--)
29 {
30 int n,m,p=0;
31 char str[128];
32 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
33 r1.clear();r2.clear();
34 while(m--)
35 {
36 scanf("%s",str);
37 char *t=strtok(str,",");
38 data[p][0].first=(*t)-'X';
39 data[p][0].second=atoi(t+2);
40 t=strtok(NULL," ");
41 data[p][1].first=(*t)-'X';
42 data[p][1].second=atoi(t+2);
43 if(data[p][0].first>data[p][1].first) swap(data[p][0],data[p][1]);
44 pair< pair<int,int>,pair<int,int> > tt;
45 tt.first=data[p][0];
46 tt.second=data[p][1];
47 if(data[p][0].second>=1&&data[p][0].second<=n&&data[p][1].second>=1&&data[p][1].second<=n&&r1.find(tt)==r1.end()) p++,r1.insert(tt);
48 }
49 m=p;
50 for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
51 for(int j=i+1;j<m;j++)
52 if(data[i][0]==data[j][0]&&data[i][1].first!=data[j][1].first||
53 data[i][1]==data[j][0]&&data[i][0].first!=data[j][1].first||
54 data[i][0]==data[j][1]&&data[i][1].first!=data[j][0].first||
55 data[i][1]==data[j][1]&&data[i][0].first!=data[j][0].first)
56 {
57 node t;
58 t.p[data[i][0].first]=data[i][0].second;
59 t.p[data[i][1].first]=data[i][1].second;
60 t.p[data[j][0].first]=data[j][0].second;
61 t.p[data[j][1].first]=data[j][1].second;
62 r2[t]++;
63 }
64 int total=m*n;
65 for(map<node,int>::iterator i=r2.begin();i!=r2.end();i++)
66 if(i->second==1) total--;
67 else total-=2;
68 printf("%d\n",total);
69 }
70 //system("pause");
71 return 0;
72 }
73