使用LoadLibrary函数调用DLL中的函数的方法一般被称为“显式”调用,意义和使用lib的“隐式”调用相对应。
LoadLibrary调用DLL中的函数的方法比较简单,通过GetProcAddress获得函数的在DLL的地址就可以访问了,但DLL中的Class访问就相对很复杂了(目前我就发现这一种显式调用方式,哪位有其他方法么?)。一个简单的情况就是Class的函数在调用是,其名称是什么?还有Class的contructor函数怎么调用?下面的代码将演示下这些问题。
这里是DLL的文件:
DllMain.h
1 #ifndef __DLLMAIN_H__
#ifndef __DLLMAIN_H__
2 #define __DLLMAIN_H__
#define __DLLMAIN_H__
3
4 #include <string>
#include <string>
5
6 #define DllExport __declspec(dllexport)
#define DllExport __declspec(dllexport)
7
8 extern "C" int DllExport Func(int x);
extern "C" int DllExport Func(int x);
9
10 extern "C" class DllExport CA
extern "C" class DllExport CA
11

 {
{
12 public:
public:
13 CA(int x);
CA(int x);
14 ~CA();
~CA();
15
16 int Func0();
int Func0();
17 int Func(int x);
int Func(int x);
18 const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const;
const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const;
19 protected:
protected:
20 int _x;
int _x;
21 };
};
22
23
24 #endif
#endif
DllMain.cpp
1 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
2
3 #include "DllMain.h"
#include "DllMain.h"
4
5 int Func(int x)
int Func(int x)
6

 {
{
7 return x * 10;
return x * 10;
8 }
}
9
10 CA::CA(int x)
CA::CA(int x)
11 : _x(x)
: _x(x)
12

 {
{
13 std::cout << "contructor" << std::endl;
std::cout << "contructor" << std::endl;
14 }
}
15
16 CA::~CA()
CA::~CA()
17

 {
{
18 std::cout << "destructor" << std::endl;
std::cout << "destructor" << std::endl;
19 }
}
20
21 int CA::Func0()
int CA::Func0()
22

 {
{
23 return _x;
return _x;
24 }
}
25
26 int CA::Func(int x)
int CA::Func(int x)
27

 {
{
28 return _x * x;
return _x * x;
29 }
}
30
31 const std::string& CA::FuncS(int x, const std::string &str) const
const std::string& CA::FuncS(int x, const std::string &str) const
32

 {
{
33 return str;
return str;
34 }
}
35
这里需要.def文件了,因为Class在DLL中的命名不像函数命名那么简单,会被转义的,像CA::Func(int)在DLL的export表中就是
?Func@CA@@QAEHH@Z,具体定义说明可参看《xxx的自我修养》一书。因此,这里需要使用.def文件对函数进行重命名,下面是DllMain.def文件内容:
1 LIBRARY TESTDLL
LIBRARY TESTDLL
2 EXPORTS
EXPORTS
3 Func = Func
Func = Func
4 CA::CA(int) = ??0CA@@QAE@H@Z
CA::CA(int) = ??0CA@@QAE@H@Z
5 CA::~CA = ??1CA@@QAE@XZ
CA::~CA = ??1CA@@QAE@XZ
6 CA::Func0 = ?Func0@CA@@QAEHXZ
CA::Func0 = ?Func0@CA@@QAEHXZ
7 CA::Func(int) = ?Func@CA@@QAEHH@Z
CA::Func(int) = ?Func@CA@@QAEHH@Z
8 ;CA::FuncS(int,std::basic_string<char>&) = ?FuncS@CA@@QBEABV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@HABV23@@Z
;CA::FuncS(int,std::basic_string<char>&) = ?FuncS@CA@@QBEABV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@HABV23@@Z
9 CA::FuncS = ?FuncS@CA@@QBEABV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@HABV23@@Z
CA::FuncS = ?FuncS@CA@@QBEABV?$basic_string@DU?$char_traits@D@std@@V?$allocator@D@2@@std@@HABV23@@Z
多说一句,这里.def的编写很需要Depends(Dependency Walker)工具的支持,其是查看DLL的首选工具啊。。
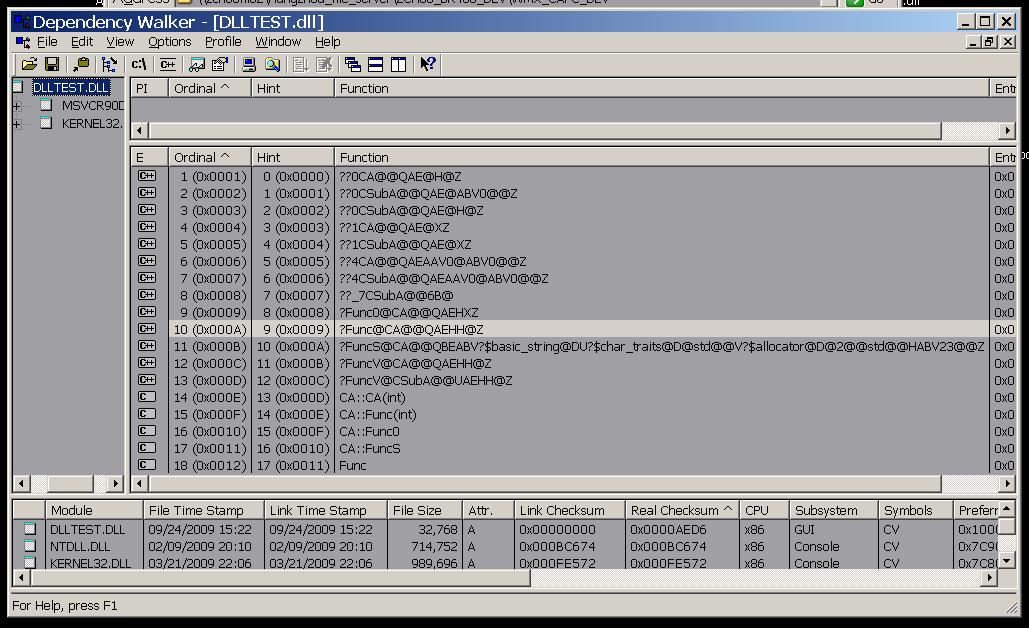
编译DLL,用下面代码进行测试:
LoadLib.cpp
1 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
2 #include <string>
#include <string>
3
4 #include <windows.h>
#include <windows.h>
5
6 //#include "DllMain.h"
//#include "DllMain.h"
7
8 #define DllExport __declspec(dllexport)
#define DllExport __declspec(dllexport)
9
10 extern "C" int DllExport Func(int x);
extern "C" int DllExport Func(int x);
11
12 extern "C" class DllExport CA
extern "C" class DllExport CA
13

 {
{
14 public:
public:
15 CA(int x);
CA(int x);
16 ~CA();
~CA();
17
18 int Func0();
int Func0();
19 int Func(int x);
int Func(int x);
20 const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const;
const std::string& FuncS(int x, const std::string& str) const;
21
22 private:
private:
23 int _x;
int _x;
24 };
};
25
26 typedef int (*func)(int);
typedef int (*func)(int);
27 typedef void (WINAPI *PCTOR)(int);
typedef void (WINAPI *PCTOR)(int);
28 typedef int (WINAPI *func0)(void);
typedef int (WINAPI *func0)(void);
29 typedef int (WINAPI *funcc)(int);
typedef int (WINAPI *funcc)(int);
30 typedef const std::string& (WINAPI *funcs)(int,const std::string&);
typedef const std::string& (WINAPI *funcs)(int,const std::string&);
31 typedef void (WINAPI *PDTOR)(void);
typedef void (WINAPI *PDTOR)(void);
32
33 int main()
int main()
34

 {
{
35 HINSTANCE hdll;
HINSTANCE hdll;
36 hdll = LoadLibraryA(("../DLLTEST/Debug/DLLTEST.dll"));
hdll = LoadLibraryA(("../DLLTEST/Debug/DLLTEST.dll"));
37 if(hdll != NULL)
if(hdll != NULL)
38

 {
{
39 func pf = (func)GetProcAddress(hdll, "Func");
func pf = (func)GetProcAddress(hdll, "Func");
40 std::cout << pf(10) << std::endl;
std::cout << pf(10) << std::endl;
41 CA* a = (CA*)malloc(sizeof(CA));
CA* a = (CA*)malloc(sizeof(CA));
42 PCTOR pc = (PCTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::CA(int)");
PCTOR pc = (PCTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::CA(int)");
43
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a }
44 pc(5);
pc(5);
45 func0 pf0 = (func0)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func0");
func0 pf0 = (func0)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func0");
46
 _asm
_asm  {MOV ECX, a }
{MOV ECX, a }
47 std::cout << pf0() << std::endl;
std::cout << pf0() << std::endl;
48 funcc pfc = (funcc)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func(int)");
funcc pfc = (funcc)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::Func(int)");
49
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a }
50 std::cout << pfc(10) << std::endl;
std::cout << pfc(10) << std::endl;
51 funcs pfs = (funcs)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::FuncS");
funcs pfs = (funcs)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::FuncS");
52
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a }
53 std::cout << pfs(0, std::string("hello world")) << std::endl;
std::cout << pfs(0, std::string("hello world")) << std::endl;
54 PDTOR pd = (PDTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::~CA");
PDTOR pd = (PDTOR)GetProcAddress(hdll, "CA::~CA");
55
 _asm
_asm  { MOV ECX, a }
{ MOV ECX, a }
56 pd();
pd();
57 free(a);
free(a);
58 }
}
59 FreeLibrary(hdll);
FreeLibrary(hdll);
60
61 return 0;
return 0;
62 }
}
结果还算正常:
1 100
100
2 contructor
contructor
3 5
5
4 50
50
5 hello world
hello world
6 destructor
destructor
7
上面的代码基本演示了DLL中Class的简单使用,包括对contructor、destrunctor的调用,有参、无参、多参函数调用,不知道有啥缺陷,但至少Work了,嘿嘿~
由上述代码可以看出,这种“显式”使用DLL中的Class是非常繁琐和危险的事情,因此我觉得能用“隐式”就不要用“显式”,能静态就不要用动态。。。
注意到没,代码没有演示继承和虚函数,那是因此我加入Virtual函数,程序就会core,实在搞不定,这里也就没法给出好的方案来,不知道哪位有啥建议么。。。
上面代码参考了如下地址:
http://www.codeproject.com/dll/classesexportedusingLL.asp http://blog.csdn.net/jdcb2001/archive/2006/11/21/1401569.aspx