Optimal Keypad
Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536K
Total Submit:168 Accepted:80
Description
Optimus Mobiles produces mobile phones that support SMS messages. The Mobiles have a keypad of 12 keys, numbered 1 to 12. There is a character string assigned to each key. To type in the n-th character in the character string of a particular key, one should press the key n times. Optimus Mobiles wishes to solve the problem of assigning character strings to the keys such that for typing a random text out of a dictionary of common words, the average typing effort (i.e. the average number of keystrokes) is minimal.
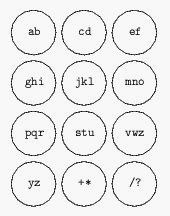
Figure 1To be more precise, consider a set of characters {a, b, c,..., z, +, *, /, ?} printed on a label tape as in Fig. 2. We want to cut the tape into 12 pieces each containing one or more characters. The 12 labels are numbered 1 to 12 from left to right and will be assigned to the keypad keys in that order.

Figure 2You are to write a program to find the 11 cutting positions for a given dictionary of common words. The cutting positions should minimize the average number of keystrokes over all common words in the dictionary. Your output should be a string of 11 characters, where character i in this string is the first character of the (i+1)
th label.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t (1 <= t <= 10), the number of test cases. Each test case starts with a line, containing an integer M (1 <= M <= 10000), the number of common words in the test case. In each M subsequent line, there is a common word. Each common word contains at most 30 characters from the alphabet {a, b, c,..., z, +, *, /, ?}.
Output
The output contains one line per test case containing an optimal cut string. Obviously, there may be more than a single optimal cut string, so print the optimal cut string which is the smallest one in lexicographic order.
Sample Input
2
2
hi
ok
5
hello
bye
how
when
who
Sample Output
bcdefghijko
bcdefhlnowy
Source
Tehran 2003
 #include
<
iostream
>
#include
<
iostream
>
 using
namespace
std;
using
namespace
std;

 const
int
INF
=
100000000
;
const
int
INF
=
100000000
;

 int
f[
13
][
30
][
30
];
int
f[
13
][
30
][
30
];
 int
s[
13
][
30
][
30
];
int
s[
13
][
30
][
30
];
 int
l[
13
][
30
][
30
];
int
l[
13
][
30
][
30
];

 char
c[]
=
char
c[]
=
 {
'
a
'
,
'
b
'
,
'
c
'
,
'
d
'
,
'
e
'
,
'
f
'
,
'
g
'
,
'
h
'
,
'
i
'
,
'
j
'
,
'
k
'
,
'
l
'
,
'
m
'
,
'
n
'
,
'
o
'
{
'
a
'
,
'
b
'
,
'
c
'
,
'
d
'
,
'
e
'
,
'
f
'
,
'
g
'
,
'
h
'
,
'
i
'
,
'
j
'
,
'
k
'
,
'
l
'
,
'
m
'
,
'
n
'
,
'
o
'
 ,
'
p
'
,
'
q
'
,
'
r
'
,
'
s
'
,
'
t
'
,
'
u
'
,
'
v
'
,
'
w
'
,
'
x
'
,
'
y
'
,
'
z
'
,
'
+
'
,
'
*
'
,
'
/
'
,
'
?
'
}
;
,
'
p
'
,
'
q
'
,
'
r
'
,
'
s
'
,
'
t
'
,
'
u
'
,
'
v
'
,
'
w
'
,
'
x
'
,
'
y
'
,
'
z
'
,
'
+
'
,
'
*
'
,
'
/
'
,
'
?
'
}
;

 void
OutPut(
int
k,
int
i,
int
j)
void
OutPut(
int
k,
int
i,
int
j)


 {
{
 if
(l[k][i][j]
>=
0
)
if
(l[k][i][j]
>=
0
)


 {
{
 OutPut(l[k][i][j], i, s[k][i][j]);
OutPut(l[k][i][j], i, s[k][i][j]);

 printf(
"
%c
"
, c[s[k][i][j]
+
1
]);
printf(
"
%c
"
, c[s[k][i][j]
+
1
]);

 OutPut(k
-
l[k][i][j], s[k][i][j]
+
1
, j);
OutPut(k
-
l[k][i][j], s[k][i][j]
+
1
, j);
 }
}
 }
}

 void
Solve()
void
Solve()


 {
{
 int
n;
int
n;
 int
i, j, k, p, q, t, e;
int
i, j, k, p, q, t, e;

 int
cntLable[
300
]
=
int
cntLable[
300
]
=
 {
0
}
;
{
0
}
;
 int
sum;
int
sum;
 char
tmpS[
31
];
char
tmpS[
31
];
 scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
n);
scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
n);
 for
(i
=
0
; i
<
n; i
++
)
for
(i
=
0
; i
<
n; i
++
)


 {
{
 scanf(
"
%s
"
, tmpS);
scanf(
"
%s
"
, tmpS);
 for
(j
=
0
; j
<
strlen(tmpS); j
++
)
for
(j
=
0
; j
<
strlen(tmpS); j
++
)
 cntLable[tmpS[j]]
++
;
cntLable[tmpS[j]]
++
;
 }
}

 for
(k
=
1
; k
<=
12
; k
++
)
for
(k
=
1
; k
<=
12
; k
++
)
 for
(i
=
0
; i
<
30
; i
++
)
for
(i
=
0
; i
<
30
; i
++
)
 for
(j
=
0
; j
<
30
; j
++
)
for
(j
=
0
; j
<
30
; j
++
)


 {
{
 f[k][i][j]
=
INF;
f[k][i][j]
=
INF;
 s[k][i][j]
=
-
1
;
s[k][i][j]
=
-
1
;
 l[k][i][j]
=
-
1
;
l[k][i][j]
=
-
1
;
 }
}

 //
init k=1
//
init k=1
 for
(i
=
0
; i
<
30
; i
++
)
for
(i
=
0
; i
<
30
; i
++
)


 {
{
 sum
=
0
;
sum
=
0
;
 for
(j
=
i, k
=
1
; j
<
30
; j
++
, k
++
)
for
(j
=
i, k
=
1
; j
<
30
; j
++
, k
++
)


 {
{
 sum
+=
cntLable[c[j]]
*
k;
sum
+=
cntLable[c[j]]
*
k;
 f[
1
][i][j]
=
sum;
f[
1
][i][j]
=
sum;
 }
}
 }
}

 for
(k
=
2
; k
<=
12
; k
++
)
for
(k
=
2
; k
<=
12
; k
++
)
 for
(i
=
0
; i
<
30
; i
++
)
for
(i
=
0
; i
<
30
; i
++
)
 for
(j
=
i
+
k
-
1
; j
<
30
; j
++
)
for
(j
=
i
+
k
-
1
; j
<
30
; j
++
)


 {
{
 for
(t
=
i; t
<
j; t
++
)
for
(t
=
i; t
<
j; t
++
)


 {
{
 e
=
k
-
1
<
t
-
i
+
1
?
k
-
1
: t
-
i
+
1
;
e
=
k
-
1
<
t
-
i
+
1
?
k
-
1
: t
-
i
+
1
;
 for
(p
=
1
; p
<=
e; p
++
)
for
(p
=
1
; p
<=
e; p
++
)
 if
(f[k][i][j]
>
f[p][i][t]
+
f[k
-
p][t
+
1
][j])
if
(f[k][i][j]
>
f[p][i][t]
+
f[k
-
p][t
+
1
][j])


 {
{
 f[k][i][j]
=
f[p][i][t]
+
f[k
-
p][t
+
1
][j];
f[k][i][j]
=
f[p][i][t]
+
f[k
-
p][t
+
1
][j];
 s[k][i][j]
=
t;
s[k][i][j]
=
t;
 l[k][i][j]
=
p;
l[k][i][j]
=
p;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}

 OutPut(
12
,
0
,
29
);
OutPut(
12
,
0
,
29
);
 printf(
"
\n
"
);
printf(
"
\n
"
);
 }
}

 int
main()
int
main()


 {
{
 int
n;
int
n;
 scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
n);
scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
n);
 while
(n
--
!=
0
)
while
(n
--
!=
0
)


 {
{
 Solve();
Solve();
 }
}
 return
0
;
return
0
;
 }
}
posted on 2006-09-26 18:51
豪 阅读(507)
评论(1) 编辑 收藏 引用 所属分类:
ACM题目