Picture
Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:10000K
Total Submit:742 Accepted:411
Description
A number of rectangular posters, photographs and other pictures of the same shape are pasted on a wall. Their sides are all vertical or horizontal. Each rectangle can be partially or totally covered by the others. The length of the boundary of the union of all rectangles is called the perimeter.
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.
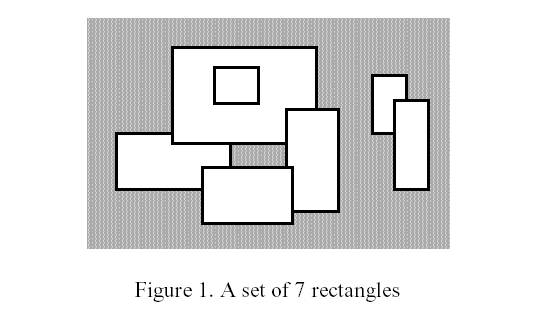
The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.

The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The first line contains the number of rectangles pasted on the wall. In each of the subsequent lines, one can find the integer coordinates of the lower left vertex and the upper right vertex of each rectangle. The values of those coordinates are given as ordered pairs consisting of an x-coordinate followed by a y-coordinate.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. The output must contain a single line with a non-negative integer which corresponds to the perimeter for the input rectangles.
Sample Input
7
-15 0 5 10
-5 8 20 25
15 -4 24 14
0 -6 16 4
2 15 10 22
30 10 36 20
34 0 40 16
Sample Output
228
Source
IOI 1998
做这道题之前我用线段树的结构过了几个题目 效果没有我想象的好
但是这道题明显就出了差距 直接离散化与用线段树来做效果差了有将近10倍!
线段树的基本应用:请参考这篇文章
http://www.cppblog.com/sicheng/archive/2006/11/24/15640.html
这里我们再加上测度与连续段的作用:
(一)、
测度
由于线段树结构递归定义,其测度也可以递归定义。增加数据域
Lines_Tree.M
表示以该结点为根的子树的测度。
M
取值如下:
a[j] – a[i]
该结点
Count>0
M = 0
该结点为叶结点且
Count=0
Leftchild
↑
.M + Rightchild
↑
.M
该结点为内部结点且
Count=0
据此,可以用
Lines_Tree.UpData
来动态地维护
Lines_Tree.M
。
UpData
在每一次执行
Insert
或
Delete
之后执行。定义如下:
Procedure Lines_Tree.UpData
1
if count > 0
2
then M
ß
a[j] – [i] {
盖满区间,测度为
a[j] – a[i]}
3
else if j - i = 1 {
是否叶结点
}
4
then M
ß
0 {
该结点是叶结点
}
5
else M
ß
Leftchild
↑
.M + Rightchild
↑
.M
{
内部结点
}
UpData
的复杂度为
O(1)
,则用
UpData
来动态维护测度后执行根结点的
Insert
与
Delete
的复杂度仍为
O(logN)
。
(二)、
连续段数
这里的连续段数指的是区间的并可以分解为多少个独立的区间。如
[1
,
2]
∪[2,3]∪
[5
,
6]
可以分解为两个区间
[1
,
3]
与
[5
,
6]
,则连续段数为
2
。增加一个数据域
Lines_Tree.line
表示该结点的连续段数。
Line
的讨论比较复杂,内部结点不能简单地将左右孩子的
Line
相加。所以再增加
Lines_Tree.lbd
与
Lines_Tree.rbd
域。定义如下:
1
左端点
I
被描述区间盖到
lbd =
0
左端点
I
不被描述区间盖到
1
右端点
J
被描述区间盖到
rbd =
0
右端点
J
不被描述区间盖到
lbd
与
rbd
的实现:
1
该结点
count > 0
lbd = 0
该结点是叶结点且
count = 0
leftchild
↑
.lbd
该结点是内部结点且
Count=0
1
该结点
count > 0
rbd = 0
该结点是叶结点且
count = 0
rightchild
↑
.rbd
该结点是内部结点且
Count=0
有了
lbd
与
rbd
,
Line
域就可以定义了:
1
该结点
count > 0
Line = 0
该结点是叶结点且
count = 0
Leftchild
↑
.Line + Rightchild
↑
.Line - 1
当该结点是内部结点且
Count=0
,
Leftchild
↑
.rbd = 1
且
Rightchild
↑
.lbd = 1
Leftchild
↑
.Line + Rightchild
↑
.Line
当该结点是内部结点且
Count=0
,
Leftchild
↑
.rbd
与
Rightchild
↑
.lbd
不都为
1
据此,可以定义
UpData’
动态地维护
Line
域。与
UpData
相似,
UpData’
也在每一次执行
Insert
或
Delete
后执行。定义如下:
Procedure Lines_Tree.UpData’
1
if count > 0 {
是否盖满结点表示的区间
}
2
then lbd
ß
1
3
rbd
ß
1
4
Line
ß
1
5
else if j - i = 1 {
是否为叶结点
}
6
then lbd
ß
0 {
进行到这一步,如果为叶结点,
count = 0}
7
rbd
ß
0
8
line
ß
0
9
else line
ß
Leftchild
↑
.line + Rightchild
↑
.line -
Leftchild
↑
.rbd * Rightchild
↑
.lbd
{
用乘法确定
Leftchild
↑
.rbd
与
Rightchild
↑
.lbd
是否同时为
1}
于是我按下面的步骤重写了程序:
1.
以矩形顶点坐标切割平面,实现横纵坐标的离散化并建立映射
X_Map
、
Y_Map
。
2.
事件排序
3.
Root.Build(1, N*2)
4.
Nowm
ß
0
5.
NowLine
ß
0
6.
Ans
ß
0
7.
for I
ß
1 to
事件的最大编号
8.
do if I
是插入事件
9.
then Root.Insert(Y_Map.Coord[
事件线段顶点
1]
,
Y_Map.Coord[
事件线段顶点
2])
10.
else Root.Delete(Y_Map.Coord[
事件线段顶点
1]
,
Y_Map.Coord[
事件线段顶点
2])
11.
nowM
ß
Root.M
12.
nowLine
ß
Root.Line
13.
ans
ß
ans + lastLine * 2 * (X_Map[I] – Y_Map[I-1])
14.
ans
ß
ans + |nowM – lastM|
15.
lasM
ß
nowM
16.
lastLine
ß
nowLine
参考论文《IOI98试题PICTURE谈起 陈宏》
 #include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdio.h
>
 #include
<
stdlib.h
>
#include
<
stdlib.h
>

 const
int
maxn
=
5010
;
const
int
maxn
=
5010
;
 //
写一个线段树的过程
//
写一个线段树的过程
 struct
Lines_tree
struct
Lines_tree


 {
{
 Lines_tree
*
lchild,
*
rchild;
Lines_tree
*
lchild,
*
rchild;
 int
m;
//
测度
int
m;
//
测度
 int
cnt;
//
count
int
cnt;
//
count
 int
lines;
//
连续段数
int
lines;
//
连续段数
 int
lbd, rbd;
//
左右端点是否被覆盖
int
lbd, rbd;
//
左右端点是否被覆盖
 int
f, r;
//
左右端点
int
f, r;
//
左右端点
 }
;
}
;
 Lines_tree
*
root;
Lines_tree
*
root;

 struct
rec
struct
rec
 {
int
x, y, x1, y1;}
r[maxn];
{
int
x, y, x1, y1;}
r[maxn];
 struct
Line
struct
Line


 {
{
 int
x, y1, y2;
int
sign;
int
x, y1, y2;
int
sign;

 Line(
int
a,
int
b,
int
c,
int
d):x(a), y1(b), y2(c), sign(d)
Line(
int
a,
int
b,
int
c,
int
d):x(a), y1(b), y2(c), sign(d)
 {}
{}

 Line(
void
):x(
0
),y1(
0
),y2(
0
),sign(
0
)
Line(
void
):x(
0
),y1(
0
),y2(
0
),sign(
0
)
 {}
{}
 }
line[
2
*
maxn
+
10
];
}
line[
2
*
maxn
+
10
];
 int
nr;
int
nr;
 int
ans;
int
ans;

 void
make_tree(
int
a,
int
b, Lines_tree
*
node)
void
make_tree(
int
a,
int
b, Lines_tree
*
node)


 {
{
 node
->
lines
=
0
; node
->
m
=
0
; node
->
cnt
=
0
;
node
->
lines
=
0
; node
->
m
=
0
; node
->
cnt
=
0
;
 node
->
lbd
=
0
; node
->
rbd
=
0
;
node
->
lbd
=
0
; node
->
rbd
=
0
;
 node
->
lchild
=
NULL; node
->
rchild
=
NULL;
node
->
lchild
=
NULL; node
->
rchild
=
NULL;
 node
->
f
=
a; node
->
r
=
b;
node
->
f
=
a; node
->
r
=
b;
 if
(b
-
a
>
1
)
if
(b
-
a
>
1
)


 {
{
 node
->
lchild
=
new
Lines_tree;
node
->
lchild
=
new
Lines_tree;
 make_tree(a, (a
+
b)
/
2
, node
->
lchild);
make_tree(a, (a
+
b)
/
2
, node
->
lchild);
 node
->
rchild
=
new
Lines_tree;
node
->
rchild
=
new
Lines_tree;
 make_tree((a
+
b)
/
2
, b, node
->
rchild);
make_tree((a
+
b)
/
2
, b, node
->
rchild);
 }
}
 }
}

 void
make(
int
a,
int
b)
void
make(
int
a,
int
b)


 {
{
 root
=
new
Lines_tree;
root
=
new
Lines_tree;
 make_tree(a, b, root);
make_tree(a, b, root);
 }
}

 void
update(Lines_tree
*
now)
//
lbd, rbd, m的计算都在这个里面!
void
update(Lines_tree
*
now)
//
lbd, rbd, m的计算都在这个里面!


 {
{
 if
(now
->
cnt
>
0
) now
->
m
=
now
->
r
-
now
->
f;
if
(now
->
cnt
>
0
) now
->
m
=
now
->
r
-
now
->
f;
 else
if
(now
->
r
==
now
->
f
+
1
) now
->
m
=
0
;
else
if
(now
->
r
==
now
->
f
+
1
) now
->
m
=
0
;
 else
now
->
m
=
now
->
lchild
->
m
+
now
->
rchild
->
m;
else
now
->
m
=
now
->
lchild
->
m
+
now
->
rchild
->
m;
 }
}

 void
update2(Lines_tree
*
now)
void
update2(Lines_tree
*
now)


 {
{

 if
(now
->
cnt
>
0
)
if
(now
->
cnt
>
0
)
 { now
->
lbd
=
1
; now
->
rbd
=
1
; now
->
lines
=
1
; }
{ now
->
lbd
=
1
; now
->
rbd
=
1
; now
->
lines
=
1
; }

 else
if
(now
->
f
+
1
==
now
->
r)
else
if
(now
->
f
+
1
==
now
->
r)
 {now
->
lbd
=
0
; now
->
rbd
=
0
; now
->
lines
=
0
;}
{now
->
lbd
=
0
; now
->
rbd
=
0
; now
->
lines
=
0
;}
 else
else


 {
{
 now
->
lbd
=
now
->
lchild
->
lbd; now
->
rbd
=
now
->
rchild
->
rbd;
now
->
lbd
=
now
->
lchild
->
lbd; now
->
rbd
=
now
->
rchild
->
rbd;
 now
->
lines
=
now
->
lchild
->
lines
+
now
->
rchild
->
lines
-
now
->
lchild
->
rbd
*
now
->
rchild
->
lbd;
now
->
lines
=
now
->
lchild
->
lines
+
now
->
rchild
->
lines
-
now
->
lchild
->
rbd
*
now
->
rchild
->
lbd;
 }
}
 }
}

 void
insert(
int
a,
int
b, Lines_tree
*
now)
void
insert(
int
a,
int
b, Lines_tree
*
now)


 {
{
 if
(a
<=
now
->
f
&&
b
>=
now
->
r)
if
(a
<=
now
->
f
&&
b
>=
now
->
r)
 now
->
cnt
++
;
now
->
cnt
++
;
 if
(now
->
r
-
now
->
f
>
1
)
if
(now
->
r
-
now
->
f
>
1
)


 {
{
 if
(a
<
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) insert(a, b, now
->
lchild);
if
(a
<
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) insert(a, b, now
->
lchild);
 if
(b
>
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) insert(a, b, now
->
rchild);
if
(b
>
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) insert(a, b, now
->
rchild);
 }
}
 update(now);
update(now);
 update2(now);
update2(now);
 }
}

 void
del(
int
a,
int
b, Lines_tree
*
now)
void
del(
int
a,
int
b, Lines_tree
*
now)


 {
{
 if
(a
<=
now
->
f
&&
b
>=
now
->
f)
if
(a
<=
now
->
f
&&
b
>=
now
->
f)


 {
{
 if
(a
==
now
->
f) now
->
lbd
=
0
;
if
(a
==
now
->
f) now
->
lbd
=
0
;
 if
(b
==
now
->
r) now
->
rbd
=
0
;
if
(b
==
now
->
r) now
->
rbd
=
0
;
 now
->
cnt
--
;
now
->
cnt
--
;
 }
}
 if
(now
->
r
-
now
->
f
>
1
)
if
(now
->
r
-
now
->
f
>
1
)


 {
{
 if
(a
<
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) del(a, b, now
->
lchild);
if
(a
<
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) del(a, b, now
->
lchild);
 if
(b
>
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) del(a, b, now
->
rchild);
if
(b
>
(now
->
f
+
now
->
r)
/
2
) del(a, b, now
->
rchild);
 }
}
 update(now);
update(now);
 update2(now);
update2(now);
 }
}

 int
cmp(
const
void
*
a,
const
void
*
b)
int
cmp(
const
void
*
a,
const
void
*
b)


 {
{
 return
(
*
(Line
*
)a).x
-
(
*
(Line
*
)b).x;
//
这里不要写成->
return
(
*
(Line
*
)a).x
-
(
*
(Line
*
)b).x;
//
这里不要写成->
 }
}

 void
init()
void
init()


 {
{
 //
initiation
//
initiation
 //
input
//
input
 int
i;
int
i;
 scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
nr);
scanf(
"
%d
"
,
&
nr);
 for
(i
=
0
; i
<
nr; i
++
)
for
(i
=
0
; i
<
nr; i
++
)


 {
{
 scanf(
"
%d%d%d%d
"
,
&
r[i].x,
&
r[i].y,
&
r[i].x1,
&
r[i].y1);
scanf(
"
%d%d%d%d
"
,
&
r[i].x,
&
r[i].y,
&
r[i].x1,
&
r[i].y1);
 line[
2
*
i]
=
Line(r[i].x, r[i].y, r[i].y1,
0
);
line[
2
*
i]
=
Line(r[i].x, r[i].y, r[i].y1,
0
);
 line[
2
*
i
+
1
]
=
Line(r[i].x1, r[i].y, r[i].y1,
1
);
line[
2
*
i
+
1
]
=
Line(r[i].x1, r[i].y, r[i].y1,
1
);
 }
}
 qsort(line, nr
*
2
,
sizeof
(line[
0
]), cmp);
qsort(line, nr
*
2
,
sizeof
(line[
0
]), cmp);
 //
pretreatment
//
pretreatment
 }
}

 void
work()
void
work()


 {
{
 int
nowM
=
0
;
int
nowM
=
0
;
 int
nowLine
=
0
;
int
nowLine
=
0
;
 int
lastM
=
0
;
int
lastM
=
0
;
 int
lastLine
=
0
;
int
lastLine
=
0
;
 int
i;
int
i;
 for
(i
=
0
; i
<
nr
*
2
; i
++
)
for
(i
=
0
; i
<
nr
*
2
; i
++
)


 {
{
 if
(line[i].sign
==
0
)
if
(line[i].sign
==
0
)
 insert(line[i].y1, line[i].y2, root);
insert(line[i].y1, line[i].y2, root);
 else
del(line[i].y1, line[i].y2, root);
else
del(line[i].y1, line[i].y2, root);
 nowM
=
root
->
m;
nowM
=
root
->
m;
 nowLine
=
root
->
lines;
nowLine
=
root
->
lines;
 ans
+=
lastLine
*
2
*
(line[i].x
-
line[i
-
1
].x);
ans
+=
lastLine
*
2
*
(line[i].x
-
line[i
-
1
].x);
 ans
+=
abs(nowM
-
lastM);
ans
+=
abs(nowM
-
lastM);
 lastM
=
nowM;
lastM
=
nowM;
 lastLine
=
nowLine;
lastLine
=
nowLine;
 }
}
 }
}

 void
output()
void
output()


 {
{
 printf(
"
%d\n
"
, ans);
printf(
"
%d\n
"
, ans);
 }
}

 int
main()
int
main()


 {
{
 //
freopen("t.in", "r", stdin);
//
freopen("t.in", "r", stdin);
 make(
-
10000
,
10000
);
make(
-
10000
,
10000
);
 init();
init();
 work();
work();
 output();
output();
 return
0
;
return
0
;
 }
}