前段时间用C#做网站,用到了大量数据库相关的东西。网站采用3层结构,即数据访问层(Data Access Layer),业务逻辑层(Business Logic Layer),页面表现层().做了一段时间,发现向数据访问层和业务逻辑层加入新的类,数据库的表结构改了,还要对应的修改数据访问层和业务逻辑层的代码,这个工作很是繁琐,无聊,而且容易出错。做了几次之后就想有什么办法可以让机器自动完成呢?
联想到以前看过Java似乎有个Hibernate,可以很方便的实现对象关系映射(ORM),即自动的从数据库的表生成对应的对象,.Net也应该有类似的功能吧。于是找啊找,发现了很多.Net的ORM工具,不过都有缺点,就是代码得依赖于那些ORM工具,我希望能够让机器按我的要求生成我自己的代码,这样就更加灵活了。
于是乎,发现了CodeSmith和MyGeneration,CodeSmith是 网上传的.NET 程序员十种必备工具之一,我们写代码时,经常需要重复完成某些特定的任务,例如编写数据访问代码或者生成自定义集合。我们可以用CodeSmith编写模板自动完成这些任务,从而不仅提高工作效率,而且能够自动完成那些最为乏味的任务。可惜,CodeSmith是需要注册的,试用版只能用15天。而MyGeneration基本上和CodeSmith的功能差不多哦,但是他是开源的。我选软件的原则是能开源免费的就用,实在没替代了才选那些需要注册的,有版权的软件。所以就选MyGeneration了。
用过一段时间后感觉MyGeneration主要是为了自动生成数据库相关的代码的,可能C#用得比较多,其实我们可以用它生成任何代码,C++,JavaScript...而且还不仅仅局限于数据库,其他方面的代码也可以用MyGeneration自动生成。比如我们经常用数据访问层和业务逻辑层,用MyGeneration就可以自动生成这些代码,我们可以不用手动写代码了。比如数据访问层,我们需要调用一个存储过程,用MyGeneration我们只需要选择生成存储过程代码的模板,执行一下脚本,然后在界面上选择数据库上某个存储过程,然后就自动生成了数据库访问代码,整个过程只需要点几下鼠标,代码就自动生成了。这对于需要大量操作数据库的程序员来说,效率是多大的提升啊。
废话少说,还是来点实在的吧。首先声明,我的MyGeneration版本是:1.3.0.3
安装完MyGeneration后,第一次启动会要求进行一些数据库相关的配置。如图:
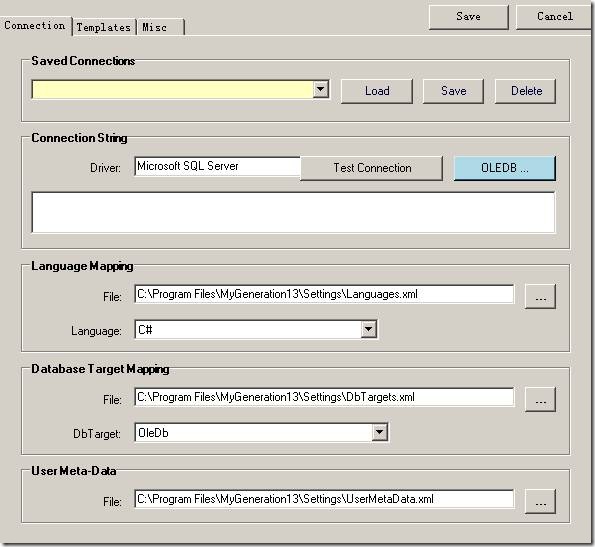
ConnectionString: 就是指定连接哪个数据库了,填好这个就可以点确定了。
下面来看一看其他的项都是什么。
Language Mapping:就是指定数据库和对象基本类型的映射关系。让我们打开Languages.xml文件看一下吧:
1. <Language From="SQL" To="C#">
2. <Type From="bigint" To="long" />
3. <Type From="binary" To="object" />
4. <Type From="bit" To="bool" />
5. <Type From="char" To="string" />
6. <Type From="datetime" To="DateTime" />
7. <Type From="decimal" To="decimal" />
8. <Type From="float" To="double" />
9. <Type From="image" To="byte[]" />
10. <Type From="int" To="int" />
11. <Type From="money" To="decimal" />
12. <Type From="nchar" To="string" />
13. <Type From="ntext" To="string" />
14. <Type From="numeric" To="decimal" />
15. <Type From="nvarchar" To="string" />
16. <Type From="real" To="float" />
17. <Type From="smalldatetime" To="DateTime" />
18. <Type From="smallint" To="short" />
19. <Type From="smallmoney" To="decimal" />
20. <Type From="text" To="string" />
21. <Type From="timestamp" To="byte[]" />
22. <Type From="tinyint" To="byte" />
23. <Type From="uniqueidentifier" To="Guid" />
24. <Type From="varbinary" To="byte[]" />
25. <Type From="varchar" To="string" />
26. <Type From="xml" To="string" />
27. <Type From="sql_variant" To="object" />
28. </Language>
这是里面的一段内容,很明显,是数据库SQL的字段转到C#是什么类型,里面没有C++的,假如我们要让它支持C++的话,需要在这里加入SQL到C++的类型转换。
Database Target Mapping:先看里面的内容吧:
1. <DbTarget From="ACCESS" To="DAO">
2. <Type From="Text" To="DAO.dbText" />
3. <Type From="Memo" To="DAO.dbMemo" />
4. <Type From="DateTime" To="DAO.dbDate" />
5. <Type From="Currency" To="DAO.dbCurrency" />
6. <Type From="Yes/No" To="DAO.dbBoolean" />
7. <Type From="OLE Object" To="DAO.dbLongBinary" />
8. <Type From="Hyperlink" To="DAO.dbMemo" />
9. <Type From="Double" To="DAO.dbDouble" />
10. <Type From="Replication ID" To="DAO.dbGUID" />
11. <Type From="Long" To="DAO.dbLong" />
12. <Type From="Single" To="DAO.dbSingle" />
13. <Type From="Decimal" To="DAO.dbDecimal" />
14. <Type From="Byte" To="DAO.dbByte" />
15. <Type From="Integer" To="DAO.dbInteger" />
16. </DbTarget>
呵呵,一目了然,就是Access数据库用DAO的方式访问,数据库的列的类型对应的DAO里是什么类型。
UseMetaData目前没什么用。
看看MyGeneration的界面吧:
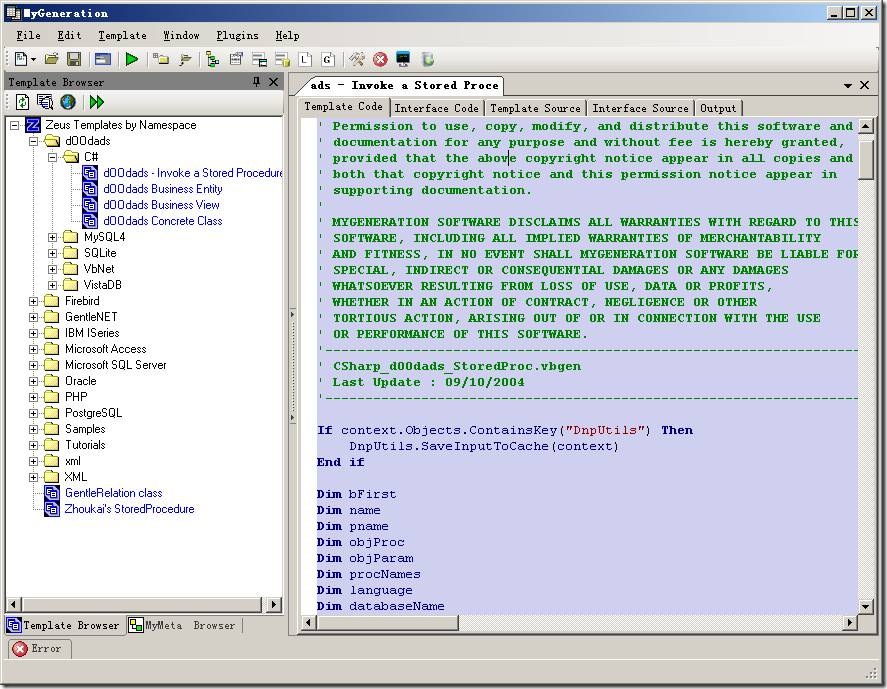
Template Browser 面板 列出了一些模板,这是自动生成代码需要用到的模板。安装的时候会自己带很多模板。
MyMeta Browser则列出了当前连接的数据库上有些什么库,表,存储过程。
工作区则是具体模板对应的代码。
先让我们体验一下吧。
展开Template Browser面板下"d00dads - C#", 双击 “d00dads - Invoke a Stored Procedure", 让工作区显示其内容,
然后点击工具栏上的 "Execute" 按钮,如图红框所示:

弹出对话框,如图:
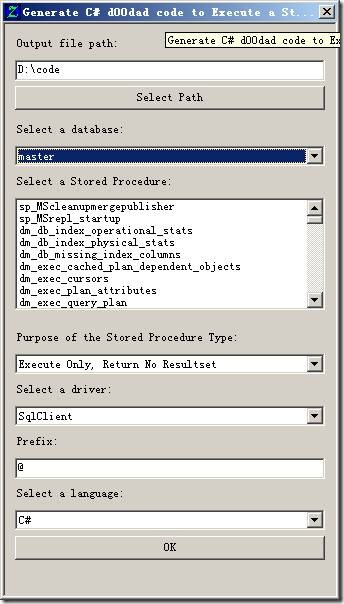
选择数据库,存储过程,存储过程类型,点确定(OK)。
然后可以看到工作区 Output 里输出了代码了。例如:
1. using System.Data;
2. using System.Collections.Specialized;
3. using System.Data.SqlClient;
4.
5.
6.
7. public virtual void dm_exec_cursors (int spid)
8. {
9. ListDictionary parameters = new ListDictionary();
10.
11. parameters.Add( new SqlParameter("@spid", SqlDbType.Int, 0), spid);
12. LoadFromSqlNoExec("dm_exec_cursors", parameters);
13. }
这就是MyGeneration自动获取了存储过程的输入参数,然后在代码里构造相应的参数,然后生成的代码。
这只是MyGeneration自带的模板生成的,大家可以试一试其他的模板的效果。
里面有自动根据表结构生成BLL的类......看下效果:
1. /*
2. '===============================================================================
3. ' Generated From - CSharp_dOOdads_BusinessEntity.vbgen
4. '
5. ' ** IMPORTANT **
6. ' How to Generate your stored procedures:
7. '
8. ' SQL = SQL_StoredProcs.vbgen
9. ' ACCESS = Access_StoredProcs.vbgen
10. ' ORACLE = Oracle_StoredProcs.vbgen
11. ' FIREBIRD = FirebirdStoredProcs.vbgen
12. ' POSTGRESQL = PostgreSQL_StoredProcs.vbgen
13. '
14. ' The supporting base class OleDbEntity is in the Architecture directory in "dOOdads".
15. '
16. ' This object is 'abstract' which means you need to inherit from it to be able
17. ' to instantiate it. This is very easilly done. You can override properties and
18. ' methods in your derived class, this allows you to regenerate this class at any
19. ' time and not worry about overwriting custom code.
20. '
21. ' NEVER EDIT THIS FILE.
22. '
23. ' public class YourObject : _YourObject
24. ' {
25. '
26. ' }
27. '
28. '===============================================================================
29. */
30. // Generated by MyGeneration Version # (1.3.0.3)
31. using System;
32. using System.Data;
33. using System.Data.OleDb;
34. using System.Collections;
35. using System.Collections.Specialized;
36. using MyGeneration.dOOdads;
37. namespace Your.Namespace
38. {
39. public abstract class _Users : OleDbEntity
40. {
41. public _Users()
42. {
43. this.QuerySource = "Users";
44. this.MappingName = "Users";
45. }
46. //=================================================================
47. // public Overrides void AddNew()
48. //=================================================================
49. //
50. //=================================================================
51. public override void AddNew()
52. {
53. base.AddNew();
54.
55. }
56.
57.
58. public override string GetAutoKeyColumn()
59. {
60. return "ID";
61. }
62. public override void FlushData()
63. {
64. this._whereClause = null;
65. this._aggregateClause = null;
66. base.FlushData();
67. }
68.
69. //=================================================================
70. // public Function LoadAll() As Boolean
71. //=================================================================
72. // Loads all of the records in the database, and sets the currentRow to the first row
73. //=================================================================
74. public bool LoadAll()
75. {
76. ListDictionary parameters = null;
77.
78. return base.LoadFromSql("[" + this.SchemaStoredProcedure + "proc_UsersLoadAll]", parameters);
79. }
80.
81. //=================================================================
82. // public Overridable Function LoadByPrimaryKey() As Boolean
83. //=================================================================
84. // Loads a single row of via the primary key
85. //=================================================================
86. public virtual bool LoadByPrimaryKey()
87. {
88. ListDictionary parameters = new ListDictionary();
89.
90. return base.LoadFromSql("[" + this.SchemaStoredProcedure + "proc_UsersLoadByPrimaryKey]", parameters);
91. }
92.
93. #region Parameters
94. protected class Parameters
95. {
96.
97. public static OleDbParameter ID
98. {
99. get
100. {
101. return new OleDbParameter("@ID", OleDbType.Integer, 0);
102. }
103. }
104.
105. public static OleDbParameter Alias
106. {
107. get
108. {
109. return new OleDbParameter("@Alias", OleDbType.VarChar, 2147483647);
110. }
111. }
112.
113. }
114. #endregion
115.
116. #region ColumnNames
117. public class ColumnNames
118. {
119. public const string ID = "ID";
120. public const string Alias = "Alias";
121. static public string ToPropertyName(string columnName)
122. {
123. if(ht == null)
124. {
125. ht = new Hashtable();
126.
127. ht[ID] = _Users.PropertyNames.ID;
128. ht[Alias] = _Users.PropertyNames.Alias;
129. }
130. return (string)ht[columnName];
131. }
132. static private Hashtable ht = null;
133. }
134. #endregion
135.
136. #region PropertyNames
137. public class PropertyNames
138. {
139. public const string ID = "ID";
140. public const string Alias = "Alias";
141. static public string ToColumnName(string propertyName)
142. {
143. if(ht == null)
144. {
145. ht = new Hashtable();
146.
147. ht[ID] = _Users.ColumnNames.ID;
148. ht[Alias] = _Users.ColumnNames.Alias;
149. }
150. return (string)ht[propertyName];
151. }
152. static private Hashtable ht = null;
153. }
154. #endregion
155. #region StringPropertyNames
156. public class StringPropertyNames
157. {
158. public const string ID = "s_ID";
159. public const string Alias = "s_Alias";
160. }
161. #endregion
162.
163. #region Properties
164.
165. public virtual Integer ID
166. {
167. get
168. {
169. return base.GetInteger(ColumnNames.ID);
170. }
171. set
172. {
173. base.SetInteger(ColumnNames.ID, value);
174. }
175. }
176. public virtual String Alias
177. {
178. get
179. {
180. return base.GetString(ColumnNames.Alias);
181. }
182. set
183. {
184. base.SetString(ColumnNames.Alias, value);
185. }
186. }
187. #endregion
188.
189. #region String Properties
190.
191. public virtual string s_ID
192. {
193. get
194. {
195. return this.IsColumnNull(ColumnNames.ID) ? string.Empty : base.GetIntegerAsString(ColumnNames.ID);
196. }
197. set
198. {
199. if(string.Empty == value)
200. this.SetColumnNull(ColumnNames.ID);
201. else
202. this.ID = base.SetIntegerAsString(ColumnNames.ID, value);
203. }
204. }
205. public virtual string s_Alias
206. {
207. get
208. {
209. return this.IsColumnNull(ColumnNames.Alias) ? string.Empty : base.GetStringAsString(ColumnNames.Alias);
210. }
211. set
212. {
213. if(string.Empty == value)
214. this.SetColumnNull(ColumnNames.Alias);
215. else
216. this.Alias = base.SetStringAsString(ColumnNames.Alias, value);
217. }
218. }
219. #endregion
220.
221.
222. private AggregateClause _aggregateClause = null;
223. #endregion
224.
225. protected override IDbCommand GetInsertCommand()
226. {
227.
228. OleDbCommand cmd = new OleDbCommand();
229. cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
230. cmd.CommandText = "[" + this.SchemaStoredProcedure + "proc_UsersInsert]";
231.
232. CreateParameters(cmd);
233.
234. return cmd;
235. }
236.
237. protected override IDbCommand GetUpdateCommand()
238. {
239.
240. OleDbCommand cmd = new OleDbCommand();
241. cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
242. cmd.CommandText = "[" + this.SchemaStoredProcedure + "proc_UsersUpdate]";
243.
244. CreateParameters(cmd);
245.
246. return cmd;
247. }
248.
249. protected override IDbCommand GetDeleteCommand()
250. {
251.
252. OleDbCommand cmd = new OleDbCommand();
253. cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
254. cmd.CommandText = "[" + this.SchemaStoredProcedure + "proc_UsersDelete]";
255.
256. OleDbParameter p;
257.
258. return cmd;
259. }
260.
261. private IDbCommand CreateParameters(OleDbCommand cmd)
262. {
263. OleDbParameter p;
264.
265. p = cmd.Parameters.Add(Parameters.ID);
266. p.SourceColumn = ColumnNames.ID;
267. p.SourceVersion = DataRowVersion.Current;
268. p = cmd.Parameters.Add(Parameters.Alias);
269. p.SourceColumn = ColumnNames.Alias;
270. p.SourceVersion = DataRowVersion.Current;
271. return cmd;
272. }
273. }
274. }
这就是自动获得表结构,然后从字段映射成类里面的成员,并且还有一些插入,更新,删除的代码。
当然自带的模板生成的代码不一定符合我们的需要,但是我们可以根据需要自己写一些模板来生成符合自己需要的代码,这也是非常容易的事,欲知如何实现,请看下回文章。
前面一篇文章讲了如何使用MyGeneration自带的模板来生成代码,现在开始讲如何自己写模板吧。
请先阅读我的前一篇MyGeneration的文章,在阅读本文,地址如下:
代码自动生成工具MyGeneration之一
要用MyGeneration就必须要和各种模板打交道。我们可以使用别人写的模板来完成我们说需要的功能,但是别人写的模板不一定最适合我们的项目里面的代码,所以有时也需要自己写一些模板来使用。下面就讲如何编写模板吧
通过File – New 菜单我们可以看到,MyGeneration支持的模板包括C#,VB.Net,Jscript,VBScript,我们可以选则自己擅长的语言来写模板。
最简单的办法就是找一个功能差不多的模板,然后在这个模板的基础上进行修改了。这个也是初学的办法,可以快速的了解如何实现特定的功能。
当然,我们要自己建一个模板,以C#模板为例吧。
假如我们要自己生成一个数据库的数据表所对应的BLL类。
在UI界面上需要我们选择是哪个数据库,那张数据表。最后生成BLL类。
选择菜单 File – New – C# Zeus Template,就打开了一个新的工作区,该模板的代码是C#的。工作区有5个Tab页,Template Code, Interface Code, Template Source, Interface Source, Output.如下图所示:
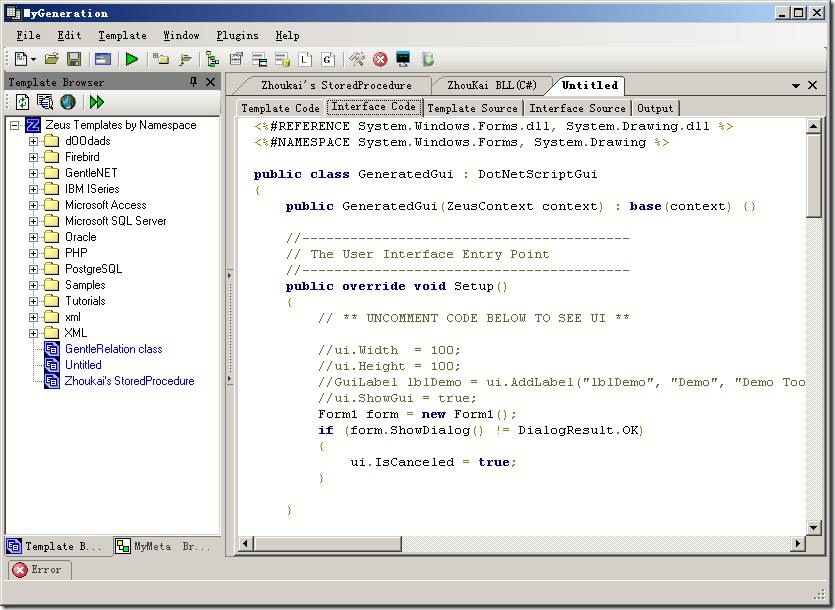
这些都干什么的呢?
这得了解一下MyGeneration内部的结构了。MyGeneration通过脚本引擎执行Template Code和Interface Code中的脚本,生成Template Source和Interface Source的代码,然后执行Interface Source显示用户界面,再执行Template Source,输出结果到Output中。
由此可见,Template Source是根据Template code生成的Interface Source是根据Interface code生成的,他们是不可编辑的。我们能用代码控制的就是Template code和Interface code了。而Interface code是主要和用户界面有关的,Template code则主要控制执行完用户界面的代码后如何输出到Output。
默认生成的Interface Code如下所示:
1. public class GeneratedGui : DotNetScriptGui
2. {
3. public GeneratedGui(ZeusContext context) : base(context) {}
4.
5.
6.
7. public override void Setup()
8. {
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14. }
15. }
Interface Code中编写用户界面有两种方法,一种是采用MyGeneration提供的GUI库,另外一种则是完全采用C#本身的界面代码编写。下图显示了MyGeneration的GUI库的帮助,从中可以看到其提供的各种GUI类。
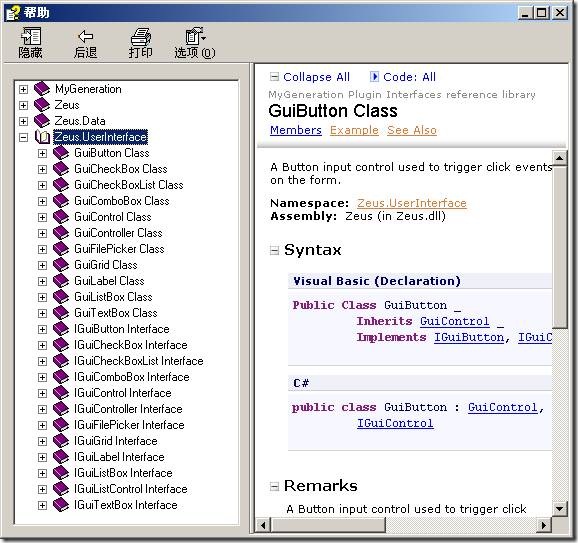
我可不想为了写个模板去学习使用MyGeneration的GUI库,这可加大了学习成本,而且所有界面都得用代码一行一行的写出来,多麻烦啊。如果能像C#那样,直接用鼠标拖拽控件就能搞定界面UI就好了。
其实,我们是可以用C#的界面库的。我的方法是这样的。先自己用VS新建一个Windows的工程,然后在窗体上摆好控件,设置各种控件的属性,并且把需要用的各种控件的事件都让VS的IDE生成好。然后把这个窗体的代码直接拷贝到MyGeneration的Interface code里面去。注意,假设我们的窗体叫Form1,我们需要拷贝Form1.Designer.cs 和Form1.cs两个文件中的代码。
然后在Interface Code最前面加入下面两行:
1. <%#REFERENCE System.Windows.Forms.dll, System.Drawing.dll %>
2. <%#NAMESPACE System.Windows.Forms, System.Drawing %>
在Setup()函数中写:
1. Form1 form = new Form1();
2. if (form.ShowDialog() != DialogResult.OK)
3. {
4. ui.IsCanceled = true;
5. }
最后所形成的Interface Code的代码如下所示:
1. <%#REFERENCE System.Windows.Forms.dll, System.Drawing.dll %>
2. <%#NAMESPACE System.Windows.Forms, System.Drawing %>
3. public class GeneratedGui : DotNetScriptGui
4. {
5. public GeneratedGui(ZeusContext context) : base(context) {}
6.
7.
8.
9. public override void Setup()
10. {
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16. Form1 form = new Form1();
17. if (form.ShowDialog() != DialogResult.OK)
18. {
19. ui.IsCanceled = true;
20. }
21. }
22. }
23. public class Form1:Form
24. {
25.
26.
27.
28. private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
29.
30.
31.
32.
33. protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
34. {
35. if (disposing && (components != null))
36. {
37. components.Dispose();
38. }
39. base.Dispose(disposing);
40. }
41. #region Windows Form Designer generated code
42.
43.
44.
45.
46. private void InitializeComponent()
47. {
48. this.comboBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox();
49. this.listBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ListBox();
50. this.button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
51. this.SuspendLayout();
52.
53.
54.
55. this.comboBox1.FormattingEnabled = true;
56. this.comboBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(22, 24);
57. this.comboBox1.Name = "comboBox1";
58. this.comboBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(233, 20);
59. this.comboBox1.TabIndex = 0;
60. this.comboBox1.SelectedIndexChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged);
61.
62.
63.
64. this.listBox1.FormattingEnabled = true;
65. this.listBox1.ItemHeight = 12;
66. this.listBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(22, 50);
67. this.listBox1.Name = "listBox1";
68. this.listBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(233, 196);
69. this.listBox1.TabIndex = 1;
70.
71.
72.
73. this.button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(180, 252);
74. this.button1.Name = "button1";
75. this.button1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23);
76. this.button1.TabIndex = 2;
77. this.button1.Text = "OK";
78. this.button1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true;
79.
80.
81.
82. this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 12F);
83. this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;
84. this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(284, 293);
85. this.Controls.Add(this.button1);
86. this.Controls.Add(this.listBox1);
87. this.Controls.Add(this.comboBox1);
88. this.MaximizeBox = false;
89. this.MinimizeBox = false;
90. this.Name = "Form1";
91. this.Text = "ZhouKai's BLL Class";
92. this.Load += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Load);
93. this.ResumeLayout(false);
94. }
95. #endregion
96. private System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox comboBox1;
97. private System.Windows.Forms.ListBox listBox1;
98. private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1;
99.
100.
101. public Form1()
102. {
103. InitializeComponent();
104. }
105. private void comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
106. {
107. }
108. private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
109. {
110. }
111. }
执行一下该模板,看有什么效果吧?是不是看到了如下的UI呢?
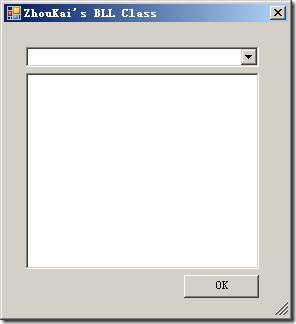
呵呵,这个只有UI,还没有数据,下次该讲如何给这个UI加上他说需要的数据啦。比如如何获得数据库的各个数据表啊之内的,然后如何输出自己说需要BLL代码和存储过程的代码啦。
呵呵,发现竟然有网站转载我的文章了,心里小小高兴一下,说明写的东西还是有点用的。
前面讲了MyGeneration的使用,以及如何自己写模板显示UI,现在开始讲如何将数据库的信息显示到UI上。
在MyGeneraion脚本系统中,有一个全局变量,叫做MyMeta,他是dbRoot类型的。通过这个全局变量,我们可以获得数据库相关的信息。这个变量在Interface Code 和Template Code中都可以使用。
从上节代码来看,我们建立Form窗口的时候,就把这个变量给传给了Form窗口
如下代码所示:
MyForm form = new MyForm(MyMeta, input);
那么dbRoot类型的MyMeta变量都有哪些功能,有哪些函数,属性可以使用呢?
我们可以查找帮助,通过MyGeneration菜单 “File – Help – MyMeta API Reference”可以打开其帮助,里面有dbRoot的详细介绍,如下图所示:
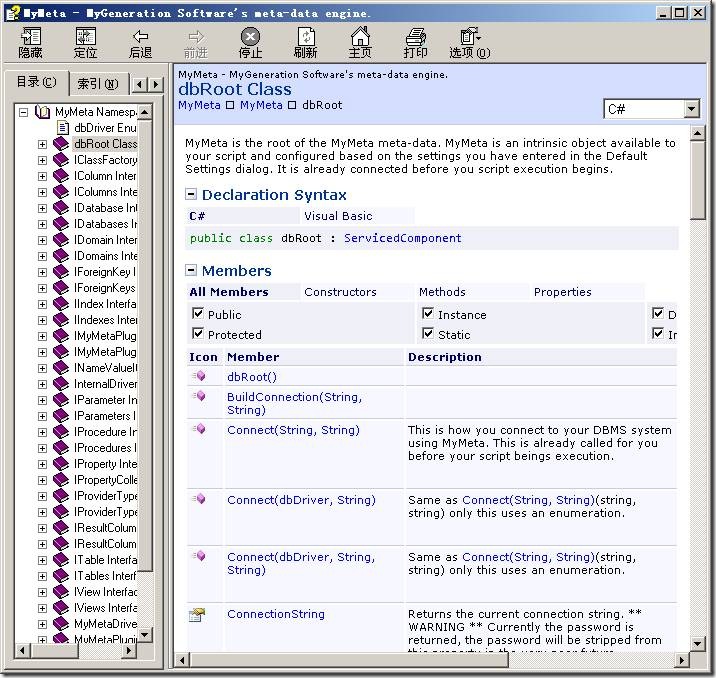
大概看一下API,然后我们就可以修改我们的模板了,将其修改如下:
1. private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
2. {
3. //获取数据库,传给ComboBox
4. comboBox1.DataSource = this.myMeta.Databases;
5. //ComboBox显示数据库名
6. this.comboBox1.DisplayMember = "Name";
7.
8. if(this.myMeta.DefaultDatabase != null)
9. {
10. //选中默认的数据库
11. this.comboBox1.SelectedIndex = this.comboBox1.FindStringExact(this.myMeta.DefaultDatabase.Name);
12. //通过IDatabase 的Tables属性取得数据库里面所有的数据表
13. //作为数据源传给ListBox
14. this.listBox1.DataSource = this.myMeta.DefaultDatabase.Tables;
15. //ListBox显示数据表的名字
16. this.listBox1.DisplayMember = "Name";
17. }
18. }
19.
就算没有注释,这代码也很好懂吧。
呵呵,由此可见,我们可以通过MyMeta得到IDataBases,然后获得ITable,在通过ITable
获得数据表的信息……反正呢,照这条线找下去,基本上数据库里有哪些表,表里有哪些字段,有哪些存储过程,任何信息都可以很容易的得到。当然了,在自己写模板之前,最好先大概看一下“MyMeta API Reference”,这样就写模板就会更得心应手了。
下面接下来看Form点击OK之后的代码吧
1. private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
2. {
3. IDatabase database = this.comboBox1.SelectedValue as IDatabase;
4. ITable table = this.listBox1.SelectedValue as ITable;
5.
6. this.zeusInput["databaseName"] = database.Name;
7. this.zeusInput["tableName"] = table.Name;
8.
9. this.DialogResult = DialogResult.OK;
10. this.Close();
11. }
这段代码得重点讲一下了,因为Interface Code是关于UI的,那么UI执行完了之后,我们就需要用到Template Code了,那么Template Code和Interface Code是如何联系在一起的呢?我们在Template Code里面如何知道Interface Code显示的UI中用户输入了什么,选择了什么?
这用到了MyGeneration的一个非常重要的类IZeusInput。
改接口的详细信息请看帮助 “File – help – Zeus API Reference”。
在这里我们简单的把UI上选中的数据库的名字和数据表的名字存在了IZeusInput变量中。大家注意看下Form的IZeumInput是如何来的吧。
这样,我们就完成了该模板的Interface Code的代码,最后形成的Interface Code就如下所示:
1. <%#REFERENCE System.Windows.Forms.dll, System.Drawing.dll %>
2. <%#NAMESPACE System.Windows.Forms, System.Drawing %>
3. public class GeneratedGui : DotNetScriptGui
4. {
5. public GeneratedGui(ZeusContext context) : base(context) {}
6. //-----------------------------------------
7. // The User Interface Entry Point
8. //-----------------------------------------
9. public override void Setup()
10. {
11. // ** UNCOMMENT CODE BELOW TO SEE UI **
12. //ui.Width = 100;
13. //ui.Height = 100;
14. //GuiLabel lblDemo = ui.AddLabel("lblDemo", "Demo", "Demo Tooltip");
15. //ui.ShowGui = true;
16. Form1 form = new Form1(MyMeta, input);
17. if (form.ShowDialog() != DialogResult.OK)
18. {
19. ui.IsCanceled = true;
20. }
21. }
22. }
23. public class Form1:Form
24. {
25. /// <summary>
26. /// Required designer variable.
27. /// </summary>
28. private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
29. /// <summary>
30. /// Clean up any resources being used.
31. /// </summary>
32. /// <param name="disposing">true if managed resources should be disposed; otherwise, false.</param>
33. protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
34. {
35. if (disposing && (components != null))
36. {
37. components.Dispose();
38. }
39. base.Dispose(disposing);
40. }
41. #region Windows Form Designer generated code
42. /// <summary>
43. /// Required method for Designer support - do not modify
44. /// the contents of this method with the code editor.
45. /// </summary>
46. private void InitializeComponent()
47. {
48. this.comboBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox();
49. this.listBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ListBox();
50. this.button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
51. this.SuspendLayout();
52. //
53. // comboBox1
54. //
55. this.comboBox1.FormattingEnabled = true;
56. this.comboBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(22, 24);
57. this.comboBox1.Name = "comboBox1";
58. this.comboBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(233, 20);
59. this.comboBox1.TabIndex = 0;
60. this.comboBox1.SelectedIndexChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged);
61. //
62. // listBox1
63. //
64. this.listBox1.FormattingEnabled = true;
65. this.listBox1.ItemHeight = 12;
66. this.listBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(22, 50);
67. this.listBox1.Name = "listBox1";
68. this.listBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(233, 196);
69. this.listBox1.TabIndex = 1;
70. //
71. // button1
72. //
73. this.button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(180, 252);
74. this.button1.Name = "button1";
75. this.button1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(75, 23);
76. this.button1.TabIndex = 2;
77. this.button1.Text = "OK";
78. this.button1.UseVisualStyleBackColor = true;
79. this.button1.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.button1_Click);
80. //
81. // Form1
82. //
83. this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 12F);
84. this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;
85. this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(284, 293);
86. this.Controls.Add(this.button1);
87. this.Controls.Add(this.listBox1);
88. this.Controls.Add(this.comboBox1);
89. this.MaximizeBox = false;
90. this.MinimizeBox = false;
91. this.Name = "Form1";
92. this.Text = "ZhouKai's BLL Class";
93. this.Load += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Load);
94. this.ResumeLayout(false);
95. }
96. #endregion
97. private System.Windows.Forms.ComboBox comboBox1;
98. private System.Windows.Forms.ListBox listBox1;
99. private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1;
100.
101.
102. private dbRoot myMeta;
103. private IZeusInput zeusInput;
104. public Form1(dbRoot myMeta, IZeusInput zeusInput)
105. {
106. this.myMeta = myMeta;
107. this.zeusInput = zeusInput;
108.
109. InitializeComponent();
110. }
111. private void comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
112. {
113. IDatabase database = this.comboBox1.SelectedValue as IDatabase;
114. if(database != null)
115. {
116. this.listBox1.DataSource = database.Tables;
117. this.listBox1.DisplayMember = "Name";
118. }
119. }
120. private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
121. {
122. //获取数据库,传给ComboBox
123. comboBox1.DataSource = this.myMeta.Databases;
124. //ComboBox显示数据库名
125. this.comboBox1.DisplayMember = "Name";
126.
127. if(this.myMeta.DefaultDatabase != null)
128. {
129. //选中默认的数据库
130. this.comboBox1.SelectedIndex = this.comboBox1.FindStringExact(this.myMeta.DefaultDatabase.Name);
131. //通过IDatabase 的Tables属性取得数据库里面所有的数据表
132. //作为数据源传给ListBox
133. this.listBox1.DataSource = this.myMeta.DefaultDatabase.Tables;
134. //ListBox显示数据表的名字
135. this.listBox1.DisplayMember = "Name";
136. }
137. }
138.
139. private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
140. {
141. IDatabase database = this.comboBox1.SelectedValue as IDatabase;
142. ITable table = this.listBox1.SelectedValue as ITable;
143.
144. this.zeusInput["databaseName"] = database.Name;
145. this.zeusInput["tableName"] = table.Name;
146.
147. this.DialogResult = DialogResult.OK;
148. this.Close();
149. }
150. }
下面来看Template Code如何写吧。目前的模板默认的Template Code如下所示:
1. <%
2. public class GeneratedTemplate : DotNetScriptTemplate
3. {
4. public GeneratedTemplate(ZeusContext context) : base(context) {}
5. //---------------------------------------------------
6. // Render() is where you want to write your logic
7. //---------------------------------------------------
8. public override void Render()
9. {
10. %>
11. You can toggle in out of script like this
12. <%
13. output.writeln("Hello world.");
14. }
15. }
16. %>
C# Template Code的语法和Asp的语法十分的类似<%=%>表示绑定某一个字段或属性
<%%>表示脚本段,我们可以在这里写符合C#语法的任何语句
其他的内容不进行解析直接用output写到最后的结果里
修改Template Code,改成如下所示:
1. <%
2. public class GeneratedTemplate : DotNetScriptTemplate
3. {
4. public GeneratedTemplate(ZeusContext context) : base(context) {}
5. public override void Render()
6. {
7. //设置输出语言...
8. MyMeta.Language = "C#";
9. MyMeta.DbTarget = "SQLClient";
10. //获得执行完UI后,我们说选中的数据库名,数据表名
11. string databaseName = input["databaseName"].ToString();
12. string tableName = input["tableName"].ToString();
13.
14. IDatabase database = MyMeta.Databases[databaseName];
15. //获得数据表的接口
16. ITable table = database.Tables[tableName];
17.
18. %>
19.
20. namespace BLL
21. {
22. using System;
23. using System.Data;
24.
25. using System.Collections;
26. using System.Collections.Generic;
27.
28. <%
29. //数据表的名称作为BLL类的类名
30. output.writeln(" public partial class " + tableName );
31. output.writeln(" { ");
32.
33. //遍历数据表中所有字段
34. foreach (IColumn column in table.Columns)
35. {
36. //将字段名第一个字母转为小写
37. string tmpColumnName = DnpUtils.SetCamelCase(column.Name);
38. output.writeln(" private " + column.LanguageType + " _" + tmpColumnName + ";");
39. output.writeln(" public " + column.LanguageType + " " + column.Name);
40. output.writeln(" {");
41. output.writeln(" get { return _" + tmpColumnName + "; }");
42. output.writeln(" set { _" + tmpColumnName + " = value; }");
43. output.writeln(" }");
44. output.writeln("");
45. }
46. output.writeln(" } ");
47. output.writeln("}");
48. }
49. }
50. %>
这代码也非常简单,基本不用解释都能看懂,不用几分钟就能自己写出来了。
运行一下该模板,看下是不是类似有如下输出呢?
1. namespace BLL
2. {
3. using System;
4. using System.Data;
5.
6. public partial class User
7. {
8. private int _id;
9. public int ID
10. {
11. get { return _id; }
12. set { _id = value; }
13. }
14. private string _userName;
15. public string UserName
16. {
17. get { return _userName; }
18. set { _userName = value; }
19. }
20. }
21. }
好了,最简单的一个生成BLL类的模板就完成了。
本来还想写下如何用MyGeneration来生成执行存储过程的函数,如何用MyGeneration来生成测试存储过程函数的代码的。我觉得完成了这个模板,基本上就可以自己查找MyGeneration的帮助中的API完成这些了,应该不用继续下去了。
继续意淫一下,假如写数据库相关的程序,有了MyGeneration,我们的工作就简单多了,我们可以自己写模板,自动生成BLL类,DAL代码,自动生成测试代码……多棒啊