3. 分箱管理
bin的英文含义是”箱柜“,当我们谈到bin,是指某个双向链表的头节点,该链表的成员节点存放着某一特定范围size的空闲chunk。通过size,我们可以快速的定位bin index,然后遍历其指向的链表,寻找合适的chunk进行分配,或者将释放的chunk插入到链表中合适的地方。
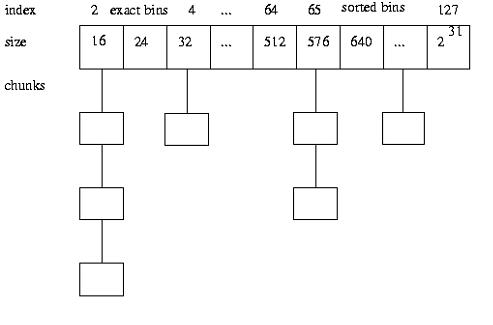
图6
程序定义了一个全局静态数组av_[]存放每种bin的头节点,
typedef struct malloc_chunk* mbinptr;
static mbinptr av_[128 * 2 + 2]
数组类型mbinptr是一个指针,大小为4个字节,数组大小为(128×2+2)*4 = 1032字节,
这就引出一个问题,既然存放头节点,节点类型为malloc_chunk,一个节点就需要16 bytes,总共有128个头节点,理应需要128*16 = 2048字节才对,现在av_[ ]才1032字节,是如何放下所有的头节点信息的呢?对于头节点而言,有效的是fd和bk,成员prev_size和size并没有用到,既然没用,那空间能否节约下来呢?可以的,看看dlmalloc是如何做到的。
#define bin_at(i) ((mbinptr)((char*)&(av_[2*(i) + 2]) - 2*4))
以分配16 bytes为例,其箱号为 16 / 8 = 2,于是,bin_at(2)-->((mbinptr)((char*)&(av_[6]) - 2*4)),最终bin_at(2)将地址 &av_[4] 强行转换为mbinptr指针,用这个指针访问fd和bk,得到的其实是av_[6]和av_[7]中存放的内容。
我们看看dlmalloc中两个特殊的分箱top和last_remainder,
#define top (bin_at(0)->fd) /* The topmost chunk */
#define last_remainder (bin_at(1)) /* remainder from last split */
top最初被称为wilderness chunk,指向dlmalloc可用内存的最高端的边界chunk,因为在边界处,top是唯一一个可以任意扩展的块(在Unix上可以通过库函数sbrk( ))。top比较特殊,它不受任何分箱管理,当其它分箱没有可用的chunk时才会用到top。在dlmalloc初始化刚完成时,整个受dlmalloc管理的内存就是一个chunk,top即指向这个chunk。
last_remainder总是指向最近被分割chunk的剩下那一部分。如果malloc( )在分配时没找到“精确匹配”的块,则优先去查看last_remainder是否够用。从局部性原理来讲,连续申请分配内存的代码总是趋向于有共同的生命周期,它们释放的chunk也就有更大的机会合并成一个大的chunk。
了解完top和last_remainder,我们继续往下看。last_remainder的箱号为1,bin_at(1)将地址 &av_[2] 强行转换为mbinptr指针,访问fd和bk,得到的其实是av_[4]和av_[5]中存放的内容,即bin_at(2)的prev_size域和bin_at(1)的fd域重叠,bin_at(2)的size域和bin_at(1)的bk域重叠,看起来像这样(方格内的数字以4个字节为单位):
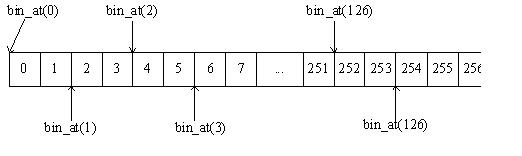
图7
同理,bin_at(1)的prev_size域和bin_at(0)的fd域重叠,bin_at(1)的size域和bin_at(0)的bk域重叠在一起。通过这种叠加使用,dlmalloc使得本该占据2048字节空间的需求变成了1032字节。这里体现了Doug Lea的一个设计宗旨:Minimizing Space,即用于heap控制的内存要最小化。原话是这样说的,
The allocator should not waste space: it should obtain as little memory from the system as possible, and shoud maintain memory in ways that minimize fragmentation--"holes" in contiguous chunks of memory that are not used by the program.
好吧,你说,必须得承认,dlmalloc确实很省空间,但是从上面这个图看来, av_[0]和av_[1]似乎没有被用到,浪费好像不符合Minimizing Space的原则哦。
当然不会,dlmalloc为达到快速检索分箱的目的,使用了一个小技巧,
#define binblocks (bin_at(0)->size) /* bitvector of nonempty blocks */
即用binblocks建立了所有分箱的一个bitmap,binblocks的bit来表示连续的4个相邻的bin是否为空,只要有一个不为空,其对应的bit置1。 binblocks实际上是av_[1],一个32位数据类型,32×4=128,正好对应128个bins。扫描时先判断binblocks的相应位,只有当bit不为空时才会真正的去扫描对应的bin。
每一个bin的用途描述如下:
#define top (bin_at(0)->fd) /* The topmost chunk */
#define last_remainder (bin_at(1)) /* remainder from last split */
由上宏定义可知,
top(topmost chunk) --> 0
last_remainder --> 1
对小于512 bytes的内存申请,箱号 = size / 8,分箱如下:
0x 0 ~ 0x 1ff --> 2 ~ 63;
大于等于512 bytes的分箱如下(以下数据用程序打印出来):
0x 200 ~ 0x 23f --> 64
0x 240 ~ 0x 27f --> 65
0x 280 ~ 0x 2bf --> 66
0x 2c0 ~ 0x 2ff --> 67
0x 300 ~ 0x 33f --> 68
0x 340 ~ 0x 37f --> 69
0x 380 ~ 0x 3bf --> 70
0x 3c0 ~ 0x 3ff --> 71
0x 400 ~ 0x 43f --> 72
0x 440 ~ 0x 47f --> 73
0x 480 ~ 0x 4bf --> 74
0x 4c0 ~ 0x 4ff --> 75
0x 500 ~ 0x 53f --> 76
0x 540 ~ 0x 57f --> 77
0x 580 ~ 0x 5bf --> 78
0x 5c0 ~ 0x 5ff --> 79
0x 600 ~ 0x 63f --> 80
0x 640 ~ 0x 67f --> 81
0x 680 ~ 0x 6bf --> 82
0x 6c0 ~ 0x 6ff --> 83
0x 700 ~ 0x 73f --> 84
0x 740 ~ 0x 77f --> 85
0x 780 ~ 0x 7bf --> 86
0x 7c0 ~ 0x 7ff --> 87
0x 800 ~ 0x 83f --> 88
0x 840 ~ 0x 87f --> 89
0x 880 ~ 0x 8bf --> 90
0x 8c0 ~ 0x 8ff --> 91
0x 900 ~ 0x 93f --> 92
0x 940 ~ 0x 97f --> 93
0x 980 ~ 0x 9bf --> 94
0x 9c0 ~ 0x 9ff --> 95
0x a00 ~ 0x bff --> 96
0x c00 ~ 0x dff --> 97
0x e00 ~ 0x fff --> 98
0x 1000 ~ 0x 11ff --> 99
0x 1200 ~ 0x 13ff --> 100
0x 1400 ~ 0x 15ff --> 101
0x 1600 ~ 0x 17ff --> 102
0x 1800 ~ 0x 19ff --> 103
0x 1a00 ~ 0x 1bff --> 104
0x 1c00 ~ 0x 1dff --> 105
0x 1e00 ~ 0x 1fff --> 106
0x 2000 ~ 0x 21ff --> 107
0x 2200 ~ 0x 23ff --> 108
0x 2400 ~ 0x 25ff --> 109
0x 2600 ~ 0x 27ff --> 110
0x 2800 ~ 0x 29ff --> 111
0x 2a00 ~ 0x 2fff --> 112
0x 3000 ~ 0x 3fff --> 113
0x 4000 ~ 0x 4fff --> 114
0x 5000 ~ 0x 5fff --> 115
0x 6000 ~ 0x 6fff --> 116
0x 7000 ~ 0x 7fff --> 117
0x 8000 ~ 0x 8fff --> 118
0x 9000 ~ 0x 9fff --> 119
0x a000 ~ 0x ffff --> 120
0x10000 ~ 0x17fff --> 121
0x18000 ~ 0x1ffff --> 122
0x20000 ~ 0x27fff --> 123
0x28000 ~ 0x3ffff --> 124
0x40000 ~ 0x7ffff --> 125
size >= 0x80000 --> 126
dlmalloc的实现使用两个宏来完成对于bin链表的插入和删除操作。宏定义frontlink(P, S, IDX, BK, FD)将某个chunk放入对应的bin链表,定义如下:
#define frontlink(P, S, IDX, BK, FD) \
{ \
if (S<MAX_SMALLBIN_SIZE) \
{ \
IDX = smallbin_index(S); \
mark_binblock(IDX); \
BK = bin_at(IDX); \
FD = BK->fd; \
P->bk = BK; \
P->fd = FD; \
FD->bk = BK->fd = P; \
} \
else \
{ \
IDX = bin_index(S); \
BK = bin_at(IDX); \
FD = BK->fd; \
if (FD == BK) mark_binblock(IDX); \
else \
{ \
while (FD != BK && S < chunksize(FD)) FD = FD->fd; \
BK = FD->bk; \
} \
P->bk = BK; \
P->fd = FD; \
FD->bk = BK->fd = P; \
} \
}
对应的逻辑示意图如下:
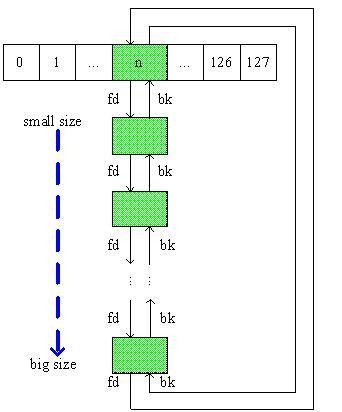
图8
如果chunk size小于512,则很好挂载,先除以8找到箱号,然后插入到头节点和头节点fd域指向的第一个节点之间,因为所有的chunk大小都一样;
如果chunk size大于等于512,则稍微麻烦一点,沿着头节点fd指针开始寻找,或者碰到size相等或更大的chunk,则插在该chunk之前;如果需挂载chunk的size
在该bin中最大,则插在最后一个chunk和头节点之间。这种最糟糕的情况会导致遍历完整个链表才能找到插入的地方,从执行效率来讲,并非最佳。在dlmalloc 2.8.3版本中,这一部分不再使用双向链表,而是使用二叉树来管理,在搜素上会更快速。
宏定义unlink(P, BK, FD)则将一个chunk从它所在的链表取走,类似于将一个节点从双向链表中解除。其定义如下:
/* take a chunk off a list */
#define unlink(P, BK, FD) \
{ \
BK = P->bk; \
FD = P->fd; \
FD->bk = BK; \
BK->fd = FD; \
}
4. 内存分配相关函数
本节主要对dlmalloc内存分配器的核心函数mALLOc()以及相关函数进行讲解,函数mALLOc用于服务应用程序的内存空间申请请求,因此也是我们平常使用得最多的两个函数(另外一个fREe())之一。下面我们先来直接看源码并同时进行分析。(下面给出的源码都已标号,标号为源文件malloc-2.6.6.c内的实际行号,未标号的行都为我给出的分析注解内容。)
4.1函数mALLOc( )
2110 #if __STD_C
2111 Void_t* mALLOc(size_t bytes)
2112 #else
2113 Void_t* mALLOc(bytes) size_t bytes;
2114 #endif
2115 {
2116 mchunkptr victim; /* inspected/selected chunk */
2117 INTERNAL_SIZE_T victim_size; /* its size */
2118 int idx; /* index for bin traversal */
2119 mbinptr bin; /* associated bin */
2120 mchunkptr remainder; /* remainder from a split */
2121 long remainder_size; /* its size */
2122 int remainder_index; /* its bin index */
2123 unsigned long block; /* block traverser bit */
2124 int startidx; /* first bin of a traversed block */
2125 mchunkptr fwd; /* misc temp for linking */
2126 mchunkptr bck; /* misc temp for linking */
2127 mbinptr q; /* misc temp */
2128
2129 INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb;
2130
2131 if ((long)bytes < 0) return 0;
2132
/*用户申请的size首先被转成系统可用的大小-->nb,即增加了4个字节,或者更 多(以满足8字节对齐的需 求),最终nb >= 16字节(系统最小的可分配size)*/
2133 nb = request2size(bytes); /* padded request size; */
2134
2135 /* Check for exact match in a bin */
2136
/*找到nb对应的bin,扫描,如果找到一个“精确”的块,则分配。所谓“精确”, 是指误差在16个字节内。*/
2137 if (is_small_request(nb)) /* Faster version for small requests */
2138 {
2139 idx = smallbin_index(nb);
2140
2141 /* No traversal or size check necessary for small bins. */
2142
2143 q = bin_at(idx);
2144 victim = last(q);
2145
2146 /* Also scan the next one, since it would have a remainder < MINSIZE */
/*如果nb对应的bin没有空闲块,则扫描下一个bin,对于smallbin而言,相邻 两个bin的size仅相差8个字节,无需为剩下的8个字节重新建立一个空闲块, 从之前的叙述我们得知,可分配的空闲块>=16字节*/
2147 if (victim == q)
2148 {
2149 q = next_bin(q);
2150 victim = last(q);
2151 }
2152 if (victim != q)
2153 {
2154 victim_size = chunksize(victim);
2155 unlink(victim, bck, fwd);
2156 set_inuse_bit_at_offset(victim, victim_size);
2157 check_malloced_chunk(victim, nb);
2158 return chunk2mem(victim);
2159 }
2160
2161 idx += 2; /* Set for bin scan below. We've already scanned 2 bins. */
2162
2163 }
2164 else
2165 {
2166 idx = bin_index(nb);
2167 bin = bin_at(idx);
2168
2169 for (victim = last(bin); victim != bin; victim = victim->bk)
2170 {
2171 victim_size = chunksize(victim);
2172 remainder_size = victim_size - nb;
2173
2174 if (remainder_size >= (long)MINSIZE) /* too big */
2175 {
2176 --idx; /* adjust to rescan below after checking last remainder */
2177 break;
2178 }
2179
/*若命中“精确”的空闲块,则从所在bin双向链表中移除,设置PREV_INUSE 标志,返回用户指针*/
2180 else if (remainder_size >= 0) /* exact fit */
2181 {
2182 unlink(victim, bck, fwd);
2183 set_inuse_bit_at_offset(victim, victim_size);
2184 check_malloced_chunk(victim, nb);
2185 return chunk2mem(victim);
2186 }
2187 }
2188
2189 ++idx;
2190
2191 }
2192
2193 /* Try to use the last split-off remainder */
2194
/*如果“精确”的chunk没有找到,而且last_remainder足够大,则在last remainder 中使用首次适应算法,该算法能让那些连续的chunk有相同或近似的生命周期,从 长期来看,有助于提升局部性和减少碎片。 */
2195 if ( (victim = last_remainder->fd) != last_remainder)
2196 {
2197 victim_size = chunksize(victim);
2198 remainder_size = victim_size - nb;
2199
/*如果last_remainder比nb大,且差值大于等于16个字节,则把剩下的部分重 新挂到last_remainder中*/
2200 if (remainder_size >= (long)MINSIZE) /* re-split */
2201 {
2202 remainder = chunk_at_offset(victim, nb);
2203 set_head(victim, nb | PREV_INUSE);
2204 link_last_remainder(remainder);
2205 set_head(remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
2206 set_foot(remainder, remainder_size);
2207 check_malloced_chunk(victim, nb);
2208 return chunk2mem(victim);
2209 }
2210
/*如果last_remainder比nb大,且差值小于16个字节,则一股脑儿都分配出去; 如果last_remainder比nb小,则有理由怀疑last_remainder也不能满足下一次内 存申请,所以把它挂到一般的bin分箱中去。
不管是那种情况,都将last_remainder清空,让它指向自己。*/
2211 clear_last_remainder;
2212
2213 if (remainder_size >= 0) /* exhaust */
2214 {
2215 set_inuse_bit_at_offset(victim, victim_size);
2216 check_malloced_chunk(victim, nb);
2217 return chunk2mem(victim);
2218 }
2219
2220 /* Else place in bin */
2221
2222 frontlink(victim, victim_size, remainder_index, bck, fwd);
2223 }
2224
2225 /*
2226 If there are any possibly nonempty big-enough blocks,
2227 search for best fitting chunk by scanning bins in blockwidth units.
2228 */
2229
/*如果适合分配的chunk还没找到,则以升序方式扫描其它bins,这里最佳适应算 法被采用,即满足需求的最小chunk被选中,分配后将剩余部分放入last_remainder。
为了加速扫描过程,Doug Lea使用了一个小技巧,
#define binblocks (bin_at(0)->size) /* bitvector of nonempty blocks */
用binblocks的bit来表示连续的4个相邻的bin是否为空,只要有一个不为空,其 对应的bit置1。binblocks实际上是av_[1],一个32位数据类型,32×4=128,正好 对应128个bins。扫描时先判断binblocks值,只有当相应的bit不为空时才会真正 的去扫描对应的bin。 */
2230 if ( (block = idx2binblock(idx)) <= binblocks)
2231 {
2232
2233 /* Get to the first marked block */
2234
/*block是binblock的某一个位,bit[n],其值为1的话表示第n*4,n*4+1,n*4+2, n*4+3个bin分箱中至少有一个bin不为空,这意味着至少有一个chunk能满足 内存申请。在扣除申请的内存后剩余的部分如果小于16个字节,则把这个 chunk全部分配给用户,如果剩余部分大于等于16个字节,则将剩余部分挂载 到last_remainder中*/
2235 if ( (block & binblocks) == 0)
2236 {
2237 /* force to an even block boundary */
2238 idx = (idx & ~(BINBLOCKWIDTH - 1)) + BINBLOCKWIDTH;
2239 block <<= 1;
2240 while ((block & binblocks) == 0)
2241 {
2242 idx += BINBLOCKWIDTH;
2243 block <<= 1;
2244 }
2245 }
2246
2247 /* For each possibly nonempty block ... */
2248 for (;;)
2249 {
2250 startidx = idx; /* (track incomplete blocks) */
2251 q = bin = bin_at(idx);
2252
2253 /* For each bin in this block ... */
2254 do
2255 {
2256 /* Find and use first big enough chunk ... */
2257
2258 for (victim = last(bin); victim != bin; victim = victim->bk)
2259 {
2260 victim_size = chunksize(victim);
2261 remainder_size = victim_size - nb;
2262
2263 if (remainder_size >= (long)MINSIZE) /* split */
2264 {
2265 remainder = chunk_at_offset(victim, nb);
2266 set_head(victim, nb | PREV_INUSE);
2267 unlink(victim, bck, fwd);
2268 link_last_remainder(remainder);
2269 set_head(remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
2270 set_foot(remainder, remainder_size);
2271 check_malloced_chunk(victim, nb);
2272 return chunk2mem(victim);
2273 }
2274
2275 else if (remainder_size >= 0) /* take */
2276 {
2277 set_inuse_bit_at_offset(victim, victim_size);
2278 unlink(victim, bck, fwd);
2279 check_malloced_chunk(victim, nb);
2280 return chunk2mem(victim);
2281 }
2282
2283 }
2284
2285 bin = next_bin(bin);
2286
2287 } while ((++idx & (BINBLOCKWIDTH - 1)) != 0);
2288
2289 /* Clear out the block bit. */
2290
2291 do /* Possibly backtrack to try to clear a partial block */
2292 {
2293 if ((startidx & (BINBLOCKWIDTH - 1)) == 0)
2294 {
2295 binblocks &= ~block;
2296 break;
2297 }
2298 --startidx;
2299 q = prev_bin(q);
2300 } while (first(q) == q);
2301
2302 /* Get to the next possibly nonempty block */
2303
2304 if ( (block <<= 1) <= binblocks && (block != 0) )
2305 {
2306 while ((block & binblocks) == 0)
2307 {
2308 idx += BINBLOCKWIDTH;
2309 block <<= 1;
2310 }
2311 }
2312 else
2313 break;
2314 }
2315 }
2316
2317
2318 /* Try to use top chunk */
2319
/*如果还没有找到适合分配的chunk,就去分割top chunk。由于top可以将memory 扩展到系统允许的上限,所以top会被认为比系统内可用的chunk都要大。*/
2320 /* Require that there be a remainder, ensuring top always exists */
2321 if ( (remainder_size = chunksize(top) - nb) < (long)MINSIZE)
2322 {
2323
2324 #if HAVE_MMAP
2325 /* If big and would otherwise need to extend, try to use mmap instead */
2326 if ((unsigned long)nb >= (unsigned long)mmap_threshold &&
2327 (victim = mmap_chunk(nb)) != 0)
2328 return chunk2mem(victim);
2329 #endif
2330
2331 /* Try to extend */
2332 malloc_extend_top(nb);
2333 if ( (remainder_size = chunksize(top) - nb) < (long)MINSIZE)
2334 return 0; /* propagate failure */
2335 }
2336
2337 victim = top;
2338 set_head(victim, nb | PREV_INUSE);
2339 top = chunk_at_offset(victim, nb);
2340 set_head(top, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
2341 check_malloced_chunk(victim, nb);
2342 return chunk2mem(victim);
2343
2344 }
4.2函数malloc_update_mallinfo( )
在使用heap分配内存时,我们往往会关注整个heap的状况,比如heap的大小,内存分配掉多少,还剩多少等。数据结构体mallinfo即是为此目的而定义,如下:
struct mallinfo {
int arena; /* total space allocated from system—从系统分给heap使用的内存大小 */
int ordblks; /* number of non-inuse chunks—未使用的chunk个数 */
int smblks; /* unused -- always zero */
int hblks; /* number of mmapped regions */
int hblkhd; /* total space in mmapped regions —通过mmap( )分配的所有内存的大小*/
int usmblks; /* unused -- always zero */
int fsmblks; /* unused -- always zero */
int uordblks; /* total allocated space —被分配使用的chunk个数*/
int fordblks; /* total non-inuse space—未被分配使用的chunk个数*/
int keepcost; /* top-most, releasable (via malloc_trim) space */
};
3047 static void malloc_update_mallinfo()
3048 {
3049 int i;
3050 mbinptr b;
3051 mchunkptr p;
3052 #if DEBUG
3053 mchunkptr q;
3054 #endif
3055
3056 INTERNAL_SIZE_T avail = chunksize(top);
3057 int navail = ((long)(avail) >= (long)MINSIZE)? 1 : 0;
3058
/*遍历所有分箱的双向链表,统计空闲块个数和总的size,并据此算出其它信息*/
3059 for (i = 1; i < NAV; ++i)
3060 {
3061 b = bin_at(i);
3062 for (p = last(b); p != b; p = p->bk)
3063 {
3064 #if DEBUG
3065 check_free_chunk(p);
3066 for (q = next_chunk(p);
3067 q < top && inuse(q) && (long)(chunksize(q)) >= (long)MINSIZE;
3068 q = next_chunk(q))
3069 check_inuse_chunk(q);
3070 #endif
3071 avail += chunksize(p);
3072 navail++;
3073 }
3074 }
3075
3076 current_mallinfo.ordblks = navail;
3077 current_mallinfo.uordblks = sbrked_mem - avail;
3078 current_mallinfo.fordblks = avail;
3079 current_mallinfo.hblks = n_mmaps;
3080 current_mallinfo.hblkhd = mmapped_mem;
3081 current_mallinfo.keepcost = chunksize(top);
3082
3083 }
5. 内存回收相关函数
5.1函数fREe( )
2371 #if __STD_C
2372 void fREe(Void_t* mem)
2373 #else
2374 void fREe(mem) Void_t* mem;
2375 #endif
2376 {
2377 mchunkptr p; /* chunk corresponding to mem */
2378 INTERNAL_SIZE_T hd; /* its head field */
2379 INTERNAL_SIZE_T sz; /* its size */
2380 int idx; /* its bin index */
2381 mchunkptr next; /* next contiguous chunk */
2382 INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsz; /* its size */
2383 INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsz; /* size of previous contiguous chunk */
2384 mchunkptr bck; /* misc temp for linking */
2385 mchunkptr fwd; /* misc temp for linking */
2386 int islr; /* track whether merging with last_remainder */
2387
2388 if (mem == 0) /* free(0) has no effect */
2389 return;
2390
2391 p = mem2chunk(mem);
2392 hd = p->size;
2393
2394 #if HAVE_MMAP
2395 if (hd & IS_MMAPPED) /* release mmapped memory. */
2396 {
2397 munmap_chunk(p);
2398 return;
2399 }
2400 #endif
2401
2402 check_inuse_chunk(p);
2403
2404 sz = hd & ~PREV_INUSE;
2405 next = chunk_at_offset(p, sz);
2406 nextsz = chunksize(next);
2407
/*如果等待释放的chunk与memory的高端相邻,则被合并入top chunk。*/
2408 if (next == top) /* merge with top */
2409 {
2410 sz += nextsz;
2411
/*查看前一个chunk是否为空闲,若是,则从所在的分箱双向链表中移除*/
2412 if (!(hd & PREV_INUSE)) /* consolidate backward */
2413 {
2414 prevsz = p->prev_size;
2415 p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsz));
2416 sz += prevsz;
2417 unlink(p, bck, fwd);
2418 }
2419
/*设置合并后chunk的size,包含PREV_INUSE,因为此时其前一个chunk必定 被分配使用了;
重新设置top;
若使用的memory超出了trim的界限,则调用malloc_trim()。*/
2420 set_head(p, sz | PREV_INUSE);
2421 top = p;
2422 if ((unsigned long)(sz) >= (unsigned long)trim_threshold)
2423 malloc_trim(top_pad);
2424 return;
2425 }
2426
/*清除下一个chunk的size域的PREV_INUSE标志,表示当前chunk出于空闲*/
2427 set_head(next, nextsz); /* clear inuse bit */
2428
2429 islr = 0;
2430
/*被释放的chunk没有紧挨top*/
/*如果前一个chunk空闲,且其前指chunk不是last_remainder, 则将前一个chunk 从所在分箱双向链表移除,否则只是置islr为1,后续仅需更新p所指chunk的size 即可*/
2431 if (!(hd & PREV_INUSE)) /* consolidate backward */
2432 {
2433 prevsz = p->prev_size;
2434 p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsz));
2435 sz += prevsz;
2436
2437 if (p->fd == last_remainder) /* keep as last_remainder */
2438 islr = 1;
2439 else
2440 unlink(p, bck, fwd);
2441 }
2442
/*下一个chunk空闲,且其前指chunk是last_remainder,则重新建立合并后的 chunk 和last_remainder之间的联系,否则只是将下一个chunk从所在分箱双向链表移除*/
2443 if (!(inuse_bit_at_offset(next, nextsz))) /* consolidate forward */
2444 {
2445 sz += nextsz;
2446
2447 if (!islr && next->fd == last_remainder) /* re-insert last_remainder */
2448 {
2449 islr = 1;
2450 link_last_remainder(p);
2451 }
2452 else
2453 unlink(next, bck, fwd);
2454 }
2455
2456
/*设置合并后chunk的size,包含PREV_INUSE,因为此时其前一个chunk必定被 分配使用了;
设置下一个chunk的prev_size,下一个chunk也必定被分配使用了,当下一个
chunk被释放时,可根据prev_size找到前一个chunk合并;
如果islr为0,则说明当前chunk和last_remainder没什么关系,需要将当前chunk 重新放入合适的分箱上向链表中*/
2457 set_head(p, sz | PREV_INUSE);
2458 set_foot(p, sz);
2459 if (!islr)
2460 frontlink(p, sz, idx, bck, fwd);
2461 }