这是严蔚敏《数据结构》配套习题册上的题目:将逆波兰式转换成波兰式,并提示错误(作为简化,只处理"+-*/"和0~9的数字)。
例如:"123*-"转换成波兰式为"-1*23"
逆波兰式"123*-"的表达式树如下:

所以这个转换过程就是:已知一个二叉树的后根遍历序列,求先根遍历序列。
我的算法是根据后根遍历的序列构造一个表达式树,进而先根遍历此树获得波兰式表达式。
定义了两个结构体:
struct Exp{
char op;
Item lhs;
Item rhs;
Exp(){};
Exp(char _op, Item _lhs, Item _rhs):op(_op), lhs(_lhs), rhs(_rhs){ }
Exp(const Exp& e):op(e.op), lhs(e.lhs), rhs(e.rhs) { }
};
表示一个表达式,也是表达式树上的一个子树。
struct Item{
char number;
shared_ptr<Exp> pExp;
bool isNumber;
explicit Item():isNumber(true), number('0'), pExp(){ }
Item(const Item& i):number(i.number), pExp(i.pExp), isNumber(i.isNumber){ }
};
表示一个节点,它可以是一个数字,或者一个表达式(pExp这里我使用的是boost库的智能指针shared_ptr,所以编译的话,需要先安装boost库)。
运行的结果如图:
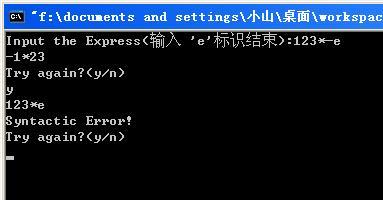
*输入时,以'e'表示输入结束。
完整的代码和可执行文件点击这里下载。权当抛砖引玉了,希望有更好算法的同学赐教。
完整的代码:


 #include <stack>
#include <stack>
 #include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
 #include <string>
#include <string>
 #include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
 #include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>
 using namespace std;
using namespace std;
 using boost::shared_ptr;
using boost::shared_ptr;

 struct Exp;
struct Exp;

 struct Item
struct Item {
{
 char number;
char number;
 shared_ptr<Exp> pExp;
shared_ptr<Exp> pExp;
 bool isNumber;
bool isNumber;

 explicit Item():isNumber(true), number('0'), pExp()
explicit Item():isNumber(true), number('0'), pExp() { }
{ }

 Item(const Item& i):number(i.number), pExp(i.pExp), isNumber(i.isNumber)
Item(const Item& i):number(i.number), pExp(i.pExp), isNumber(i.isNumber) { }
{ }
 };
};


 struct Exp
struct Exp {
{
 char op;
char op;
 Item lhs;
Item lhs;
 Item rhs;
Item rhs;

 Exp()
Exp() {};
{};

 Exp(char _op, Item _lhs, Item _rhs):op(_op), lhs(_lhs), rhs(_rhs)
Exp(char _op, Item _lhs, Item _rhs):op(_op), lhs(_lhs), rhs(_rhs) { }
{ }

 Exp(const Exp& e):op(e.op), lhs(e.lhs), rhs(e.rhs)
Exp(const Exp& e):op(e.op), lhs(e.lhs), rhs(e.rhs)  { }
{ }
 };
};


 class Error
class Error {
{
 string info;
string info;
 public:
public:

 Error(string _info):info(_info)
Error(string _info):info(_info) { }
{ }

 Error():info("")
Error():info("") { }
{ }

 string what()
string what() {return info;}
{return info;}
 };
};


 void printPorland(Exp& exp)
void printPorland(Exp& exp) {
{
 cout << exp.op ;
cout << exp.op ;
 if(exp.lhs.isNumber) cout << exp.lhs.number;
if(exp.lhs.isNumber) cout << exp.lhs.number;
 else printPorland(*exp.lhs.pExp);
else printPorland(*exp.lhs.pExp);
 if(exp.rhs.isNumber) cout << exp.rhs.number;
if(exp.rhs.isNumber) cout << exp.rhs.number;
 else printPorland(*exp.rhs.pExp);
else printPorland(*exp.rhs.pExp);
 return;
return;
 }
}

 int main()
int main()


 {
{
 stack<Item> ExpStack;
stack<Item> ExpStack;
 char tmpChar;
char tmpChar;
 Item tmpItem;
Item tmpItem;
 Item tmpLhs;
Item tmpLhs;
 Item tmpRhs;
Item tmpRhs;
 string numbers = "0123456789";
string numbers = "0123456789";
 string operators = "+-*/";
string operators = "+-*/";

 cout<<"Input the Express(输入 'e'标识结束):";
cout<<"Input the Express(输入 'e'标识结束):";

 do
do {
{

 try
try {
{

 while(cin>>tmpChar)
while(cin>>tmpChar) {
{
 if(tmpChar == 'e') break; //e为结束符
if(tmpChar == 'e') break; //e为结束符
 else if(find(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), //是一个数字
else if(find(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), //是一个数字

 tmpChar)!=numbers.end())
tmpChar)!=numbers.end()) {
{
 tmpItem.isNumber = true;
tmpItem.isNumber = true;
 tmpItem.number = tmpChar;
tmpItem.number = tmpChar;
 ExpStack.push(tmpItem);//数字入栈
ExpStack.push(tmpItem);//数字入栈

 }else if(find(operators.begin(), operators.end(), //是一个操作符
}else if(find(operators.begin(), operators.end(), //是一个操作符

 tmpChar)!=operators.end())
tmpChar)!=operators.end()) {
{
 //操作符每次要对应两个被操作数,否则语法错误
//操作符每次要对应两个被操作数,否则语法错误
 if(ExpStack.size()<2) throw Error("Syntactic Error!");
if(ExpStack.size()<2) throw Error("Syntactic Error!");

 //操作符两边的元素出栈
//操作符两边的元素出栈
 tmpRhs = ExpStack.top();
tmpRhs = ExpStack.top();
 ExpStack.pop();
ExpStack.pop();
 tmpLhs = ExpStack.top();
tmpLhs = ExpStack.top();
 ExpStack.pop();
ExpStack.pop();

 tmpItem.isNumber = false; //非数字,是一个表达式
tmpItem.isNumber = false; //非数字,是一个表达式
 tmpItem.pExp = shared_ptr<Exp>(new Exp(tmpChar, tmpLhs, tmpRhs));
tmpItem.pExp = shared_ptr<Exp>(new Exp(tmpChar, tmpLhs, tmpRhs));

 ExpStack.push(tmpItem); //表达式入栈
ExpStack.push(tmpItem); //表达式入栈


 }else
}else  { // 未知字符
{ // 未知字符
 throw Error("Unknow Character!");
throw Error("Unknow Character!");
 }
}
 }
}

 if(ExpStack.size()!=1) throw Error("Syntactic Error!");
if(ExpStack.size()!=1) throw Error("Syntactic Error!");

 tmpItem = ExpStack.top();
tmpItem = ExpStack.top();
 ExpStack.pop();
ExpStack.pop();

 if(tmpItem.isNumber) cout << tmpItem.number <<endl;
if(tmpItem.isNumber) cout << tmpItem.number <<endl;
 else printPorland(*tmpItem.pExp);
else printPorland(*tmpItem.pExp);
 cout << endl;
cout << endl;


 }catch(Error& e)
}catch(Error& e) {
{
 cout << e.what() << endl;
cout << e.what() << endl;
 getline(cin, string()); //跳过错误的当前行
getline(cin, string()); //跳过错误的当前行
 }
}

 cout << "Try again?(y/n)" << endl;
cout << "Try again?(y/n)" << endl;
 cin >> tmpChar;
cin >> tmpChar;
 }while(tmpChar == 'y' || tmpChar == 'Y');
}while(tmpChar == 'y' || tmpChar == 'Y');

 return 0;
return 0;
 }
}

posted on 2006-12-05 14:45
小山日志 阅读(2178)
评论(0) 编辑 收藏 引用 所属分类:
Aha! Algorithm!